filmov
tv
Band Theory of Solids

Показать описание
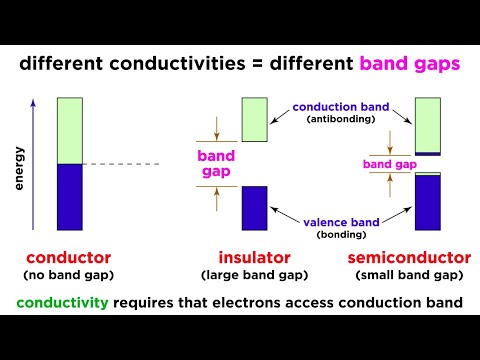
Band Theory of Solids Band theory of solids is a quantum-mechanical theory of motion of electrons in solids. Energy bands are located differently in various substances, as well as in various forms of the same substance. According to these bands' relative position substances are divided into three big groups. Conductors - conduction and valence bands are overlapping and thus create one band called conduction band. In this way, electron can freely travel between them having acquired any acceptably low energy. Thus when potential difference is applied to solids, electrons can freely travel from the point with lesser potential to the one with bigger potential creating electric current. All metals are conductors. Dielectrics - the bands are not overlapping. Distance between them is more than 4 electron-volts. Thus considerable energy is required to move the electron from valence band to conduction band. That is why dielectrics virtually do not conduct current. Semiconductors - the bands are not overlapping. Distance between them is more than 4 electron-volts. As compared with dielectrics, lesser energy is required to move the electron from valence band to conduction band. That is why pure semiconductors (also called intrinsic or undoped) conduct current poorly. Band theory is the basis of a contemporary theory of solids. It helped to understand nature and explain the most important properties of metals, semiconductors, and dielectrics. Band gap value between valence and conduction bands is a key value in band theory. It determines optical and electrical properties of a material. Conductivity properties of semiconductors depend heavily on temperature, as a thermal mechanism of transferring energy to the electron is considered to be one of the main ones. Conductivity can be increased by creating an allowed energy level in the band gap by means of doping. All semiconductor devices are made in this way. These are, for example, solar cells (i.e. converters of light into energy), diodes, transistors, solid lasers, and other devices.
Комментарии
 0:08:22
0:08:22
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:10:15
0:10:15
 0:17:05
0:17:05
 0:15:07
0:15:07
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:21:47
0:21:47
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:10:19
0:10:19
 1:26:35
1:26:35
 0:32:48
0:32:48
 1:21:53
1:21:53
 0:23:55
0:23:55
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:16:06
0:16:06
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:13:56
0:13:56
 0:26:12
0:26:12
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:10:05
0:10:05