filmov
tv
Structure Of Hair Follicle - Hair Color - How Does Hair Growth Work
Показать описание
In this video we discuss the structure of hair, how does hair grow and how does hair color work? We also look at the function of the sebaceous gland and the function of the arrector pili muscle.
Transcript/notes
Hair structure, hair color and hair growth.
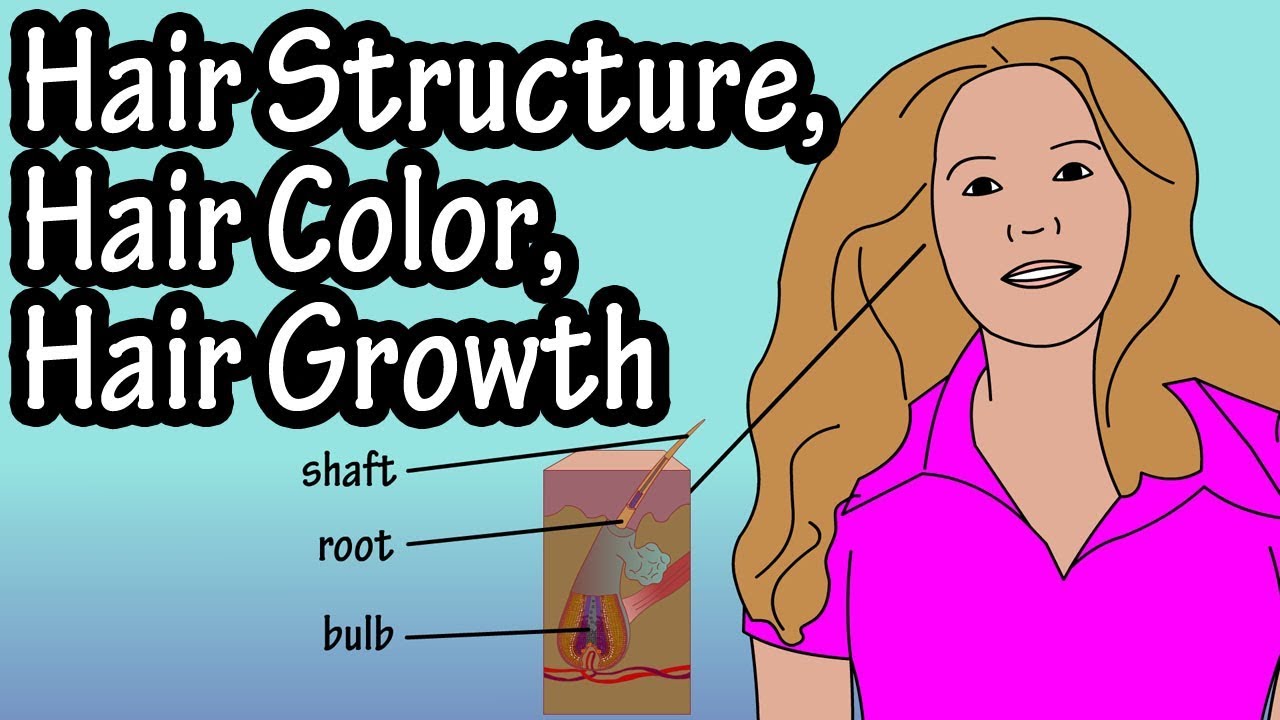
Hair consists of 3 main sections, the hair bulb, the hair root and the hair shaft. The hair shaft is the top portion of the hair that extends out from the surface of the skin. The hair root extends from the bulb to the surface of the skin, and the bulb extends from the root deeper into the dermal layer of the skin.
The hair follicle is the sac or tube that surrounds the hair root and extends into the dermis and it consists of an outer connective tissue sheath that originates from the dermis and an external epithelial root sheath and an internal epithelial root sheath.
At the bottom of the follicle in the hair bulb is the germinal matrix which consists of epithelial cells. Protruding into the germinal matrix is the hair papilla which is composed of connective tissue and houses nerves and blood vessels that nourish the germinal matrix. Melanocyte cells are located in the germinal matrix, and they produce the pigment that gives hair its color.
The hair blade consists of 3 sections, the medulla, located in the middle, the cortex and the cuticle.
A sebaceous gland is located here, and an arrector pili muscle is located here. We will cover these in a minute.
Hair is formed by cells in the germinal matrix which undergo mitosis, or cell division, and move upwards in the follicle and become keratinized. Keratinized cells being cells that were once alive, but filled with the keratin protein as they matured, causing them to lose their organelles and die.
Hair on the scalp typically grows about a ½ inch per month or 5 inches per year with body hair growing more slowly. Scalp hair can live between 2 and 6 years, then die and are replaced by new hairs. As we age hair may thin, or baldness can develop with heredity being the main cause.
Hair color is determined by the melanocyte cells mentioned earlier. Melanocytes release the pigment melanin which enters into the keratinized cells and gives the hair its color. There are 2 types of pigments that are released, a dark eumelanin and a lighter pheomelanin, which blend to form a wide range of colors. Hormonal and environmental factors can contribute to hair color as well. As we age, melanin production decreases which makes hair appear grey and eventually melanin production completely stops producing white hair.
The sebaceous gland mentioned earlier secretes an oily substance called sebum which lubricates and conditions hair and skin preventing it from becoming dry, brittle or easily damaged. And the arrector pili muscle is activated as a response to an emotional state or cold temperatures. It pulls the hair follicle, elevating the hair, producing goose bumps.
Timestamps
0:00 The 3 main sections of hair
0:21 The hair follicle
1:11 How hair is formed
1:27 Hair growth over time
1:45 Hair color
Transcript/notes
Hair structure, hair color and hair growth.
Hair consists of 3 main sections, the hair bulb, the hair root and the hair shaft. The hair shaft is the top portion of the hair that extends out from the surface of the skin. The hair root extends from the bulb to the surface of the skin, and the bulb extends from the root deeper into the dermal layer of the skin.
The hair follicle is the sac or tube that surrounds the hair root and extends into the dermis and it consists of an outer connective tissue sheath that originates from the dermis and an external epithelial root sheath and an internal epithelial root sheath.
At the bottom of the follicle in the hair bulb is the germinal matrix which consists of epithelial cells. Protruding into the germinal matrix is the hair papilla which is composed of connective tissue and houses nerves and blood vessels that nourish the germinal matrix. Melanocyte cells are located in the germinal matrix, and they produce the pigment that gives hair its color.
The hair blade consists of 3 sections, the medulla, located in the middle, the cortex and the cuticle.
A sebaceous gland is located here, and an arrector pili muscle is located here. We will cover these in a minute.
Hair is formed by cells in the germinal matrix which undergo mitosis, or cell division, and move upwards in the follicle and become keratinized. Keratinized cells being cells that were once alive, but filled with the keratin protein as they matured, causing them to lose their organelles and die.
Hair on the scalp typically grows about a ½ inch per month or 5 inches per year with body hair growing more slowly. Scalp hair can live between 2 and 6 years, then die and are replaced by new hairs. As we age hair may thin, or baldness can develop with heredity being the main cause.
Hair color is determined by the melanocyte cells mentioned earlier. Melanocytes release the pigment melanin which enters into the keratinized cells and gives the hair its color. There are 2 types of pigments that are released, a dark eumelanin and a lighter pheomelanin, which blend to form a wide range of colors. Hormonal and environmental factors can contribute to hair color as well. As we age, melanin production decreases which makes hair appear grey and eventually melanin production completely stops producing white hair.
The sebaceous gland mentioned earlier secretes an oily substance called sebum which lubricates and conditions hair and skin preventing it from becoming dry, brittle or easily damaged. And the arrector pili muscle is activated as a response to an emotional state or cold temperatures. It pulls the hair follicle, elevating the hair, producing goose bumps.
Timestamps
0:00 The 3 main sections of hair
0:21 The hair follicle
1:11 How hair is formed
1:27 Hair growth over time
1:45 Hair color
Комментарии
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:02:50
0:02:50
 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:06:30
0:06:30
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:08:38
0:08:38
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:17:34
0:17:34
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:27:14
0:27:14
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:07:11
0:07:11
 0:11:42
0:11:42
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:02:27
0:02:27
 0:14:18
0:14:18