filmov
tv
Combustion analysis simplified

Показать описание
Combustion analysis is a scientific method used to determine the elemental composition of a sample by measuring the amounts of carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen that are produced when the sample is burned in a controlled environment. This technique is commonly used in the analysis of organic compounds, such as fuels, plastics, and pharmaceuticals, to determine the amounts of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen present in the sample.
During combustion analysis, the sample is burned in the presence of excess oxygen, which ensures that all of the carbon in the sample is converted to carbon dioxide, and all of the hydrogen is converted to water. The nitrogen in the sample is converted to nitrogen gas, which is then measured along with the carbon dioxide and water using specialized analytical equipment.
The combustion process is typically carried out using a combustion tube, which is filled with an oxidizing agent such as copper oxide or magnesium perchlorate, along with the sample being analyzed. The tube is heated to a high temperature using a furnace or other heating source, causing the sample to combust and release carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen gas.
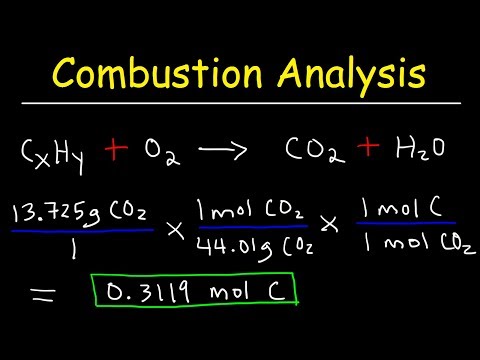
The amounts of carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen produced are then measured using various analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography or infrared spectroscopy, and the elemental composition of the sample is calculated based on these measurements.
Combustion analysis is an important tool in many fields, including environmental science, materials science, and biochemistry. It allows researchers to accurately determine the elemental composition of a wide range of organic compounds, which can provide valuable information about their properties and potential applications.
During combustion analysis, the sample is burned in the presence of excess oxygen, which ensures that all of the carbon in the sample is converted to carbon dioxide, and all of the hydrogen is converted to water. The nitrogen in the sample is converted to nitrogen gas, which is then measured along with the carbon dioxide and water using specialized analytical equipment.
The combustion process is typically carried out using a combustion tube, which is filled with an oxidizing agent such as copper oxide or magnesium perchlorate, along with the sample being analyzed. The tube is heated to a high temperature using a furnace or other heating source, causing the sample to combust and release carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen gas.
The amounts of carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen produced are then measured using various analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography or infrared spectroscopy, and the elemental composition of the sample is calculated based on these measurements.
Combustion analysis is an important tool in many fields, including environmental science, materials science, and biochemistry. It allows researchers to accurately determine the elemental composition of a wide range of organic compounds, which can provide valuable information about their properties and potential applications.
 0:16:49
0:16:49
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:13:24
0:13:24
 0:07:26
0:07:26
 0:06:11
0:06:11
 0:08:02
0:08:02
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:10:47
0:10:47
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:12:10
0:12:10
 0:09:56
0:09:56
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:07:19
0:07:19
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:09:32
0:09:32
 0:10:04
0:10:04
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:02:45
0:02:45