filmov
tv
Class A Commutation (Basics, Circuit, Working, Waveform & Modes) Explained in Power Electronics

Показать описание
Class A Commutation or Self Commutation or Load Commutation is explained with the following points:
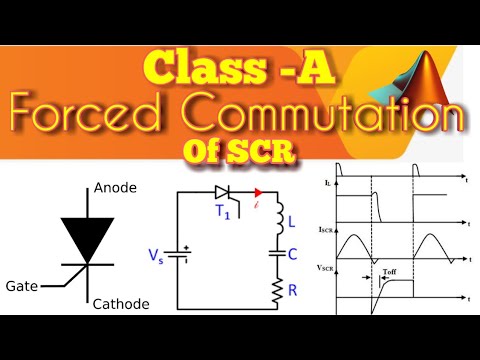
1. Basics of Class A Commutation
2. Circuit of Class A Commutation
3. Working of Class A Commutation
4. Waveform of Class A Commutation
5. Modes of Class A Commutation
6. SCR turn OFF by Load Commutation
Chapter-wise detailed Syllabus of the Power Electronics Course is as follows:
Power Diode, Power BJT, SCR - Silicon Controlled Rectifier, Dynamic Characteristics of SCR, Gate Characteristics of SCR, SCR Triggering methods, Turn of OFF process of SCR, SCR Protection, Thermal Protection of SCR, Two Transistor Analogy of SCR, SCR Mounting, Resistor Triggering of SCR, RC Triggering of SCR, Methods to improve di/dt ratings of SCR, UJT - Uni Junction Transistor, UJT as Relaxation Oscillator, PUT - Programmable Unijunction Transistor, PUT as Relaxation Oscillator, TRIAC in Power electronics, Modes of TRIAC, DIAC in Power electronics, Comparison of SCR, DIAC and TRIAC, SCS - Silicon Controlled Switch, MCT - MOS Controlled Thyristor, Power MOSFET, Comparison of Power BJT and Power MOSFET, IGBT - Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor, LASCR - Light Activated SCR, GTO - Gate Turn OFF Thyristor, Series Connection of SCR, Parallel Connection of SCR.
Class A Commutation, Class B Commutation, Class C Commutation, Class D Commutation, Class E Commutation, Class F Commutation.
Basics of Converter, Rectifier and filter, Halfwave controlled rectifier, Single phase full wave controlled rectifier, Fullwave bridge controlled rectifier, Symmetrical Semiconverter, Asymmetrical Semiconverter, Three Phase Half wave rectifier, Three phase half wave controlled rectifier.
Series Inverter, Parallel Inverter, Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter, Signal Phase Full Bridge Inverter, Three Phase Inverter 120 Degree Mode, Three Phase Inverter 180 Degree Mode, PWM Inverter.
Control Strategies of Chopper, Step Up Chopper, Step Down Chopper, Class A Chopper, Class B Chopper, Class C Chopper, Class D Chopper, Class E Chopper, Jones Chopper, Morgan Chopper.
Cycloconverter, Basics of Cycloconverter, Step Up Bridge Cycloconverter, Step Down Bridge Cycloconverter, Step Down Cycloconverter, Step Up Cycloconverter, Three Phase to Single Phase Cycloconverter.
Buck Converter, Boost Converter, Buck Boost Converter, Flyback Converter with discontinuous mode, Flyback Converter with continuous mode, Isolated Forward Converter.
On Line UPS, Off Line UPS, SMPS, Comparison of SMPS with Linear Power Supply, Dielectric Heating, Induction Heating, Battery Charger.
Engineering Funda channel is all about Engineering and Technology. Here this video is a part of Power Electronics.
#Thyristor #Commutation #PowerElectronics @EngineeringFunda
1. Basics of Class A Commutation
2. Circuit of Class A Commutation
3. Working of Class A Commutation
4. Waveform of Class A Commutation
5. Modes of Class A Commutation
6. SCR turn OFF by Load Commutation
Chapter-wise detailed Syllabus of the Power Electronics Course is as follows:
Power Diode, Power BJT, SCR - Silicon Controlled Rectifier, Dynamic Characteristics of SCR, Gate Characteristics of SCR, SCR Triggering methods, Turn of OFF process of SCR, SCR Protection, Thermal Protection of SCR, Two Transistor Analogy of SCR, SCR Mounting, Resistor Triggering of SCR, RC Triggering of SCR, Methods to improve di/dt ratings of SCR, UJT - Uni Junction Transistor, UJT as Relaxation Oscillator, PUT - Programmable Unijunction Transistor, PUT as Relaxation Oscillator, TRIAC in Power electronics, Modes of TRIAC, DIAC in Power electronics, Comparison of SCR, DIAC and TRIAC, SCS - Silicon Controlled Switch, MCT - MOS Controlled Thyristor, Power MOSFET, Comparison of Power BJT and Power MOSFET, IGBT - Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor, LASCR - Light Activated SCR, GTO - Gate Turn OFF Thyristor, Series Connection of SCR, Parallel Connection of SCR.
Class A Commutation, Class B Commutation, Class C Commutation, Class D Commutation, Class E Commutation, Class F Commutation.
Basics of Converter, Rectifier and filter, Halfwave controlled rectifier, Single phase full wave controlled rectifier, Fullwave bridge controlled rectifier, Symmetrical Semiconverter, Asymmetrical Semiconverter, Three Phase Half wave rectifier, Three phase half wave controlled rectifier.
Series Inverter, Parallel Inverter, Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter, Signal Phase Full Bridge Inverter, Three Phase Inverter 120 Degree Mode, Three Phase Inverter 180 Degree Mode, PWM Inverter.
Control Strategies of Chopper, Step Up Chopper, Step Down Chopper, Class A Chopper, Class B Chopper, Class C Chopper, Class D Chopper, Class E Chopper, Jones Chopper, Morgan Chopper.
Cycloconverter, Basics of Cycloconverter, Step Up Bridge Cycloconverter, Step Down Bridge Cycloconverter, Step Down Cycloconverter, Step Up Cycloconverter, Three Phase to Single Phase Cycloconverter.
Buck Converter, Boost Converter, Buck Boost Converter, Flyback Converter with discontinuous mode, Flyback Converter with continuous mode, Isolated Forward Converter.
On Line UPS, Off Line UPS, SMPS, Comparison of SMPS with Linear Power Supply, Dielectric Heating, Induction Heating, Battery Charger.
Engineering Funda channel is all about Engineering and Technology. Here this video is a part of Power Electronics.
#Thyristor #Commutation #PowerElectronics @EngineeringFunda
Комментарии
 0:16:08
0:16:08
 0:06:12
0:06:12
 0:04:44
0:04:44
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:10:06
0:10:06
 0:18:29
0:18:29
 0:09:17
0:09:17
 0:08:21
0:08:21
 0:09:12
0:09:12
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:14:58
0:14:58
 0:14:59
0:14:59
 0:12:19
0:12:19
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:17:30
0:17:30
 0:09:22
0:09:22
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:13:00
0:13:00
 0:16:41
0:16:41
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:13:32
0:13:32
 0:14:23
0:14:23
 0:18:39
0:18:39