filmov
tv
Alkaloids and their Biosynthesis

Показать описание
#plants #mscbotany #alkaloids #bioactivecompounds #secondarymetabolites
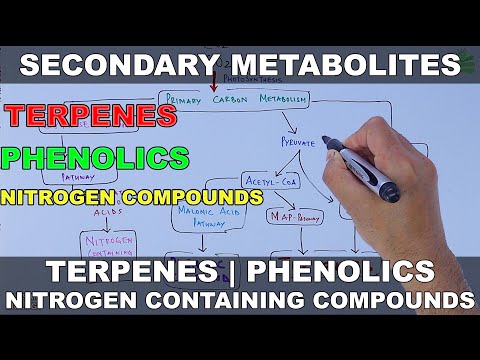
Alkaloids are products of secondary metabolism of plants
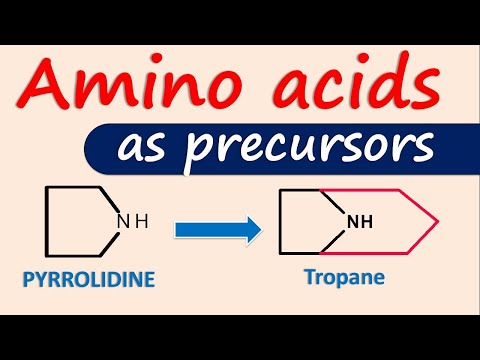
defined as natural compounds with a basic character–containing one nitrogen atom in a heterocyclic ring structure. The term “alkaloid” was coined by Meissner in 1819. Alkaloids are usually colorless but several colored alkaloids are also reported. The main toxic effects of alkaloids: Alkaloids are generally occur in all parts of the plant, but accumulated only in particular organ. The organ in which alkaloids accumulated is not always the site of their synthesis. True alkaloids are rarely occur in lower plants.
Nearly 300 alkaloids belonging to more than 24 classes are found in the skin of amphibians. Some indole and isoquinoline alkaloids were isolated from mammals including mammalian morphine. disturbances of the central nervous system, digestive processes, reproduction, and the immune system.
Taxonomical classification
This classification is based on the distribution of alkaloids in various plant families, like solanaceous or papilionaceous alkaloids.
Pharmacological classification
This classification is based on the physiological action or biological activity of alkaloids on animals like CNS stimulants or depressants, sympathomimetics, analgesics, purgatives, etc.
Alkaloids are products of secondary metabolism of plants
defined as natural compounds with a basic character–containing one nitrogen atom in a heterocyclic ring structure. The term “alkaloid” was coined by Meissner in 1819. Alkaloids are usually colorless but several colored alkaloids are also reported. The main toxic effects of alkaloids: Alkaloids are generally occur in all parts of the plant, but accumulated only in particular organ. The organ in which alkaloids accumulated is not always the site of their synthesis. True alkaloids are rarely occur in lower plants.
Nearly 300 alkaloids belonging to more than 24 classes are found in the skin of amphibians. Some indole and isoquinoline alkaloids were isolated from mammals including mammalian morphine. disturbances of the central nervous system, digestive processes, reproduction, and the immune system.
Taxonomical classification
This classification is based on the distribution of alkaloids in various plant families, like solanaceous or papilionaceous alkaloids.
Pharmacological classification
This classification is based on the physiological action or biological activity of alkaloids on animals like CNS stimulants or depressants, sympathomimetics, analgesics, purgatives, etc.
 0:12:20
0:12:20
 0:12:41
0:12:41
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:13:46
0:13:46
 0:09:32
0:09:32
 0:35:10
0:35:10
 0:48:12
0:48:12
 0:11:00
0:11:00
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:08:46
0:08:46
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:30:39
0:30:39
 0:26:54
0:26:54
 0:16:50
0:16:50
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:23:21
0:23:21
 1:24:08
1:24:08
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:10:00
0:10:00
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:44:28
0:44:28
 0:01:12
0:01:12