filmov
tv
Collisions - Momentum - IB Physics

Показать описание
There are three types of collisions we deal with in physics: Elastic collisions (two objects bouncing off each other), inelastic collisions (two objects sticking together) and "explosions" (one object splitting into two). To predict the motion of objects after a collision, we use conservation of momentum: the total momentum of both objects before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision.
Collisions - Momentum - IB Physics
Conservation of Momentum In Two Dimensions - 2D Elastic & Inelastic Collisions - Physics Problem...
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
Impulse and Momentum
A2.7 Momentum and collisions [IB Physics SL/HL]
Impulse and Momentum - Formulas and Equations - College Physics
Collisions: Crash Course Physics #10
Elastic Collisions In One Dimension Physics Problems - Conservation of Momentum & Kinetic Energy
Conservation of momentum - IB Physics
GCSE Physics - Momentum Part 1 of 2 - Conservation of Momentum Principle
Momentum and impulse [IB Physics SL/HL]
Most Collisions Are Secretly in One Dimension
IB Physics Topic 2.4: Momentum and Impulse
Momentum Magic Or The Collision Rule #learnphysics #11thgrade #memorize #Mechanics
Momentum Collisions in 2D
What is Momentum? - IB Physics
Visualizing Mechanics: Conservation of Linear Momentum in Inelastic Collision
Which car will recoil faster? #science #physics #momentum #collision
Conservation of Momentum - IB Physics
26.1 Momentum in Collisions
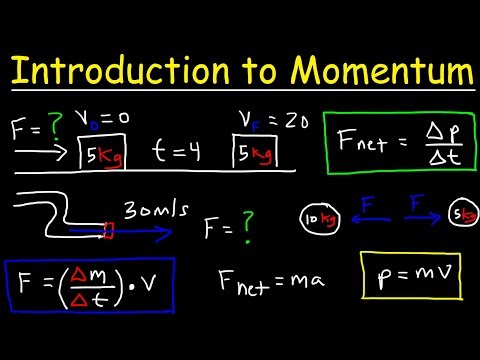
Introduction to Momentum, Force, Newton's Second Law, Conservation of Linear Momentum, Physics
Law of Conservation of Momentum
Best Conservation of Momentum Mind Bender!
[ARCHIVED] Collisions, Momentum, Newton's 3rd Law
Комментарии
 0:16:53
0:16:53
 0:10:25
0:10:25
 0:05:14
0:05:14
 0:05:15
0:05:15
 0:10:52
0:10:52
 0:15:25
0:15:25
 0:09:21
0:09:21
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:15:49
0:15:49
 0:07:26
0:07:26
 0:13:04
0:13:04
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:12:00
0:12:00
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:11:29
0:11:29
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:15:23
0:15:23
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:00:48
0:00:48
![[ARCHIVED] Collisions, Momentum,](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/XVfBfeDy6do/hqdefault.jpg) 0:26:20
0:26:20