filmov
tv
Form Partial Differential Equation from Z= f(y/x) | Elimination of arbitrary functions

Показать описание
I hope u enjoyed the video and learnt something. Do share your queries, doubts, suggestions and other things in the comments section.
Also, check similar videos on my channel or ask for the same if you can't find it.
If you find any error in the question, solution, concept or in the explanation do mention that out in comments as well.
Here's a list of my popular Playlists↓
Engineering Mathematics ↓↓
Previous Year Questions Examwise:
Thanks.
Happy Learning!
Also, check similar videos on my channel or ask for the same if you can't find it.
If you find any error in the question, solution, concept or in the explanation do mention that out in comments as well.
Here's a list of my popular Playlists↓
Engineering Mathematics ↓↓
Previous Year Questions Examwise:
Thanks.
Happy Learning!
How to form a Partial Differential Equation by Eliminating Arbitrary Constants.-Example 1
Weak Solutions of a PDE and Why They Matter
2. Formation of PDE by Elimination of Arbitrary Constants | Problem#1 | Complete Concept | PDE
Form Partial Differential Equation from Z= f(y/x) | Elimination of arbitrary functions
01.06. Weak Form of the Partial Differential Equation (Part 1)
canonical form || hyperbolic partial differential equations|| transformation of pde
First Order Partial Differential Equation -Solution of Lagrange Form
Form PDE from Φ(x+y+z, x²+y²-z²)= 0 | Formation of P.D.E. by eliminating arbitrary functions
Lec-02 | Solving Methods of Differential Equation | Differential Equation | Engineering Mathematics
Difference Between Partial and Total Derivative
Partial Differential Equation – Formation by Elimination of Arbitrary Functions | f(u,v) = 0 | Form3...
elliptic partial differential equations|| canonical form|| pde
Non Linear Partial Differential Equations Standard Form-I By GP Sir
Problem 1 | Eliminating Arbitrary Function |Formation of PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS |
Hyperbolic,parabolic and elliptical form of partial differential equations
Formation of partial differential equation by eliminating arbitrary constants 1
🔵01 - Differential Equations, Order, Degree, Ordinary and Partial Differential Equation
Form Partial Differential Equation from x+y+z= f(x²+y²+z²) | Elimination of arbitrary functions
Introduction to Partial Differential Equations: Definitions/Terminology
parabolic partial differential equations|| canonical form
Form a Partial differential Equation by eliminating f from f(x+y+z, x^2+ y^2 - z^2 )=0
PDE Canonical Forms of First Order Linear PDE
Canonical form | Second order PDE | Hyperbolic
Formation of PDE by eliminating arbitrary constants in 2Z= x²/a² + y²/b²
Комментарии
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:08:03
0:08:03
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:12:30
0:12:30
 0:22:02
0:22:02
 0:16:29
0:16:29
 0:21:59
0:21:59
 2:35:19
2:35:19
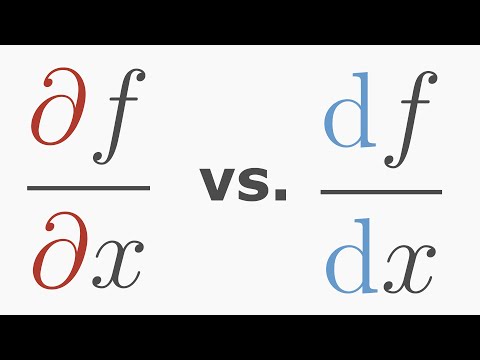 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:26:31
0:26:31
 0:15:06
0:15:06
 0:13:06
0:13:06
 0:06:50
0:06:50
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:21:50
0:21:50
 0:09:07
0:09:07
 0:09:07
0:09:07
 0:17:01
0:17:01
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:42:03
0:42:03
 0:43:46
0:43:46
 0:08:02
0:08:02