filmov
tv
Understanding Geometric Mean in Excel | Geometric vs. Arithmetic Mean

Показать описание
✅The geometric mean is a powerful statistical tool that provides valuable insights into data analysis, especially when dealing with growth rates, financial returns, and other multiplicative processes. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the concept of geometric mean, its applications, and how to effectively use it in Microsoft Excel. We will compare the geometric mean vs. the average.
The geometric mean is a measure of central tendency that uses multiplication rather than addition to calculate the average of a set of numbers. It's particularly useful when working with data that involves rates of change or growth over time.
✅Geometric Mean vs. Arithmetic Mean
While the arithmetic mean (commonly referred to as the average) is calculated by summing up all values and dividing by the count, the geometric mean multiplies all values and then takes the nth root, where n is the number of values in the dataset. This fundamental difference makes the geometric mean more suitable for certain types of data analysis.
The geometric mean is particularly useful in various scenarios because it provides a more accurate measure of central tendency for data sets that are multiplicative or vary exponentially. Here are a few reasons why you might use the geometric mean:
1. Proportional Growth: It’s ideal for data that grows or shrinks proportionally, such as interest rates, population growth, or investment returns.
2. Normalization: It helps in normalizing data that spans several orders of magnitude, making it easier to compare.
3. Multiplicative Relationships: When dealing with ratios or percentages, the geometric mean gives a better central tendency than the arithmetic mean.
4. Logarithmic Data: For data that is log-normally distributed, the geometric mean is more representative of the central location.
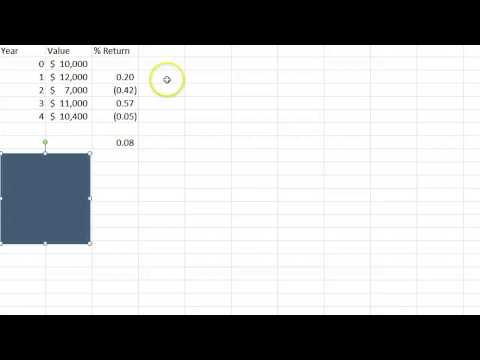
For example, if you’re comparing the performance of different investment portfolios over time, the geometric mean will give you a better sense of the average rate of return, accounting for the compounding effect.
✅Chapters/Bookmarks
00:00 Introduction to Geometric Mean
00:21 Understanding Geometric Mean vs Average
00:33 Example 1: Basic Calculation
02:16 Example 2: Employee Task Duration
03:45 Example 3: Financial Investment
05:43 Conclusion and Additional ResourcesAnd make sure you subscribe to my channel!
✅When to Use Geometric Mean
The geometric mean is particularly useful in the following scenarios:
1) Calculating average growth rates
2) Analyzing investment returns
3) Evaluating performance metrics that involve multiplicative relationships
4) Studying biological growth or population dynamics
✅Calculating Geometric Mean in Excel
Excel provides a built-in function for calculating the geometric mean, making it easy to apply this statistical measure to your data.
Using the GEOMEAN Function
To calculate the geometric mean in Excel, you can use the GEOMEAN function. Here's the basic syntax:
=GEOMEAN(number1, [number2], ...)
Where number1, number2, etc., represent the values or range of cells containing the numbers you want to calculate the geometric mean for.✅Calculating Geometric Mean in Excel
Excel provides a built-in function for calculating the geometric mean, making it easy to apply this statistical measure to your data.
✅Using the GEOMEAN Function
To calculate the geometric mean in Excel, you can use the GEOMEAN function. Here's the basic syntax:
=GEOMEAN(number1, [number2], ...)
Where number1, number2, etc., represent the values or range of cells containing the numbers you want to calculate the geometric mean for.
-- EQUIPMENT USED ---------------------------------
-- SOFTWARE USED ---------------------------------
DISCLAIMER: Links included in this description might be affiliate links. If you purchase a product or service with the links I provide, I may receive a small commission. There is no additional charge to you! Thank you for supporting my channel, so I can continue to provide you with free content each week!
The geometric mean is a measure of central tendency that uses multiplication rather than addition to calculate the average of a set of numbers. It's particularly useful when working with data that involves rates of change or growth over time.
✅Geometric Mean vs. Arithmetic Mean
While the arithmetic mean (commonly referred to as the average) is calculated by summing up all values and dividing by the count, the geometric mean multiplies all values and then takes the nth root, where n is the number of values in the dataset. This fundamental difference makes the geometric mean more suitable for certain types of data analysis.
The geometric mean is particularly useful in various scenarios because it provides a more accurate measure of central tendency for data sets that are multiplicative or vary exponentially. Here are a few reasons why you might use the geometric mean:
1. Proportional Growth: It’s ideal for data that grows or shrinks proportionally, such as interest rates, population growth, or investment returns.
2. Normalization: It helps in normalizing data that spans several orders of magnitude, making it easier to compare.
3. Multiplicative Relationships: When dealing with ratios or percentages, the geometric mean gives a better central tendency than the arithmetic mean.
4. Logarithmic Data: For data that is log-normally distributed, the geometric mean is more representative of the central location.
For example, if you’re comparing the performance of different investment portfolios over time, the geometric mean will give you a better sense of the average rate of return, accounting for the compounding effect.
✅Chapters/Bookmarks
00:00 Introduction to Geometric Mean
00:21 Understanding Geometric Mean vs Average
00:33 Example 1: Basic Calculation
02:16 Example 2: Employee Task Duration
03:45 Example 3: Financial Investment
05:43 Conclusion and Additional ResourcesAnd make sure you subscribe to my channel!
✅When to Use Geometric Mean
The geometric mean is particularly useful in the following scenarios:
1) Calculating average growth rates
2) Analyzing investment returns
3) Evaluating performance metrics that involve multiplicative relationships
4) Studying biological growth or population dynamics
✅Calculating Geometric Mean in Excel
Excel provides a built-in function for calculating the geometric mean, making it easy to apply this statistical measure to your data.
Using the GEOMEAN Function
To calculate the geometric mean in Excel, you can use the GEOMEAN function. Here's the basic syntax:
=GEOMEAN(number1, [number2], ...)
Where number1, number2, etc., represent the values or range of cells containing the numbers you want to calculate the geometric mean for.✅Calculating Geometric Mean in Excel
Excel provides a built-in function for calculating the geometric mean, making it easy to apply this statistical measure to your data.
✅Using the GEOMEAN Function
To calculate the geometric mean in Excel, you can use the GEOMEAN function. Here's the basic syntax:
=GEOMEAN(number1, [number2], ...)
Where number1, number2, etc., represent the values or range of cells containing the numbers you want to calculate the geometric mean for.
-- EQUIPMENT USED ---------------------------------
-- SOFTWARE USED ---------------------------------
DISCLAIMER: Links included in this description might be affiliate links. If you purchase a product or service with the links I provide, I may receive a small commission. There is no additional charge to you! Thank you for supporting my channel, so I can continue to provide you with free content each week!
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:06:41
0:06:41
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:02:13
0:02:13
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:10:12
0:10:12
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:03:40
0:03:40
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:07:15
0:07:15
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:17:24
0:17:24
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:10:09
0:10:09