filmov
tv
Car AC system animation

Показать описание
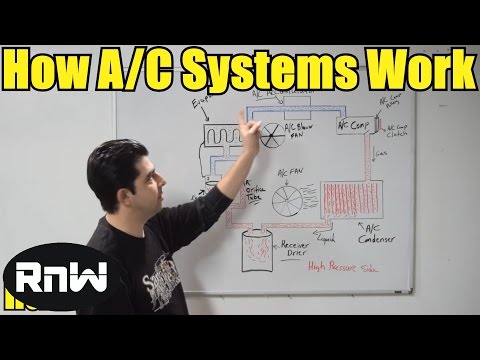
Compressor
Power unit of the system that separates the low-pressure side from the high-pressure side
Takes in low-pressure gas and compresses it into high-temperature/high-pressure gas
Mounted to front of engine and driven by serpentine belt
Condenser
Reduces temperature of refrigerant while it maintains high pressure
Refrigerant changes from gaseous state to liquid state as it cools
Similar to the engine radiator, it uses forced air (fan or vehicle movement) to transfer heat
Mounted in front of vehicle, behind grill
Dryer
Removes water from the refrigerant using a desiccant (drying agent)
Has some system-filtering properties
Mounted on high-pressure side of system, between condenser and metering device
Metering Device
Either expansion valve or fixed orifice tube
Lowers refrigerant pressure, which quickly drops refrigerant temperature
Refrigerant is still in liquid form after leaving metering device
Mounted on high-pressure side of system, between dryer and firewall
Evaporator
Refrigerant changes back to gaseous state in the evaporator, causing a cooling effect
Cabin air is cooled and dried as it blows across the evaporator
Only component mounted inside passenger compartment, behind dashboard
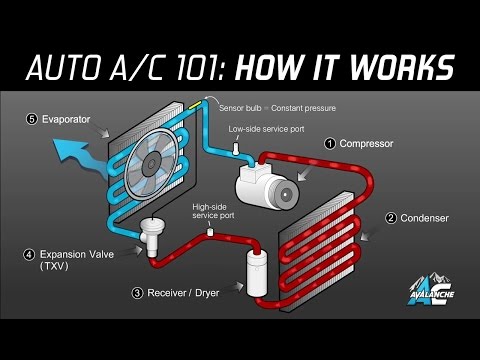
Path and characteristics of refrigerant
Low-temperature/low-pressure refrigerant enters the compressor (gas)
High-temperature/high-pressure refrigerant leaves the compressor (gas)
Refrigerant cools and converts to liquid in the condenser
Still under high pressure
Receiver/dryer removes water from refrigerant
Expansion valve reduces refrigerant pressure
Refrigerant converts back to gaseous state in the evaporator
Absorbs heat; when air blows across evaporator, it is cool and dry
Power unit of the system that separates the low-pressure side from the high-pressure side
Takes in low-pressure gas and compresses it into high-temperature/high-pressure gas
Mounted to front of engine and driven by serpentine belt
Condenser
Reduces temperature of refrigerant while it maintains high pressure
Refrigerant changes from gaseous state to liquid state as it cools
Similar to the engine radiator, it uses forced air (fan or vehicle movement) to transfer heat
Mounted in front of vehicle, behind grill
Dryer
Removes water from the refrigerant using a desiccant (drying agent)
Has some system-filtering properties
Mounted on high-pressure side of system, between condenser and metering device
Metering Device
Either expansion valve or fixed orifice tube
Lowers refrigerant pressure, which quickly drops refrigerant temperature
Refrigerant is still in liquid form after leaving metering device
Mounted on high-pressure side of system, between dryer and firewall
Evaporator
Refrigerant changes back to gaseous state in the evaporator, causing a cooling effect
Cabin air is cooled and dried as it blows across the evaporator
Only component mounted inside passenger compartment, behind dashboard
Path and characteristics of refrigerant
Low-temperature/low-pressure refrigerant enters the compressor (gas)
High-temperature/high-pressure refrigerant leaves the compressor (gas)
Refrigerant cools and converts to liquid in the condenser
Still under high pressure
Receiver/dryer removes water from refrigerant
Expansion valve reduces refrigerant pressure
Refrigerant converts back to gaseous state in the evaporator
Absorbs heat; when air blows across evaporator, it is cool and dry
Комментарии
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:05:55
0:05:55
 0:18:55
0:18:55
 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:09:48
0:09:48
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:14:24
0:14:24
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:07:03
0:07:03
 0:11:50
0:11:50
 0:10:24
0:10:24
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:01:47
0:01:47