filmov
tv
DNA extraction and purification from bacteria | DNA quantity, purity and quality measurement |

Показать описание
Extraction and purification of DNA from Bacterial cells:
Process:
1)cell lysis
2)enzyme treatment
3)phenol chloroform extraction (for separation of DNA from protein molecules)
4)alcohol precipitation or column purification
Detection and quantification:
1)absorbence mesurement
2)gel electrophoresis
There are three basic and two optional steps in a DNA extraction:[3]
Cells which are to be studied need to be collected.
Breaking the cell membranes open to expose the DNA along with the cytoplasm within (cell lysis).
Lipids from the cell membrane and the nucleus are broken down with detergents and surfactants.
Breaking proteins by adding a protease (optional).
Breaking RNA by adding an RNase (optional).
The solution is treated with concentrated salt solution to make debris such as broken proteins, lipids and RNA to clump together.
Centrifugation of the solution, which separates the clumped cellular debris from the DNA.
DNA purification from detergents, proteins, salts and reagents used during cell lysis step. The most commonly used procedures are:
Ethanol precipitation usually by ice-cold ethanol or isopropanol. Since DNA is insoluble in these alcohols, it will aggregate together, giving a pellet upon centrifugation. Precipitation of DNA is improved by increasing of ionic strength, usually by adding sodium acetate.
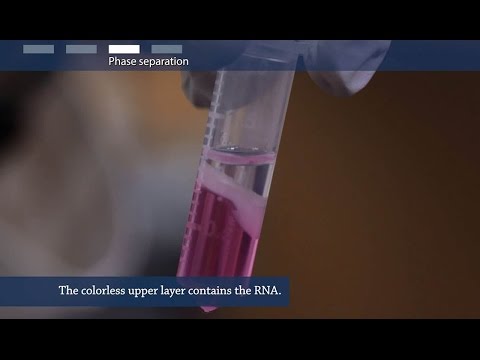
Phenol–chloroform extraction in which phenol denatures proteins in the sample. After centrifugation of the sample, denaturated proteins stay in the organic phase while aqueous phase containing nucleic acid is mixed with the chloroform that removes phenol residues from solution.
Minicolumn purification that relies on the fact that the nucleic acids may bind (adsorption) to the solid phase (silica or other) depending on the pH and the salt concentration of the buffer.
Cellular and histone proteins bound to the DNA can be removed either by adding a protease or by having precipitated the proteins with sodium or ammonium acetate, or extracted them with a phenol-chloroform mixture prior to the DNA-precipitation.
After isolation, the DNA is dissolved in slightly alkaline buffer, usually in the TE buffer, or in ultra-pure water.
Комментарии
 0:12:36
0:12:36
 0:08:14
0:08:14
 0:17:21
0:17:21
 0:12:32
0:12:32
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:11:53
0:11:53
 0:01:04
0:01:04
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:01:32
0:01:32
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:22:04
0:22:04
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:10:43
0:10:43
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:10:32
0:10:32
 0:01:42
0:01:42
 0:21:45
0:21:45