filmov
tv
The Feynman-Kac formula, partial differential equations and Brownian motion [QCT21/22, Seminar #12]

Показать описание
By Nicolas Robles (RAND Corporation).
Abstract: We propose an algorithm based on variational quantum imaginary time evolution for solving the Feynman-Kac partial differential equation resulting from a multidimensional system of stochastic differential equations. We utilize the correspondence between the Feynman-Kac partial differential equation (PDE) and the Wick-rotated Schrödinger equation for this purpose. The results for a (2+1) dimensional Feynman-Kac system obtained through the variational quantum algorithm are then compared against classical ODE solvers and Monte Carlo simulation. We see a remarkable agreement between the classical methods and the quantum variational method for an illustrative example on six and eight qubits. In the non-trivial case of PDEs which are preserving probability distributions – rather than preserving the ℓ2-norm – we introduce a proxy norm which is efficient in keeping the solution approximately normalized throughout the evolution. The algorithmic complexity and costs associated to this methodology, in particular for the extraction of properties of the solution, are investigated. Future research topics in the areas of quantitative finance and other types of PDEs are also discussed.
Biography: Nicolas was a computational scientist at IBM Quantum in New York before joining RAND Corporation as an applied mathematician. His areas of expertise are quantum simulation of stochastic processes with applications to chemistry and quantitative finance in addition to post quantum cryptography.
Nicolas earned a PhD in mathematics with a specialization in analytic number theory from Zurich, Switzerland, as well as master's degrees in theoretical physics and mathematics from Imperial College London and the University of Cambridge. His favorite topics of mathematics include graph theory, combinatorics, game theory, operations research as well as probability and stochastic calculus. Prior to joining IBM, Nicolas was a J L Doob Research Assistant Professor of Mathematics at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and also worked in investment banking at JPMorgan Chase, Nomura, UBS and Bank of America Merrill Lynch.
Away from work, Nicolas enjoys golf, skiing, soccer, board games, spending time with his dogs and his family.
Abstract: We propose an algorithm based on variational quantum imaginary time evolution for solving the Feynman-Kac partial differential equation resulting from a multidimensional system of stochastic differential equations. We utilize the correspondence between the Feynman-Kac partial differential equation (PDE) and the Wick-rotated Schrödinger equation for this purpose. The results for a (2+1) dimensional Feynman-Kac system obtained through the variational quantum algorithm are then compared against classical ODE solvers and Monte Carlo simulation. We see a remarkable agreement between the classical methods and the quantum variational method for an illustrative example on six and eight qubits. In the non-trivial case of PDEs which are preserving probability distributions – rather than preserving the ℓ2-norm – we introduce a proxy norm which is efficient in keeping the solution approximately normalized throughout the evolution. The algorithmic complexity and costs associated to this methodology, in particular for the extraction of properties of the solution, are investigated. Future research topics in the areas of quantitative finance and other types of PDEs are also discussed.
Biography: Nicolas was a computational scientist at IBM Quantum in New York before joining RAND Corporation as an applied mathematician. His areas of expertise are quantum simulation of stochastic processes with applications to chemistry and quantitative finance in addition to post quantum cryptography.
Nicolas earned a PhD in mathematics with a specialization in analytic number theory from Zurich, Switzerland, as well as master's degrees in theoretical physics and mathematics from Imperial College London and the University of Cambridge. His favorite topics of mathematics include graph theory, combinatorics, game theory, operations research as well as probability and stochastic calculus. Prior to joining IBM, Nicolas was a J L Doob Research Assistant Professor of Mathematics at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and also worked in investment banking at JPMorgan Chase, Nomura, UBS and Bank of America Merrill Lynch.
Away from work, Nicolas enjoys golf, skiing, soccer, board games, spending time with his dogs and his family.
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 1:12:48
1:12:48
 0:25:16
0:25:16
 1:03:50
1:03:50
 1:03:50
1:03:50
 0:17:30
0:17:30
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:41:08
0:41:08
 1:13:39
1:13:39
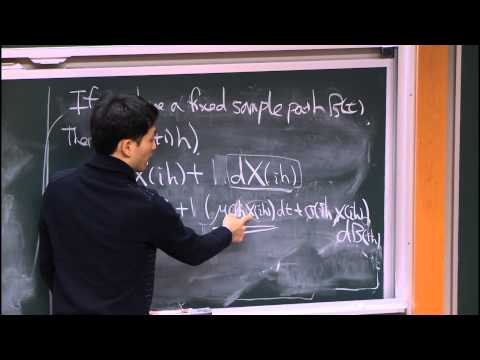 0:56:05
0:56:05
 0:48:40
0:48:40
 0:29:43
0:29:43
 0:34:31
0:34:31
 0:25:39
0:25:39
 0:53:57
0:53:57
 0:42:38
0:42:38
 0:11:34
0:11:34
 1:25:52
1:25:52
 0:17:39
0:17:39
 0:50:45
0:50:45
 0:12:00
0:12:00
 0:22:56
0:22:56
 0:29:58
0:29:58
 0:01:24
0:01:24