filmov
tv
Is it possible for Rh positive parents to have Rh negative child?

Показать описание
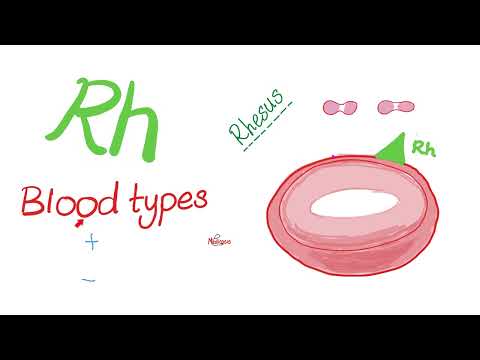
Rh blood groups refer to a system of blood group antigens present on the surface of red blood cells. The term "Rh" stands for Rhesus, which is derived from the Rhesus monkey, as the antigen was first discovered in these animals.
The Rh blood group system is one of the most clinically significant blood group systems after the ABO system. It involves a specific antigen called the Rh factor, also known as the D antigen. Individuals who have the Rh factor on their red blood cells are classified as Rh-positive (Rh+), while those who lack the Rh factor are classified as Rh-negative (Rh-).
Rh blood group compatibility is crucial during blood transfusions and pregnancies. Rh-negative individuals can receive blood from both Rh-positive and Rh-negative donors, whereas Rh-positive individuals can only receive blood from Rh-positive donors. In pregnancy, Rh-negative mothers carrying an Rh-positive fetus can develop antibodies against the Rh factor, potentially causing complications in subsequent pregnancies.
Rh blood groups are inherited genetically. If both parents are Rh-positive, their children can either be Rh-positive or Rh-negative. However, if one parent is Rh-negative and the other is Rh-positive, there is a chance of having Rh-positive children.
Routine blood typing includes determining an individual's Rh blood group along with the ABO blood group. This information helps ensure safe blood transfusions, compatible organ donations, and proper prenatal care.
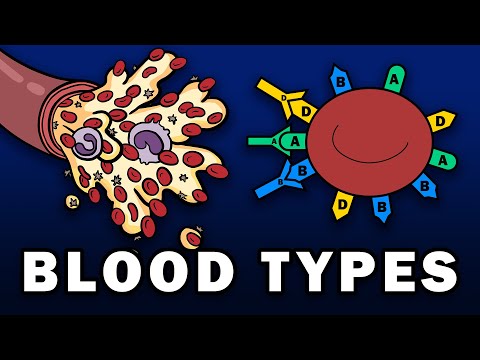
It's important to note that the Rh blood group system has various other antigens besides the D antigen, such as C, c, E, and e antigens. These additional antigens contribute to further subdivisions within the Rh blood groups and are relevant in certain medical situations.
Overall, understanding Rh blood groups is essential for medical professionals to provide appropriate and safe care for individuals requiring blood transfusions or prenatal care.
The Rh blood group system is one of the most clinically significant blood group systems after the ABO system. It involves a specific antigen called the Rh factor, also known as the D antigen. Individuals who have the Rh factor on their red blood cells are classified as Rh-positive (Rh+), while those who lack the Rh factor are classified as Rh-negative (Rh-).
Rh blood group compatibility is crucial during blood transfusions and pregnancies. Rh-negative individuals can receive blood from both Rh-positive and Rh-negative donors, whereas Rh-positive individuals can only receive blood from Rh-positive donors. In pregnancy, Rh-negative mothers carrying an Rh-positive fetus can develop antibodies against the Rh factor, potentially causing complications in subsequent pregnancies.
Rh blood groups are inherited genetically. If both parents are Rh-positive, their children can either be Rh-positive or Rh-negative. However, if one parent is Rh-negative and the other is Rh-positive, there is a chance of having Rh-positive children.
Routine blood typing includes determining an individual's Rh blood group along with the ABO blood group. This information helps ensure safe blood transfusions, compatible organ donations, and proper prenatal care.
It's important to note that the Rh blood group system has various other antigens besides the D antigen, such as C, c, E, and e antigens. These additional antigens contribute to further subdivisions within the Rh blood groups and are relevant in certain medical situations.
Overall, understanding Rh blood groups is essential for medical professionals to provide appropriate and safe care for individuals requiring blood transfusions or prenatal care.
Комментарии
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:09:43
0:09:43
 0:07:08
0:07:08
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:10:54
0:10:54
 0:16:05
0:16:05
 0:00:57
0:00:57
![[DEMO] Poplee Socle](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/cWWFyEFCQgM/hqdefault.jpg) 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:12:16
0:12:16
 0:12:07
0:12:07
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:09:12
0:09:12
 0:01:25
0:01:25
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:19:55
0:19:55
 0:00:42
0:00:42
 0:09:22
0:09:22
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:08:22
0:08:22
 0:07:18
0:07:18
 0:14:37
0:14:37