filmov
tv
DNA vs RNA Class 10 CBSE #shorts

Показать описание
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) are both nucleic acids that play crucial roles in the storage, expression, and transmission of genetic information. Here are the key differences between them:
Sugar Component:
DNA contains deoxyribose sugar.
RNA contains ribose sugar.
Bases:
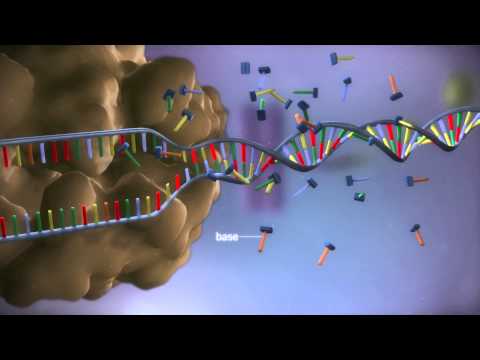
DNA has four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
RNA has the same bases except uracil (U) replaces thymine (T).
Structure:
DNA typically exists as a double-stranded helix.
RNA is generally single-stranded, although some types can be double-stranded in specific biological processes.
Function:
DNA primarily serves as the genetic material, carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses.
RNA is involved in various cellular roles including coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. It plays a crucial role in protein synthesis as well as carrying out the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes.
Stability:
DNA is more stable due to the presence of the thymine base and the double-stranded structure.
RNA is more prone to chemical degradation and has a shorter lifespan compared to DNA.
Location:
DNA is primarily found in the cell nucleus and in some organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts.
RNA can be found in the nucleus as well as in the cytoplasm and other parts of the cell.
Understanding these fundamental differences is crucial for comprehending the diverse roles DNA and RNA play in the functioning of living organisms.
#science #biology #cbse #class10 #ncert #physicswallah #unacademy #zoology #selfstudy #studymaterial #allen #neet #exam #byjus #aakash #education #learning #pw #vedantu #icse #lifescience #dna #rna #boardexam #board #boards
Sugar Component:
DNA contains deoxyribose sugar.
RNA contains ribose sugar.
Bases:
DNA has four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
RNA has the same bases except uracil (U) replaces thymine (T).
Structure:
DNA typically exists as a double-stranded helix.
RNA is generally single-stranded, although some types can be double-stranded in specific biological processes.
Function:
DNA primarily serves as the genetic material, carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses.
RNA is involved in various cellular roles including coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. It plays a crucial role in protein synthesis as well as carrying out the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes.
Stability:
DNA is more stable due to the presence of the thymine base and the double-stranded structure.
RNA is more prone to chemical degradation and has a shorter lifespan compared to DNA.
Location:
DNA is primarily found in the cell nucleus and in some organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts.
RNA can be found in the nucleus as well as in the cytoplasm and other parts of the cell.
Understanding these fundamental differences is crucial for comprehending the diverse roles DNA and RNA play in the functioning of living organisms.
#science #biology #cbse #class10 #ncert #physicswallah #unacademy #zoology #selfstudy #studymaterial #allen #neet #exam #byjus #aakash #education #learning #pw #vedantu #icse #lifescience #dna #rna #boardexam #board #boards
Комментарии
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:10:50
0:10:50
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:59:29
0:59:29
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:04:41
0:04:41
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:08:47
0:08:47
 0:11:15
0:11:15
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:00:06
0:00:06