filmov
tv
Spark Tutorial : Different ways to create RDD with examples?

Показать описание
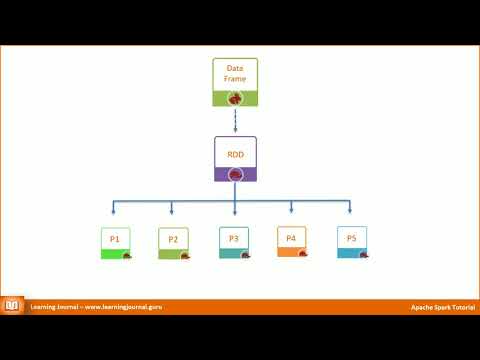
There are three ways to create an RDD.
The first way to create an RDD is to parallelize an object collection, meaning
converting it to a distributed dataset that can be operated in parallel. This is simple and doesn’t require any data files.
This approach is often used to quickly try a feature or do some experimenting in Spark.
The way to parallelize an object collection is to call the parallelize method of the
SparkContext class.
First way to create RDD:
-------------------------------
val sc=new SparkContext("local[*]","union");
val stringList = Array("Welcome to spark tutorials","Spark examples")
Second way to create RDD:
-------------------------------
The second way to create an RDD is to read a dataset from a storage system, which
can be a local computer file system, HDFS, Cassandra, Amazon S3, and so on.
The first argument of the textFile method is an URI that points to a path or a file on the local machine or to a remote storage system. When it starts with an hdfs:// prefix, it
points to a path or a file that resides on HDFS, and when it starts with an s3n:// prefix, then it points to a path or a file that resides on AWS S3.
If a URI points to a directory, then the textFile method will read all the files in that directory.
The textFile method assumes each file is a text file and each line is delimited by a new line. The textFile method returns an RDD that represents all the lines in all the
files.
Third way to create RDD:
-------------------------------
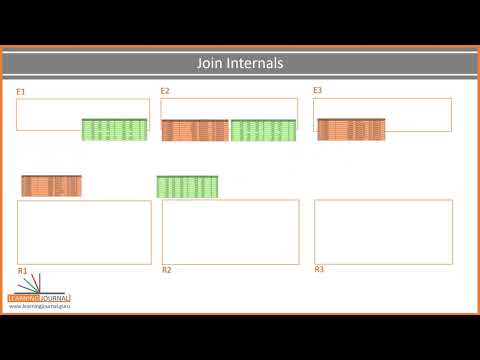
The third way to create an RDD is by invoking one of the transformation operations on an existing RDD.
The first way to create an RDD is to parallelize an object collection, meaning
converting it to a distributed dataset that can be operated in parallel. This is simple and doesn’t require any data files.
This approach is often used to quickly try a feature or do some experimenting in Spark.
The way to parallelize an object collection is to call the parallelize method of the
SparkContext class.
First way to create RDD:
-------------------------------
val sc=new SparkContext("local[*]","union");
val stringList = Array("Welcome to spark tutorials","Spark examples")
Second way to create RDD:
-------------------------------
The second way to create an RDD is to read a dataset from a storage system, which
can be a local computer file system, HDFS, Cassandra, Amazon S3, and so on.
The first argument of the textFile method is an URI that points to a path or a file on the local machine or to a remote storage system. When it starts with an hdfs:// prefix, it
points to a path or a file that resides on HDFS, and when it starts with an s3n:// prefix, then it points to a path or a file that resides on AWS S3.
If a URI points to a directory, then the textFile method will read all the files in that directory.
The textFile method assumes each file is a text file and each line is delimited by a new line. The textFile method returns an RDD that represents all the lines in all the
files.
Third way to create RDD:
-------------------------------
The third way to create an RDD is by invoking one of the transformation operations on an existing RDD.
 1:49:02
1:49:02
 0:15:40
0:15:40
 7:15:32
7:15:32
 0:17:16
0:17:16
 6:41:07
6:41:07
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:20:20
0:20:20
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 7:19:46
7:19:46
 0:19:54
0:19:54
 0:02:39
0:02:39
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:09:15
0:09:15
 0:10:01
0:10:01
 0:38:20
0:38:20
 0:32:23
0:32:23
 0:58:12
0:58:12
 0:14:30
0:14:30
 0:08:32
0:08:32
 0:13:32
0:13:32
 0:06:41
0:06:41
 7:48:37
7:48:37