filmov
tv
Karen Uhlenbeck | The Noether Theorems in Geometry: Then and Now

Показать описание
Math Science Literature Lecture, 12/9/21
Speaker: Karen Uhlenbeck (Institute for Advanced Study)
Title: The Noether Theorems in Geometry: Then and Now
Abstract: The 1918 Noether theorems were a product of the general search for energy and momentum conservation in Einstein’s newly formulated theory of general relativity. Although widely referred to as the connection between symmetry and conservation laws, the theorems themselves are often not understood properly and hence have not been as widely used as they might be. In the first part of the talk, I outline a brief history of the theorems, explain a bit of the language, translate the first theorem into coordinate invariant language and give a few examples. I will mention only briefly their importance in physics and integrable systems. In the second part of the talk, I describe why they are still relevant in geometric analysis: how they underlie standard techniques and why George Daskalopoulos and I came to be interested in them for our investigation into the best Lipschitz maps of Bill Thurston. Some applications to integrals on a domain a hyperbolic surface leave open possibilities for applications to integrals on domains which are locally symmetric spaces of higher dimension. The talk finishes with an example or two from the literature.
Speaker: Karen Uhlenbeck (Institute for Advanced Study)
Title: The Noether Theorems in Geometry: Then and Now
Abstract: The 1918 Noether theorems were a product of the general search for energy and momentum conservation in Einstein’s newly formulated theory of general relativity. Although widely referred to as the connection between symmetry and conservation laws, the theorems themselves are often not understood properly and hence have not been as widely used as they might be. In the first part of the talk, I outline a brief history of the theorems, explain a bit of the language, translate the first theorem into coordinate invariant language and give a few examples. I will mention only briefly their importance in physics and integrable systems. In the second part of the talk, I describe why they are still relevant in geometric analysis: how they underlie standard techniques and why George Daskalopoulos and I came to be interested in them for our investigation into the best Lipschitz maps of Bill Thurston. Some applications to integrals on a domain a hyperbolic surface leave open possibilities for applications to integrals on domains which are locally symmetric spaces of higher dimension. The talk finishes with an example or two from the literature.
Комментарии
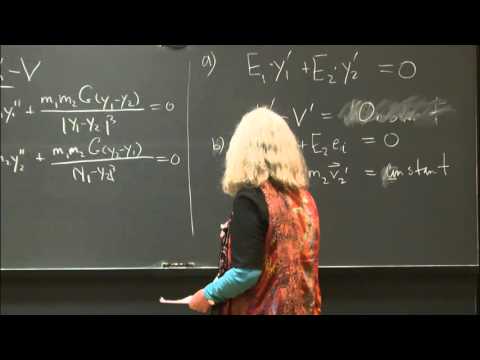 0:56:10
0:56:10
 1:24:26
1:24:26
 1:02:03
1:02:03
 1:01:44
1:01:44
 1:02:09
1:02:09
 1:09:11
1:09:11
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:06:30
0:06:30
 0:12:24
0:12:24
 0:07:30
0:07:30
 0:50:25
0:50:25
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 1:15:15
1:15:15
 1:02:34
1:02:34
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:01:02
0:01:02
 0:29:56
0:29:56
 0:58:02
0:58:02
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:51:08
0:51:08
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:41:56
0:41:56