filmov
tv
Waste Water Treatment Process| Sewage Treatment Plant | STP | Working Principal of Treatment Plant

Показать описание
A sewage treatment plant, also known as a wastewater treatment plant, is a facility designed to remove contaminants from wastewater, primarily from household sewage. It involves physical, chemical, and biological processes to treat the water and produce environmentally safe treated wastewater (or treated effluent).
### Key Components of a Sewage Treatment Plant
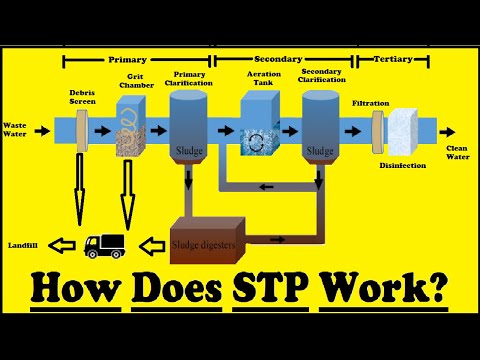
1. **Preliminary Treatment**
- **Screening:** Removes large objects like rags, sticks, and plastics.
- **Grit Removal:** Eliminates sand, gravel, and other heavy particles.
2. **Primary Treatment**
- **Sedimentation Tanks:** Allow solids to settle, forming sludge, which can be removed from the bottom.
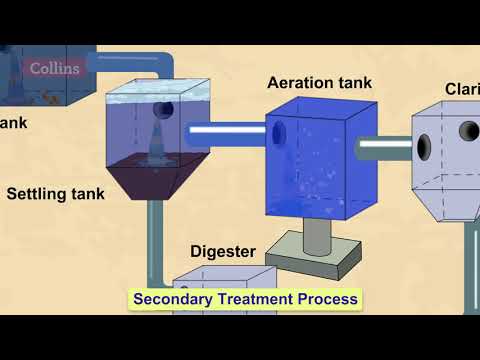
3. **Secondary Treatment**
- **Biological Treatment:** Uses microorganisms to consume organic matter in the wastewater. Common methods include:
- **Activated Sludge Process:** Aerobic bacteria degrade organic pollutants.
- **Trickling Filters:** Wastewater is spread over a bed of stones or other material, and microorganisms on the surface break down the waste.
- **Lagoons/Ponds:** Wastewater is held in large ponds where natural biological processes occur.
4. **Tertiary Treatment (Advanced Treatment)**
- **Filtration:** Removes residual suspended solids.
- **Disinfection:** Kills remaining pathogens. Methods include chlorination, UV radiation, or ozonation.
- **Nutrient Removal:** Targets nitrogen and phosphorus to prevent eutrophication of water bodies.
5. **Sludge Treatment and Disposal**
- **Thickening:** Reduces the water content of the sludge.
- **Digestion:** Biological treatment to stabilize the sludge, often producing biogas.
- **Dewatering:** Further reduces water content to make sludge easier to handle.
- **Disposal or Reuse:** Treated sludge can be used as fertilizer, incinerated, or disposed of in landfills.
### Typical Process Flow in a Sewage Treatment Plant
1. **Inlet: * Raw sewage enters the plant.
2. **Screening and Grit Removal: * Large debris and grit are removed.
3. **Primary Clarifier: * Solids settle to the bottom; scum is removed from the surface.
4. **Aeration Tank: * Air is pumped in to support aerobic bacteria that break down organic matter.
5. **Secondary Clarifier: ** More solids settle, forming secondary sludge.
6. **Disinfection: ** Treated water is disinfected to remove pathogens.
7. **Effluent Discharge: ** Treated water is released into local waterways.
8. **Sludge Treatment: ** Sludge from primary and secondary clarifiers is treated and disposed of.
Watch more Video
#Step-up & Step - Down Transformer
#Working of Transformer
#Componentes of IC Engine
Here are tags related to a sewage treatment plant:
#wastewatertreatment
#sewagetreatment
#environmentalengineering
#BiologicalTreatment
#SludgeManagement
#NutrientRemoval
#AerationTank
#sedimentation
#PrimaryClarifier
#secondary
#tertiary #treatment
#Grit removal
#screening
#disinfection
#pathogen n
#sustainable #watermanagement
### Key Components of a Sewage Treatment Plant
1. **Preliminary Treatment**
- **Screening:** Removes large objects like rags, sticks, and plastics.
- **Grit Removal:** Eliminates sand, gravel, and other heavy particles.
2. **Primary Treatment**
- **Sedimentation Tanks:** Allow solids to settle, forming sludge, which can be removed from the bottom.
3. **Secondary Treatment**
- **Biological Treatment:** Uses microorganisms to consume organic matter in the wastewater. Common methods include:
- **Activated Sludge Process:** Aerobic bacteria degrade organic pollutants.
- **Trickling Filters:** Wastewater is spread over a bed of stones or other material, and microorganisms on the surface break down the waste.
- **Lagoons/Ponds:** Wastewater is held in large ponds where natural biological processes occur.
4. **Tertiary Treatment (Advanced Treatment)**
- **Filtration:** Removes residual suspended solids.
- **Disinfection:** Kills remaining pathogens. Methods include chlorination, UV radiation, or ozonation.
- **Nutrient Removal:** Targets nitrogen and phosphorus to prevent eutrophication of water bodies.
5. **Sludge Treatment and Disposal**
- **Thickening:** Reduces the water content of the sludge.
- **Digestion:** Biological treatment to stabilize the sludge, often producing biogas.
- **Dewatering:** Further reduces water content to make sludge easier to handle.
- **Disposal or Reuse:** Treated sludge can be used as fertilizer, incinerated, or disposed of in landfills.
### Typical Process Flow in a Sewage Treatment Plant
1. **Inlet: * Raw sewage enters the plant.
2. **Screening and Grit Removal: * Large debris and grit are removed.
3. **Primary Clarifier: * Solids settle to the bottom; scum is removed from the surface.
4. **Aeration Tank: * Air is pumped in to support aerobic bacteria that break down organic matter.
5. **Secondary Clarifier: ** More solids settle, forming secondary sludge.
6. **Disinfection: ** Treated water is disinfected to remove pathogens.
7. **Effluent Discharge: ** Treated water is released into local waterways.
8. **Sludge Treatment: ** Sludge from primary and secondary clarifiers is treated and disposed of.
Watch more Video
#Step-up & Step - Down Transformer
#Working of Transformer
#Componentes of IC Engine
Here are tags related to a sewage treatment plant:
#wastewatertreatment
#sewagetreatment
#environmentalengineering
#BiologicalTreatment
#SludgeManagement
#NutrientRemoval
#AerationTank
#sedimentation
#PrimaryClarifier
#secondary
#tertiary #treatment
#Grit removal
#screening
#disinfection
#pathogen n
#sustainable #watermanagement
 0:10:03
0:10:03
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:07:48
0:07:48
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:10:50
0:10:50
 0:11:12
0:11:12
 0:10:55
0:10:55
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:12:29
0:12:29
 0:11:38
0:11:38
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:25:39
0:25:39
 0:58:03
0:58:03
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:12:26
0:12:26
 0:11:42
0:11:42
 0:08:37
0:08:37
 0:32:13
0:32:13
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:19:19
0:19:19