filmov
tv
Visualizing the Concepts of EMF, Electric Potential, Electric Current, & Resistance (NSO | Olympiad)

Показать описание
Mayank Bomb explains Concept of EMF and Potential Difference
=================================
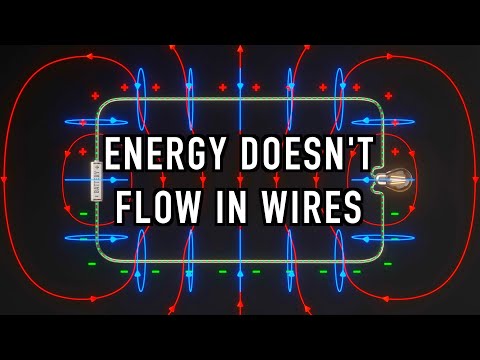
EMF is the work done inside the battery to separate the charges- What we mean by this is that to transport a unit charge from the cathode to the anode inside the battery takes an amount of work equal to W, then W is the potential difference between the terminals of the battery. This
Potential differences or voltages are measured in volts (V) named after Alessandro Volta was an Italian scientist credited as the inventor of the electric battery.
Electric Potential
==============
The EMF generated by the battery is externally available in the circuit as the potential difference- the energy from work done internally by battery is available as this potential difference and now do work in the circuit.
This is similar to the work done by you in paddling the cycle up the hill. Now this work done is stored as gravitational potential energy which can be used to do work- you can now move downhill without doing any more work.
Electric Current
=============
An electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge past a point or region. It is measured in Ampere (SI base unit). Named after André-Marie Ampère a French scientist who inventor of numerous applications- such as the solenoid and early improvements to electrical telegraph
Electric Resistance
================
Electrical Resistance is the opposition provided by materials to flow of electric current. The ohm (symbol: Ω) is the SI derived unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm- A teacher and inventor of ohms law. Ohms law states that the current flow through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference (voltage) and inversely proportional to the resistance.
=================================
EMF is the work done inside the battery to separate the charges- What we mean by this is that to transport a unit charge from the cathode to the anode inside the battery takes an amount of work equal to W, then W is the potential difference between the terminals of the battery. This
Potential differences or voltages are measured in volts (V) named after Alessandro Volta was an Italian scientist credited as the inventor of the electric battery.
Electric Potential
==============
The EMF generated by the battery is externally available in the circuit as the potential difference- the energy from work done internally by battery is available as this potential difference and now do work in the circuit.
This is similar to the work done by you in paddling the cycle up the hill. Now this work done is stored as gravitational potential energy which can be used to do work- you can now move downhill without doing any more work.
Electric Current
=============
An electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge past a point or region. It is measured in Ampere (SI base unit). Named after André-Marie Ampère a French scientist who inventor of numerous applications- such as the solenoid and early improvements to electrical telegraph
Electric Resistance
================
Electrical Resistance is the opposition provided by materials to flow of electric current. The ohm (symbol: Ω) is the SI derived unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm- A teacher and inventor of ohms law. Ohms law states that the current flow through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference (voltage) and inversely proportional to the resistance.
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:08:06
0:08:06
 0:10:18
0:10:18
 0:14:44
0:14:44
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:01:32
0:01:32
 0:02:21
0:02:21
 0:14:48
0:14:48
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:00:43
0:00:43
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:12:05
0:12:05
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:04:59
0:04:59
 0:06:41
0:06:41
 0:08:01
0:08:01
 0:08:36
0:08:36
 0:07:29
0:07:29
 0:09:43
0:09:43