filmov
tv
Moore's Law

Показать описание
Hello World,
I'm Imagination. Today I am going to talk about Moore's law.
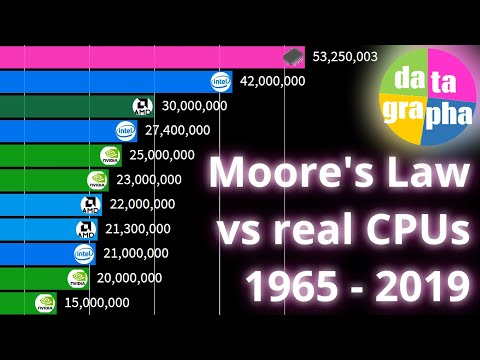
Moore's Law is the observation made in 1965 by Gordon Moore, co-founder of Intel, that the number of transistors per square inch on integrated circuits had doubled every year since the integrated circuit was invented. Today, however, the doubling of installed transistors on silicon chips occurs closer to every 18 months instead of every two years.
Gordon Moore did not call his observation "Moore's Law," nor did he set out to create a "law." Moore made that statement based on noticing emerging trends in chip manufacturing at Intel. Eventually, Moore's insight became a prediction, which in turn became the golden rule known as Moore's Law.
Moore's Law effectively means that approximately every two years personal computers and other electronic devices can do twice as many new, innovative, and unexpected things than before
- Moore's Law makes it virtually certain that two or four or six or more years from now, we'll be doing more things we didn't expect to do with electronic devices. Some of those things will be new, without any traditional precedents
- New things. New opportunities. New competitors. Old companies evolving or dying. New companies rising. A changing media landscape. If you think you've seen a lot change so far, you ain't seen nothing yet!
But,Why does the law exist ?
It exists because ,Manufacturers wishing to keep up with the law,Competition between manufactures,Successive technologies providing better design tools,Customer demand for better products and Man's constant struggle to advance knowledge.
The capabilities of many digital electronic devices are strongly linked to Moore's law such as Processing Speed, Memory capacity, sensors, and even the size of pixels in digital cameras. All of these are improving at exponential rates.The exponential improvement has dramatically enhanced the impact of digital electronics in nearly every segment of the world economy.The exponential growth of Moore's Law will continue beyond the use of integrated circuits into technologies that will lead to technological singularity.
But,Will The Moore's Law ever collapse ?
Physicist say its already happening.
Moores law is said to be breaking down, according to theoretical physicist Michio Kaku. He's talking about the so-called law that says the number of transistors that can be fit on a computer chip will double every 18 months, resulting in periodic increases in computing power.
Michio Kaku said...
"In about ten years or so, we will see the collapse of Moore's law. In fact all ready we see a slowing down of Moore's law. Computer power simply cannot maintain its rapid exponential rise using standard silicon technology .when Moore's law finally collapse by the end of the next decade, we will simply tweak it a bit with chip-like computers in three dimensions. we may have to go to molecular computers and perhaps late in the 21st century quantum computers"
So,What's Next For Computers ? A few possiblitities are:
- Molecular transistors
- Or further down the road, quantum computers
- Until then, Intel, AMD, and other chip makers will continue to squeeze every last ounce of speed and power they can from silicon designs.
That's all for today. Thanks for watching
I'm Imagination. Today I am going to talk about Moore's law.
Moore's Law is the observation made in 1965 by Gordon Moore, co-founder of Intel, that the number of transistors per square inch on integrated circuits had doubled every year since the integrated circuit was invented. Today, however, the doubling of installed transistors on silicon chips occurs closer to every 18 months instead of every two years.
Gordon Moore did not call his observation "Moore's Law," nor did he set out to create a "law." Moore made that statement based on noticing emerging trends in chip manufacturing at Intel. Eventually, Moore's insight became a prediction, which in turn became the golden rule known as Moore's Law.
Moore's Law effectively means that approximately every two years personal computers and other electronic devices can do twice as many new, innovative, and unexpected things than before
- Moore's Law makes it virtually certain that two or four or six or more years from now, we'll be doing more things we didn't expect to do with electronic devices. Some of those things will be new, without any traditional precedents
- New things. New opportunities. New competitors. Old companies evolving or dying. New companies rising. A changing media landscape. If you think you've seen a lot change so far, you ain't seen nothing yet!
But,Why does the law exist ?
It exists because ,Manufacturers wishing to keep up with the law,Competition between manufactures,Successive technologies providing better design tools,Customer demand for better products and Man's constant struggle to advance knowledge.
The capabilities of many digital electronic devices are strongly linked to Moore's law such as Processing Speed, Memory capacity, sensors, and even the size of pixels in digital cameras. All of these are improving at exponential rates.The exponential improvement has dramatically enhanced the impact of digital electronics in nearly every segment of the world economy.The exponential growth of Moore's Law will continue beyond the use of integrated circuits into technologies that will lead to technological singularity.
But,Will The Moore's Law ever collapse ?
Physicist say its already happening.
Moores law is said to be breaking down, according to theoretical physicist Michio Kaku. He's talking about the so-called law that says the number of transistors that can be fit on a computer chip will double every 18 months, resulting in periodic increases in computing power.
Michio Kaku said...
"In about ten years or so, we will see the collapse of Moore's law. In fact all ready we see a slowing down of Moore's law. Computer power simply cannot maintain its rapid exponential rise using standard silicon technology .when Moore's law finally collapse by the end of the next decade, we will simply tweak it a bit with chip-like computers in three dimensions. we may have to go to molecular computers and perhaps late in the 21st century quantum computers"
So,What's Next For Computers ? A few possiblitities are:
- Molecular transistors
- Or further down the road, quantum computers
- Until then, Intel, AMD, and other chip makers will continue to squeeze every last ounce of speed and power they can from silicon designs.
That's all for today. Thanks for watching
 0:01:02
0:01:02
 0:05:33
0:05:33
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:07:27
0:07:27
 0:02:23
0:02:23
 0:14:42
0:14:42
 0:23:41
0:23:41
 0:23:36
0:23:36
 0:04:41
0:04:41
 0:21:27
0:21:27
 0:11:52
0:11:52
 0:12:49
0:12:49
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:13:50
0:13:50
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:20:39
0:20:39
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:06:06
0:06:06
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:14:35
0:14:35