filmov
tv
What is Solid Geometry?

Показать описание
Welcome back MechanicaLEi, did you know that Pythagoreans were the first to deal with regular solids but the Platonists were the first to study Solid Geometry? This makes us wonder, what is Solid Geometry?
Before we jump in check out the previous part of this series to learn about What two and three dimensional Laplace equations are?
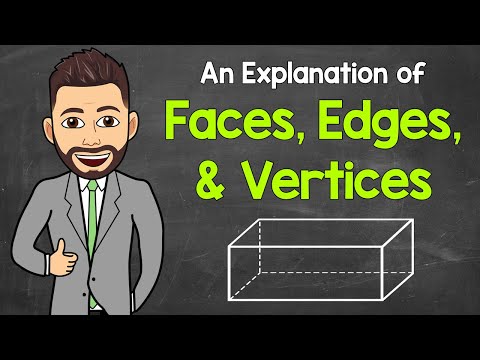
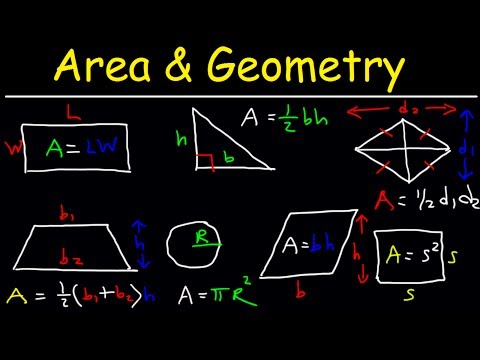
Now, Solid geometry deals with the measurements of volumes of various three-dimensional figures including pyramids, prisms and other polyhedrons. It consists of two intersections: First, an intersection of surfaces forming an intersection curve which is the intersection line of two non-parallel planes in Euclidean three dimensional space. In general, an intersection curve consists of the common points of two transversally intersecting surfaces, meaning that at any common point the surface normals are not parallel. Second, Interpenetration of solids when one solid penetrates another solid then their surfaces intersect and at the junction of intersection a typical curve is formed, which remains common to both solids. this curve is called curve of intersection.
In addition to frontal, horizontal or profile planes which offer the principal orthographic views, additional planes are set up so as to be parallel to the edges and faces which should be shown in true sizes. The views projected on these auxiliary planes are called Auxiliary Views and the technique used is called Auxiliary projection Technique. This technique helps promote visualization of solid-solid projection and is mainly drafted out on drawing sheets.
Hence, we first saw what Solid Geometry is and then went on to find out what auxiliary views are?
In the next episode of MechanicaLEi find out What Machine Elements are?
Attributions:
Before we jump in check out the previous part of this series to learn about What two and three dimensional Laplace equations are?
Now, Solid geometry deals with the measurements of volumes of various three-dimensional figures including pyramids, prisms and other polyhedrons. It consists of two intersections: First, an intersection of surfaces forming an intersection curve which is the intersection line of two non-parallel planes in Euclidean three dimensional space. In general, an intersection curve consists of the common points of two transversally intersecting surfaces, meaning that at any common point the surface normals are not parallel. Second, Interpenetration of solids when one solid penetrates another solid then their surfaces intersect and at the junction of intersection a typical curve is formed, which remains common to both solids. this curve is called curve of intersection.
In addition to frontal, horizontal or profile planes which offer the principal orthographic views, additional planes are set up so as to be parallel to the edges and faces which should be shown in true sizes. The views projected on these auxiliary planes are called Auxiliary Views and the technique used is called Auxiliary projection Technique. This technique helps promote visualization of solid-solid projection and is mainly drafted out on drawing sheets.
Hence, we first saw what Solid Geometry is and then went on to find out what auxiliary views are?
In the next episode of MechanicaLEi find out What Machine Elements are?
Attributions:
 0:02:17
0:02:17
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:30:18
0:30:18
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:08:47
0:08:47
 0:37:13
0:37:13
 0:03:45
0:03:45
 0:16:33
0:16:33
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:49:15
0:49:15
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:19:13
0:19:13
 0:25:56
0:25:56
 0:20:35
0:20:35
 2:00:24
2:00:24
 0:15:49
0:15:49
 0:22:58
0:22:58
 0:21:47
0:21:47
 0:13:39
0:13:39
 0:09:25
0:09:25
 0:24:21
0:24:21
 0:11:57
0:11:57