filmov
tv
Intro to ARP spoofing and bettercap

Показать описание
In this video I will test the man-in-the-middle tool called bettercap. I will explain the concept of ARP spoofing, install bettercap, and see how one can use it to sniff passwords on a network.
For further tutorials and trainings check out my blog:
Trainings:
Video Transcript:
Hello there. My name is Gergely Revay or Geri. Today I’m gonna talk about bettercap. This is a new tool I found recently and it got my attention because it’s a man in the middle tool. And we talk about man in the middle attacks all the time like in an assessment when we say it’s bad to send stuff unencrypted on the network because a man in the middle attacker can then sniff your network and find out your passwords or anything. When I found this tool, I thought this would be a good opportunity to play a little bit with man in the middle attacks. So what I’m gonna do today is introduce bettercap, talk a little bit about network sniffing and ARP poisoning for those people who don’t really know what that is and how it works, and then we’ll install and try bettercap, the basic features. We’ll sniff network a little bit to find some passwords and talk about what bettercap is capable of.
So let’s start with the installation. So you can see here already, I have the bettercap website on my screen. And basically the installation is not that difficult because you can just use Ruby GEM to install. Bettercap is actually a full Ruby application and you can extend it in Ruby. So it’s good for you if you know Ruby well. Now, the installation is also documented in the website so you can check it out and also do it yourself. So let’s go to a terminal. First, I’m gonna install the dependencies, which some of it is already installed in Kali but I’m not gonna check exactly and just go on with the installation. And then it’s build essential Ruby development packages and libpcap for manipulating traffic. Yeah. So now we have the dependencies. Then let’s get on with the installation of bettercap. And it’s gem install bettercap. It’s gonna take a little bit so just be patient. Okay, the installation is ready so let’s see if we can execute it. Yes. So that’s how it works. That’s a good start.
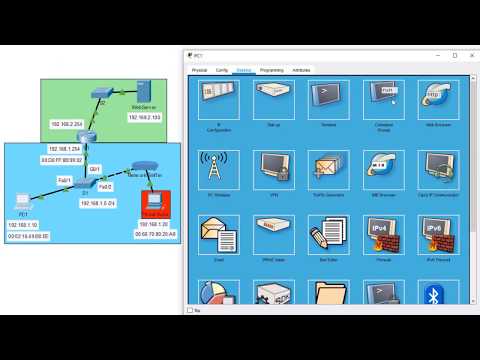
Now, before I start getting into bettercap, I will just explain quickly how this network sniffing works, how ARP poisoning works, etc. For that, let me draw for you. So what happens here, I’m gonna use two computers, the Kali what you’ve seen and a Windows 8 machine. These are both virtual machines and they’re both on the same network. So what it essentially means is that we have Internet there. And then I have a router here. I have here my Kali and I have here my victim. So normally the victim communicates with the router directly and then that goes to the Internet. That goal that we want to reach is that this communication goes to Kali and then to the router. Now, bettercap offers different methods to do this. What we are gonna use is ARP poisoning, which means that Kali has a MAC address here. It’s called MAC K, let’s call it this way. He has a MAC V, and this has a MAC R. So these are normal MAC addresses that you already know. When the victim wants to go to the Internet, he has to first send the packets to the router. So what he will ask, he will know the IP address of the router, but he wants to find out what the MAC address for that IP address so that he can send the packet. He will ask the network what is the MAC address for that particular IP address.
Now, what bettercap does is whenever such a request happens, then he will always respond hopefully as the first responder. He always say that my MAC address is for that IP. So whenever the victim or the router or anybody else on this network asks for IP address or asks for the MAC address of an IP address, our attacker with bettercap will always say that my MAC address is related to this IP address. That way, basically, the victim is gonna think that on the network he has to send his packet first here because he will think that this is the router and then bettercap will relay this packet to the router but also when a packet comes back, the router will also think -- because he will also request a MAC address – he will also think that Kali or bettercap is the victim. And then Kali will just relay again the packet to the victim. So we basically reached our goal here. Because of this ARP spoofing or ARP poisoning, all packets will cross our Kali machine through bettercap and then from this point on, basically bettercap is able to do whatever he wants with those packets. Bettercap also offers different tools to..
--Cut due to length limit--
For further tutorials and trainings check out my blog:
Trainings:
Video Transcript:
Hello there. My name is Gergely Revay or Geri. Today I’m gonna talk about bettercap. This is a new tool I found recently and it got my attention because it’s a man in the middle tool. And we talk about man in the middle attacks all the time like in an assessment when we say it’s bad to send stuff unencrypted on the network because a man in the middle attacker can then sniff your network and find out your passwords or anything. When I found this tool, I thought this would be a good opportunity to play a little bit with man in the middle attacks. So what I’m gonna do today is introduce bettercap, talk a little bit about network sniffing and ARP poisoning for those people who don’t really know what that is and how it works, and then we’ll install and try bettercap, the basic features. We’ll sniff network a little bit to find some passwords and talk about what bettercap is capable of.
So let’s start with the installation. So you can see here already, I have the bettercap website on my screen. And basically the installation is not that difficult because you can just use Ruby GEM to install. Bettercap is actually a full Ruby application and you can extend it in Ruby. So it’s good for you if you know Ruby well. Now, the installation is also documented in the website so you can check it out and also do it yourself. So let’s go to a terminal. First, I’m gonna install the dependencies, which some of it is already installed in Kali but I’m not gonna check exactly and just go on with the installation. And then it’s build essential Ruby development packages and libpcap for manipulating traffic. Yeah. So now we have the dependencies. Then let’s get on with the installation of bettercap. And it’s gem install bettercap. It’s gonna take a little bit so just be patient. Okay, the installation is ready so let’s see if we can execute it. Yes. So that’s how it works. That’s a good start.
Now, before I start getting into bettercap, I will just explain quickly how this network sniffing works, how ARP poisoning works, etc. For that, let me draw for you. So what happens here, I’m gonna use two computers, the Kali what you’ve seen and a Windows 8 machine. These are both virtual machines and they’re both on the same network. So what it essentially means is that we have Internet there. And then I have a router here. I have here my Kali and I have here my victim. So normally the victim communicates with the router directly and then that goes to the Internet. That goal that we want to reach is that this communication goes to Kali and then to the router. Now, bettercap offers different methods to do this. What we are gonna use is ARP poisoning, which means that Kali has a MAC address here. It’s called MAC K, let’s call it this way. He has a MAC V, and this has a MAC R. So these are normal MAC addresses that you already know. When the victim wants to go to the Internet, he has to first send the packets to the router. So what he will ask, he will know the IP address of the router, but he wants to find out what the MAC address for that IP address so that he can send the packet. He will ask the network what is the MAC address for that particular IP address.
Now, what bettercap does is whenever such a request happens, then he will always respond hopefully as the first responder. He always say that my MAC address is for that IP. So whenever the victim or the router or anybody else on this network asks for IP address or asks for the MAC address of an IP address, our attacker with bettercap will always say that my MAC address is related to this IP address. That way, basically, the victim is gonna think that on the network he has to send his packet first here because he will think that this is the router and then bettercap will relay this packet to the router but also when a packet comes back, the router will also think -- because he will also request a MAC address – he will also think that Kali or bettercap is the victim. And then Kali will just relay again the packet to the victim. So we basically reached our goal here. Because of this ARP spoofing or ARP poisoning, all packets will cross our Kali machine through bettercap and then from this point on, basically bettercap is able to do whatever he wants with those packets. Bettercap also offers different tools to..
--Cut due to length limit--
Комментарии
 0:15:39
0:15:39
 0:01:32
0:01:32
 0:11:35
0:11:35
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:16:46
0:16:46
 0:13:46
0:13:46
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:06:47
0:06:47
 0:07:24
0:07:24
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:08:18
0:08:18
 0:02:08
0:02:08
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:07:47
0:07:47