filmov
tv
Acute Inflammation Cellular Events | Margination | Immunology | Part 1

Показать описание
#drnajeeb #medicaleducation #medicines #margination #acuteinflammation
Acute Inflammation Cellular Events | Margination | Immunology | Part 1
Like this video?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Why sign up for premium membership? Here's why!
Membership Features for premium website members.
1. More than 1000+ Medical Lectures.
2. Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine.
3. Mobile-friendly interface with android and iOS apps.
4. English subtitles and new videos every week.
5. Download option for offline video playback.
6. Fanatic customer support and that's 24/7.
7. Fast video playback option to learn faster.
8. Trusted by over 2M+ students in 190 countries.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬ Contents of this video ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
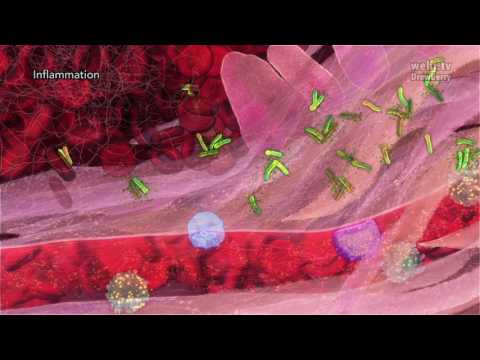
The pathogenesis of acute inflammation occurs progressively through several stages. Firstly, vasculature within and around the site of injury responds by increasing blood flow and enhancing vascular permeability. Secondly, immune cells are recruitment to the vasculature and extravasate into the injured parenchyma. Extravasated immune cells then migrate to the injured cells using gradients of chemotaxis. Once immune cells reach the site of injury they proceed to phagocytose and degrade cellular debris and any microbes which may be present. In this section, we focus on the migration of extravasated immune cells.
The predominant cell of acute inflammation is the neutrophil, which is one type of granulocytes. The migration of neutrophils occurs in four stages, including margination, rolling, adhesion and emigration (Figure 1). Margination refers to cells line up against the endothelium. Rolling means that neutrophils close contact with and roll along the endothelium. Adhesion refers to connect to the endothelial wall. Emigration means that cells move through the vessel wall to the affected area.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Join this channel to get access to the perks:
Acute Inflammation Cellular Events | Margination | Immunology | Part 1
Like this video?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Why sign up for premium membership? Here's why!
Membership Features for premium website members.
1. More than 1000+ Medical Lectures.
2. Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine.
3. Mobile-friendly interface with android and iOS apps.
4. English subtitles and new videos every week.
5. Download option for offline video playback.
6. Fanatic customer support and that's 24/7.
7. Fast video playback option to learn faster.
8. Trusted by over 2M+ students in 190 countries.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬ Contents of this video ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
The pathogenesis of acute inflammation occurs progressively through several stages. Firstly, vasculature within and around the site of injury responds by increasing blood flow and enhancing vascular permeability. Secondly, immune cells are recruitment to the vasculature and extravasate into the injured parenchyma. Extravasated immune cells then migrate to the injured cells using gradients of chemotaxis. Once immune cells reach the site of injury they proceed to phagocytose and degrade cellular debris and any microbes which may be present. In this section, we focus on the migration of extravasated immune cells.
The predominant cell of acute inflammation is the neutrophil, which is one type of granulocytes. The migration of neutrophils occurs in four stages, including margination, rolling, adhesion and emigration (Figure 1). Margination refers to cells line up against the endothelium. Rolling means that neutrophils close contact with and roll along the endothelium. Adhesion refers to connect to the endothelial wall. Emigration means that cells move through the vessel wall to the affected area.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Join this channel to get access to the perks:
Комментарии
 1:06:13
1:06:13
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:20:43
0:20:43
 0:38:52
0:38:52
 0:12:39
0:12:39
 0:20:51
0:20:51
 0:33:59
0:33:59
 0:07:36
0:07:36
 0:43:57
0:43:57
 0:11:06
0:11:06
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:19:46
0:19:46
 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:13:15
0:13:15
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:15:27
0:15:27
 0:38:37
0:38:37
 0:35:43
0:35:43
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:24:19
0:24:19
 0:28:49
0:28:49
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:04:01
0:04:01