filmov
tv
What is DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)?

Показать описание
What is DKIM?
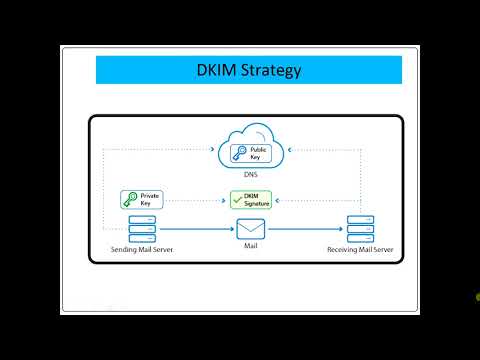
DKIM, DomainKeys Identified Mail, is used to authenticate an email. It uses a digital signature to let the email recipient know the message and content of the email was authorized by the domain owner.
How does DKIM work?
Actually it's fairly complicated in terms of generating public and private keys in order to verify the content of your email. Thankfully, most providers (including Microsoft) make it pretty easy to set up for your organization. Or they don’t let you set it up at all.
Do I need a DKIM record?
Different services provide their public DKIM in different ways. Some, like Microsoft, require you to create a DKIM record in your DNS specific to your organization, your domain. Other organizations provide their own public and private key, eliminating the need for you to make changes to your DNS.
What is a DKIM record?
This is a modified TXT record within the Domain Name System (DNS) that contains the public key for mail servers to use to authenticate the DKIM signature. It contains the public keys that are used by receiving mail servers to verify message DKIM signatures. It's the secret code you need to get into the really cool party. For some email services you need this DNS record for recipients of your emails to properly use DKIM.
DKIM, SPF, and DMARC
These acronyms are commonly used together today, but what's the difference? DKIM and SPF ensure that messages can't be sent under a spoofed domain. DMARC is the set of security rules to determine was to do when an email doesn't pass either DKIM or SPF standards. We have videos explaining SPF and DMARC in more detail if you want a better understanding of those topics. Combining DKIM, SPF, and DMARC authentication standards is the best technology to validate what's coming in and out of your domain.
If you want to make sure your emails are being delivered, DMARC has to be in your future. Want to test your domain to see where you stand? Click here for a free test of your domain, plus a way to contact us to help you figure out what’s next.
#cybersecurity #emailsecurity
DKIM, DomainKeys Identified Mail, is used to authenticate an email. It uses a digital signature to let the email recipient know the message and content of the email was authorized by the domain owner.
How does DKIM work?
Actually it's fairly complicated in terms of generating public and private keys in order to verify the content of your email. Thankfully, most providers (including Microsoft) make it pretty easy to set up for your organization. Or they don’t let you set it up at all.
Do I need a DKIM record?
Different services provide their public DKIM in different ways. Some, like Microsoft, require you to create a DKIM record in your DNS specific to your organization, your domain. Other organizations provide their own public and private key, eliminating the need for you to make changes to your DNS.
What is a DKIM record?
This is a modified TXT record within the Domain Name System (DNS) that contains the public key for mail servers to use to authenticate the DKIM signature. It contains the public keys that are used by receiving mail servers to verify message DKIM signatures. It's the secret code you need to get into the really cool party. For some email services you need this DNS record for recipients of your emails to properly use DKIM.
DKIM, SPF, and DMARC
These acronyms are commonly used together today, but what's the difference? DKIM and SPF ensure that messages can't be sent under a spoofed domain. DMARC is the set of security rules to determine was to do when an email doesn't pass either DKIM or SPF standards. We have videos explaining SPF and DMARC in more detail if you want a better understanding of those topics. Combining DKIM, SPF, and DMARC authentication standards is the best technology to validate what's coming in and out of your domain.
If you want to make sure your emails are being delivered, DMARC has to be in your future. Want to test your domain to see where you stand? Click here for a free test of your domain, plus a way to contact us to help you figure out what’s next.
#cybersecurity #emailsecurity
 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:17:15
0:17:15
 0:33:24
0:33:24
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:02:46
0:02:46
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:13:01
0:13:01
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:00:23
0:00:23