filmov
tv
Collagen Synthesis USMLE Mnemonic Preview

Показать описание
Collagen synthesis is an important process that happens through a series of both intracellular and extracellular steps.
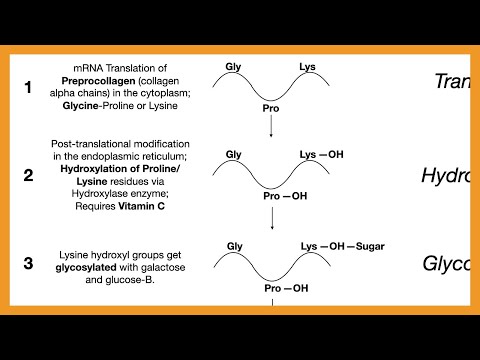
First, the translation of alpha chains forms preprocollagen. Glycine is a major part of these alpha chains, forming about ⅓ of the amino acid sequence.
Second, hydroxylation of preprocollagen occurs at proline and lysine residues. These hydroxylase enzymes require vitamin C to be present as a cofactor, and deficiencies of vitamin C, such as that seen in scurvy, can cause defects in collagen.
Third, glycosylation of hydroxylysine residues occurs. Glycosylation and other modifications enable the formation of hydrogen and disulfide bonds, which cause 3 polypeptide chains to form a triple helix, also known as procollagen. Defects in forming a triple helix are seen in Osteogenesis Imperfecta.
Fourth, procollagen exits the cell. In other words, it undergoes exocytosis to reach the extracellular matrix.
Fifth, extracellular procollagen undergoes cleavage by procollagen peptidases to form tropocollagen. Defects in this cleavage can be observed in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.
Finally, adjacent tropocollagen molecules undergo cross-linking to form mature collagen. This cross-linking occurs between lysine residues, and is catalyzed by lysyl-oxidase. Defects in cross-linking can cause some types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Note that lysyl oxidase is a copper-dependent enzyme, so copper deficiency such as seen in Menkes disease can also impair collagen cross-linking.
Study this Collagen Synthesis mnemonic and other USMLE Step 1 / NBME mnemonics with Pixorize.
#usmle #step1 #collagen #mnemonic
First, the translation of alpha chains forms preprocollagen. Glycine is a major part of these alpha chains, forming about ⅓ of the amino acid sequence.
Second, hydroxylation of preprocollagen occurs at proline and lysine residues. These hydroxylase enzymes require vitamin C to be present as a cofactor, and deficiencies of vitamin C, such as that seen in scurvy, can cause defects in collagen.
Third, glycosylation of hydroxylysine residues occurs. Glycosylation and other modifications enable the formation of hydrogen and disulfide bonds, which cause 3 polypeptide chains to form a triple helix, also known as procollagen. Defects in forming a triple helix are seen in Osteogenesis Imperfecta.
Fourth, procollagen exits the cell. In other words, it undergoes exocytosis to reach the extracellular matrix.
Fifth, extracellular procollagen undergoes cleavage by procollagen peptidases to form tropocollagen. Defects in this cleavage can be observed in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.
Finally, adjacent tropocollagen molecules undergo cross-linking to form mature collagen. This cross-linking occurs between lysine residues, and is catalyzed by lysyl-oxidase. Defects in cross-linking can cause some types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Note that lysyl oxidase is a copper-dependent enzyme, so copper deficiency such as seen in Menkes disease can also impair collagen cross-linking.
Study this Collagen Synthesis mnemonic and other USMLE Step 1 / NBME mnemonics with Pixorize.
#usmle #step1 #collagen #mnemonic
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:02:16
0:02:16
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:11:21
0:11:21
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:15:57
0:15:57
 0:08:04
0:08:04
![COLLAGEN [Mnemonic]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/degf4mBufeM/hqdefault.jpg) 0:01:05
0:01:05
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:07:45
0:07:45
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:07:07
0:07:07
 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:07:58
0:07:58
 0:11:54
0:11:54
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:00:22
0:00:22