filmov
tv
History of X-rays

Показать описание
Discusses the discovery, development and basic physics of x-ray generation.
History of X-rays
The history of X-ray: a journey through time and medical technology
How X-rays see through your skin - Ge Wang
The HORRIFIC History of X-Rays
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen and the discovery of the X-rays
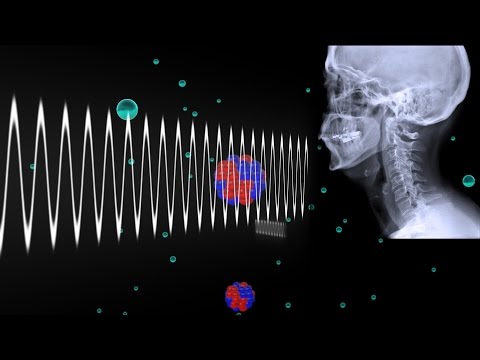
How Do X-rays Work?
The history of Radiography
How Were X Rays Discovered by Accident?
SCIATICA PAIN RELIEF TREATMENT, 5 Step Non-Surgical Treatment for Sciatica | Dr. Ruminder Birk
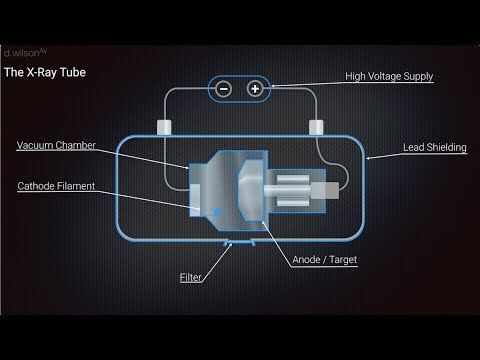
Production of X Rays animated
How do X-Rays Work?
Physics of How Wilhelm Roentgen Discovered X-rays
History of x rays
The History of X-Rays in Medicine | Then vs. Now | GoodRx
How Dangerous Are X-Rays?
How do X-rays work? | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children
The History of Radiology: Discovering X-Rays
History and Properties of X-Rays
X Ray Production Animation
The Strange History of Soviet X-Ray Records
Invention Of X-Ray | The Dr. Binocs Show | Best Learning Video for Kids | Preschool Learning
History & Production of Dental X-rays
Wilhelm Röntgen: X-rays | Heroes of Progress | Ep. 26
From Rontgen to Radiology: The History of X-Rays (Mini Documentary)
Комментарии
 0:24:21
0:24:21
 0:02:23
0:02:23
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:11:12
0:11:12
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:08:03
0:08:03
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:07:29
0:07:29
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:26:18
0:26:18
 0:02:23
0:02:23
 0:13:54
0:13:54