filmov
tv
Budget Constraints

Показать описание
Think through all of the variables that determine the price of a cup of coffee. It might help to imagine the coffee beans on the farm first. Consider the land costs and the price of the farmer’s labor. What about transportation of the beans to the roaster? There are packaging costs, oil costs, driver costs...and we’re still only talking about the beans!
Once the roasted beans finally make it to your local coffee shop, they still have to be turned in that cup of coffee. The cost of rent for the building is a factor in the price of the final good, as is the labor of the barista and the price of electricity in your area.
We’re barely scratching the surface here, but you get the idea that a ton of variables are behind the price of even a relatively simple good like a cup of coffee. What you, the consumer, are able and willing to pay is yet another one. Your salary helps set your budget constraints. And your budget constraints are a crucial variable in helping you decide whether to spend $5 on that cup of coffee, or $5 on something else.
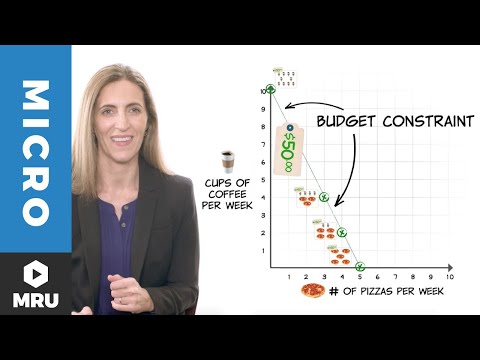
In this video, we’ll examine what budget constraints look like and how they function by graphing a simple example: $50 to spend on $5 coffees or $10 pizzas. You’ll see how the graph shifts as variables change. We’ll also use this example talk about a fundamental concept in economics that can help you make better decisions: opportunity costs.
Once the roasted beans finally make it to your local coffee shop, they still have to be turned in that cup of coffee. The cost of rent for the building is a factor in the price of the final good, as is the labor of the barista and the price of electricity in your area.
We’re barely scratching the surface here, but you get the idea that a ton of variables are behind the price of even a relatively simple good like a cup of coffee. What you, the consumer, are able and willing to pay is yet another one. Your salary helps set your budget constraints. And your budget constraints are a crucial variable in helping you decide whether to spend $5 on that cup of coffee, or $5 on something else.
In this video, we’ll examine what budget constraints look like and how they function by graphing a simple example: $50 to spend on $5 coffees or $10 pizzas. You’ll see how the graph shifts as variables change. We’ll also use this example talk about a fundamental concept in economics that can help you make better decisions: opportunity costs.
Комментарии
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:49:05
0:49:05
 0:33:31
0:33:31
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:12:11
0:12:11
 0:06:25
0:06:25
 0:09:24
0:09:24
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:06:00
0:06:00
 0:19:23
0:19:23
 0:09:44
0:09:44
 0:07:26
0:07:26
 0:05:34
0:05:34
 0:14:16
0:14:16
 0:31:56
0:31:56
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:22:58
0:22:58
 0:06:56
0:06:56
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:04:10
0:04:10