filmov
tv
L-6.1: Hard Disk Architecture in Operating System in Hindi

Показать описание
You will get full knowledge of Hard disk architecture in this video. Students find this topic little difficult so here you will get full knowledge of Hard disk architecture.
►Operating System (Complete Playlist):
Other subject-wise playlist Links:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
►Design and Analysis of algorithms (DAA):
►Database Management System:
► Theory of Computation
►Artificial Intelligence:
►Computer Networks (Complete Playlist):
►Computer Architecture (Complete Playlist):
►Structured Query Language (SQL):
►Discrete Mathematics:
►Compiler Design:
►Number System:
►Cloud Computing & BIG Data:
►Software Engineering:
►Data Structure:
►Graph Theory:
►Programming in C:
►Digital Logic:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Our social media Links:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
►For Any Query, Suggestion or notes contribution:
#DiskArchitecture #HardDiskArchitecture#operatingsystem
Комментарии
 0:11:35
0:11:35
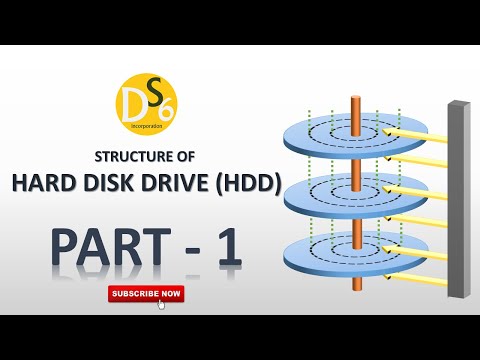 0:11:37
0:11:37
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:15:16
0:15:16
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:08:03
0:08:03
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 0:07:14
0:07:14
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:14:35
0:14:35
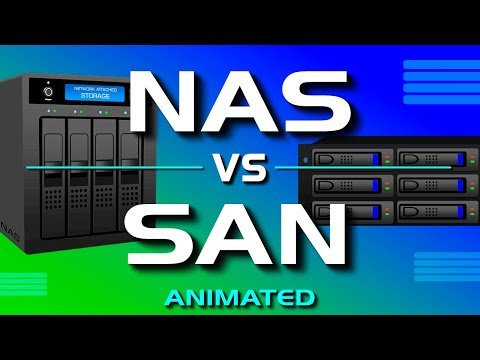 0:04:27
0:04:27
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:09:57
0:09:57
 0:12:17
0:12:17
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:05:38
0:05:38
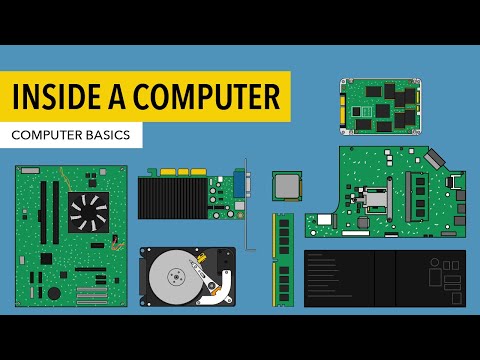 0:02:17
0:02:17
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:10:22
0:10:22
 0:22:02
0:22:02
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:06:08
0:06:08