filmov
tv
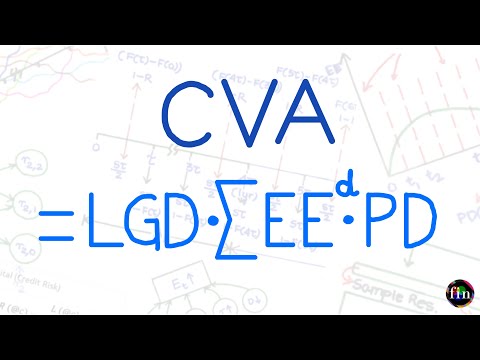
CVA Calculation for Risky Bond (Solved Example) (FRM Part 2, Book 2, Credit Risk)

Показать описание
CVA Calculation for Risky Bond (Solved Example) (FRM Part 2, Book 2, Credit Risk)
CVA Calculation on a Bond.
CFA® Level II Fixed Income - Modelling Credit Risk and Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA)
CFA Level 2 Exam Fixed Income: Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA)
CPA FRM - Credit Value Adjustments
CFA Level 2 Exam Fixed Income: Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA) Intro
CFA Level 2 Exam Fixed Income: Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA)
The Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA) and the Debt Valuation Adjustment (DVA) Calculator
Private Debt Profiles, Valuations, Risk & Return | CFA Level 3
CFA Level 2 | Fixed Income: Fair Value of Risky Bond (Zero Interest Rate Volatility)
Credit Value Adjustment (CVA) Introduction
4 New CVA Capital Charge Standardized and Advanced Formula
Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA) for a European Option | FRM Part 2 (Credit Risk) | Solved Example
CVA and DVA
Credit Value Adjustment (CVA), Exposure Amount, Probability of Default, Probability of Survival-CFA2
Credit Valuation Adjustment | Basel 2.5
Bond valuation using spot rates
Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA) Modelling
Basel III - Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA)
Risk Management in Finance: 16. Credit Value Adjustment (CVA)
Webinar: IFRS 13 - Accounting for CVA & DVA, presented by Quantifi and Deloitte
Understanding xVA , CVA , FVA , KVA , MVA , COL-VA
Wrong-way Risk (FRM Part 2 – Book 2 – Chapter 13 – CVA Part B)
Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA)
Комментарии
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:06:58
0:06:58
 0:01:33
0:01:33
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:50:56
0:50:56
 0:11:44
0:11:44
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:03:45
0:03:45
 0:15:04
0:15:04
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:16:27
0:16:27
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:14:11
0:14:11
 0:13:22
0:13:22
 0:35:43
0:35:43
 0:46:42
0:46:42
 0:30:42
0:30:42
 0:40:15
0:40:15
 0:16:08
0:16:08