filmov
tv
Ideal occlusion| ideal smile | 😊@artistryindentistry

Показать описание
#ideal occlusion, in #dentistry, refers to the optimal alignment and positioning of the teeth and jaws when the mouth is closed. It encompasses several components that contribute to proper function, #aesthetics and overall oral health. Here are the key aspects of ideal occlusion:
Alignment of Teeth: The teeth should be straight and well-aligned within the dental arches. Each tooth should have a proper relationship with its adjacent teeth, without crowding, spacing, or rotations.
Bite Relationship:
Class I Occlusion: This is considered the ideal bite relationship, where the upper teeth (maxillary arch) slightly overlap the lower teeth (mandibular arch) in the front, with the molars fitting together properly.
Class II Occlusion: In this malocclusion, the upper teeth protrude significantly over the lower teeth, leading to an overbite.
Class III Occlusion: In this malocclusion, the lower teeth protrude over the upper teeth, resulting in an underbite.
Midline Alignment: The midline of the upper and lower arches should align with the midline of the face, providing balance and symmetry.
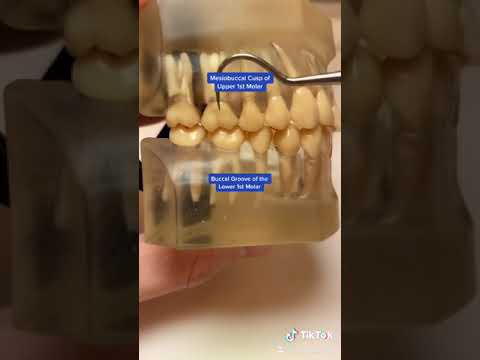
Contact Points and Occlusal Surface: Proper occlusion ensures that each tooth makes contact with its corresponding tooth in the opposing arch when the mouth is closed. The occlusal surfaces of the teeth should fit together harmoniously during chewing and biting movements.
Functionality: Ideal occlusion allows for efficient chewing, speaking, and swallowing without discomfort or strain. It prevents excessive wear and tear on the teeth and surrounding structures.
Stability: The occlusion should be stable and resistant to changes over time. This stability helps maintain the integrity of the teeth, gums, and supporting bone structures.
Healthy Supporting Structures: Ideal occlusion promotes the health of the periodontal tissues (gums and bone) by distributing forces evenly during chewing and biting, reducing the risk of periodontal disease and tooth mobility.
Achieving ideal occlusion may involve orthodontic treatment, such as braces or clear aligners, to correct misalignments and malocclusions. Additionally, occlusal adjustments may be performed to ensure proper contact and function of the teeth. Regular dental check-ups and maintenance are essential to monitor occlusal changes and address any issues promptly.
Alignment of Teeth: The teeth should be straight and well-aligned within the dental arches. Each tooth should have a proper relationship with its adjacent teeth, without crowding, spacing, or rotations.
Bite Relationship:
Class I Occlusion: This is considered the ideal bite relationship, where the upper teeth (maxillary arch) slightly overlap the lower teeth (mandibular arch) in the front, with the molars fitting together properly.
Class II Occlusion: In this malocclusion, the upper teeth protrude significantly over the lower teeth, leading to an overbite.
Class III Occlusion: In this malocclusion, the lower teeth protrude over the upper teeth, resulting in an underbite.
Midline Alignment: The midline of the upper and lower arches should align with the midline of the face, providing balance and symmetry.
Contact Points and Occlusal Surface: Proper occlusion ensures that each tooth makes contact with its corresponding tooth in the opposing arch when the mouth is closed. The occlusal surfaces of the teeth should fit together harmoniously during chewing and biting movements.
Functionality: Ideal occlusion allows for efficient chewing, speaking, and swallowing without discomfort or strain. It prevents excessive wear and tear on the teeth and surrounding structures.
Stability: The occlusion should be stable and resistant to changes over time. This stability helps maintain the integrity of the teeth, gums, and supporting bone structures.
Healthy Supporting Structures: Ideal occlusion promotes the health of the periodontal tissues (gums and bone) by distributing forces evenly during chewing and biting, reducing the risk of periodontal disease and tooth mobility.
Achieving ideal occlusion may involve orthodontic treatment, such as braces or clear aligners, to correct misalignments and malocclusions. Additionally, occlusal adjustments may be performed to ensure proper contact and function of the teeth. Regular dental check-ups and maintenance are essential to monitor occlusal changes and address any issues promptly.
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:01:49
0:01:49
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:15:58
0:15:58
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:02:25
0:02:25
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:43
0:00:43
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:10:27
0:10:27