filmov
tv
What is a Web Browser?

Показать описание
Learn what a Web Browser is and how it's different from other programs.
Follow us on social media:
------------------------------------------
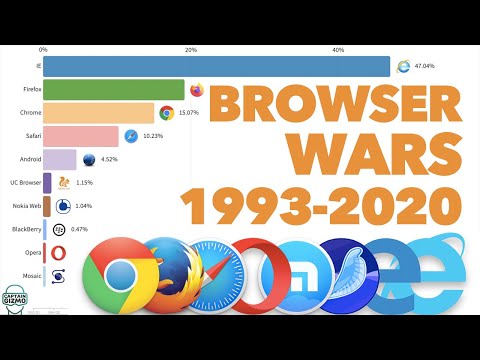
A web browser is a program on your computer, tablet, or smartphone that allows you to view websites. Some common web browsers are Internet Explorer, Safari, Chrome, and Firefox. Because web browsers are often produced by the same companies that produce operating systems and search engines, it is easy to confuse the three. An operating system, like Windows, Mac OS, Linux, or Android, is the software that is built into a computer or mobile device that allows the user to access programs, save files, and communicate with the device’s hardware. A search engine, like Google Search or Bing, is a website that helps users find the information they need on the World Wide Web. It is important to note that a web browser is also not the internet or the World Wide Web itself, just the program you use to view webpages on the World Wide Web.
A web browser is like a librarian and translator, finding the web page you requested, then converting code like this into something more user-friendly. When you request a web page, either by clicking on a hyperlink or typing a URL (universal resource locator) into the address bar, the browser sends this request to a DNS (domain name system) server. The DNS server then connects you to the server where the web page you want is stored. This server then sends the source code for the web page back to the browser. The source code is written in a variety of languages that instruct the browser about how to show the web page to the user. For example, HTML (hypertext markup language) labels the content by type, so that the browser knows what is a title, what is a paragraph, what is an image, etc. CSS (cascading style sheets) tells the browser how these different types of content should be displayed, indicating the size, position, and color of text, for example. More complicated elements of the web page, including interactive elements like chat windows, are often written in JavaScript.
In addition to finding and displaying web pages, most web browsers include features that improve the internet-going experience. For example, you can review the list of web pages you’ve previously visited using the history function, or bookmark a web page to access again later. A web browser can temporarily save some parts of the source code of web pages you’ve visited in a cache, so that if the web page is revisited, it can be displayed more quickly. The web browser may also store data using cookies, which are small pieces of data often used to save your progress on web games, or to save your login session so you don’t have to re-enter your password every time you visit a particular website. Finally, many web browsers allow you to install extensions, which offer additional features like appearance customization, ad and pop-up blocking, and password management.
Follow us on social media:
------------------------------------------
A web browser is a program on your computer, tablet, or smartphone that allows you to view websites. Some common web browsers are Internet Explorer, Safari, Chrome, and Firefox. Because web browsers are often produced by the same companies that produce operating systems and search engines, it is easy to confuse the three. An operating system, like Windows, Mac OS, Linux, or Android, is the software that is built into a computer or mobile device that allows the user to access programs, save files, and communicate with the device’s hardware. A search engine, like Google Search or Bing, is a website that helps users find the information they need on the World Wide Web. It is important to note that a web browser is also not the internet or the World Wide Web itself, just the program you use to view webpages on the World Wide Web.
A web browser is like a librarian and translator, finding the web page you requested, then converting code like this into something more user-friendly. When you request a web page, either by clicking on a hyperlink or typing a URL (universal resource locator) into the address bar, the browser sends this request to a DNS (domain name system) server. The DNS server then connects you to the server where the web page you want is stored. This server then sends the source code for the web page back to the browser. The source code is written in a variety of languages that instruct the browser about how to show the web page to the user. For example, HTML (hypertext markup language) labels the content by type, so that the browser knows what is a title, what is a paragraph, what is an image, etc. CSS (cascading style sheets) tells the browser how these different types of content should be displayed, indicating the size, position, and color of text, for example. More complicated elements of the web page, including interactive elements like chat windows, are often written in JavaScript.
In addition to finding and displaying web pages, most web browsers include features that improve the internet-going experience. For example, you can review the list of web pages you’ve previously visited using the history function, or bookmark a web page to access again later. A web browser can temporarily save some parts of the source code of web pages you’ve visited in a cache, so that if the web page is revisited, it can be displayed more quickly. The web browser may also store data using cookies, which are small pieces of data often used to save your progress on web games, or to save your login session so you don’t have to re-enter your password every time you visit a particular website. Finally, many web browsers allow you to install extensions, which offer additional features like appearance customization, ad and pop-up blocking, and password management.
Комментарии
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:08:43
0:08:43
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:08:28
0:08:28
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:02:16
0:02:16
 0:30:22
0:30:22
 0:12:25
0:12:25
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:10:18
0:10:18
 0:08:55
0:08:55
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:02:39
0:02:39
 0:11:31
0:11:31
 0:13:19
0:13:19
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:09:11
0:09:11
 0:01:51
0:01:51