filmov
tv
Standing and Stationary Waves in an open tube - A Level Physics

Показать описание
This video explains standing and stationary waves in an open tube (or open pipe) for A Level Physics.
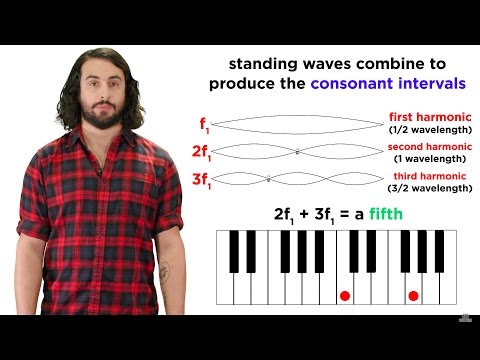
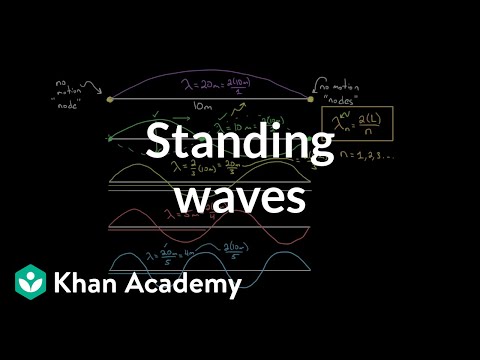
Standing waves on a string are fixed at both ends. Standing waves and stationary waves in an open tube or an open pipe are only fixed at one end (the closed end of the tube or pipe). This means that there must be a node at the closed end and an antinode at the open end. The number of nodes and antinodes in standing waves depends on whether the wave is fixed or not at one or both ends.
Thanks for watching,
Lewis
This video is recommended for anyone studying A Level Physics in the following exam boards:
AQA
CIE
Edexcel
Edexcel IAL
Eduqas
IB
OCR A
OCR B
WJEC
_____________________________________
MY PHYSICS WEBSITES
Find even more videos organised by exam board and topic at:
GCSE Physics Online
A Level Physics Online
MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL
Your support in watching this video has been invaluable! To contribute towards the free videos on YouTube, make a small donation at:
FOLLOW ME
#waves #alevelphysics #physicsonline
Standing waves on a string are fixed at both ends. Standing waves and stationary waves in an open tube or an open pipe are only fixed at one end (the closed end of the tube or pipe). This means that there must be a node at the closed end and an antinode at the open end. The number of nodes and antinodes in standing waves depends on whether the wave is fixed or not at one or both ends.
Thanks for watching,
Lewis
This video is recommended for anyone studying A Level Physics in the following exam boards:
AQA
CIE
Edexcel
Edexcel IAL
Eduqas
IB
OCR A
OCR B
WJEC
_____________________________________
MY PHYSICS WEBSITES
Find even more videos organised by exam board and topic at:
GCSE Physics Online
A Level Physics Online
MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL
Your support in watching this video has been invaluable! To contribute towards the free videos on YouTube, make a small donation at:
FOLLOW ME
#waves #alevelphysics #physicsonline
Комментарии
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:02:29
0:02:29
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:13:25
0:13:25
 0:17:16
0:17:16
 0:02:38
0:02:38
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:56
0:01:56
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:14:10
0:14:10
 0:19:30
0:19:30
 0:14:48
0:14:48
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:19:19
0:19:19
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:09:53
0:09:53
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:06:27
0:06:27
 0:09:55
0:09:55
 0:23:05
0:23:05
 0:04:30
0:04:30