filmov
tv
RNA interference

Показать описание
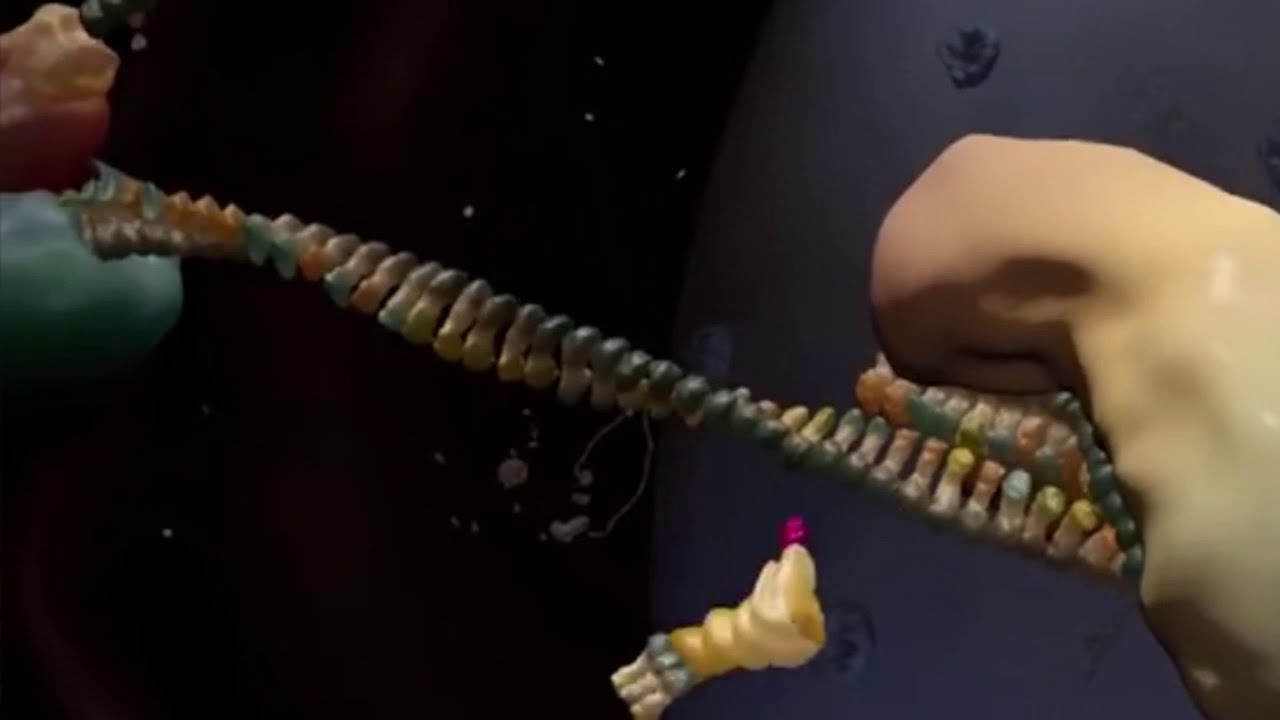
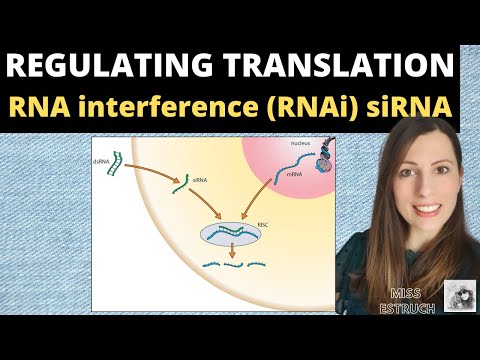
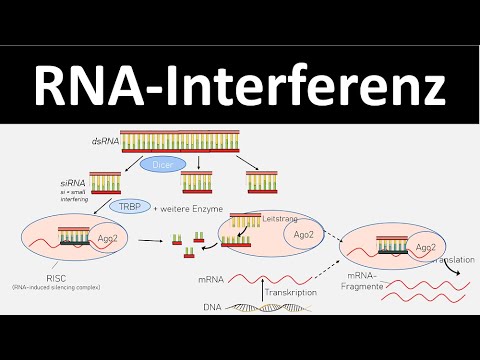
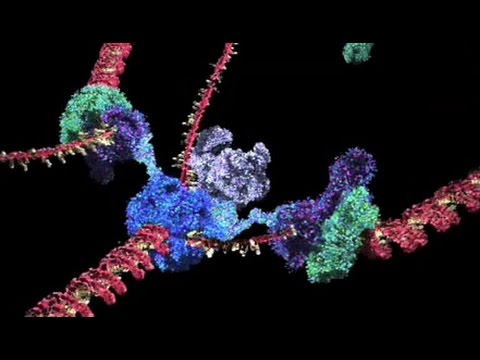
RNA interference (RNAi) is a genetic regulatory system that functions to silence the activity of specific genes. RNAi occurs naturally, through the production of nuclear-encoded pre-microRNA (pre-miRNA), and can be induced experimentally, using short segments of synthetic double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). The synthetic dsRNA employed is typically either a small hairpin RNA (shRNA) or a short interfering RNA (siRNA). In both the natural and the experimental pathways, an enzyme known as DICER is necessary for the formation of miRNA from pre-miRNA or of siRNA from shRNA. The miRNA or siRNA then binds to an enzyme-containing molecule known as RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The miRNA-RISC or siRNA-RISC complex binds to target, or complementary, messenger RNA (mRNA) sequences, resulting in the enzymatic cleavage of the target mRNA. The cleaved mRNA is rendered nonfunctional and hence is “silenced.”
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:02:56
0:02:56
 0:04:08
0:04:08
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:07:31
0:07:31
 0:10:07
0:10:07
 0:25:59
0:25:59
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:33:32
0:33:32
 0:08:18
0:08:18
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:13:00
0:13:00
 0:11:58
0:11:58
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:11:03
0:11:03
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:10:23
0:10:23
 0:15:00
0:15:00
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:10:20
0:10:20