filmov
tv
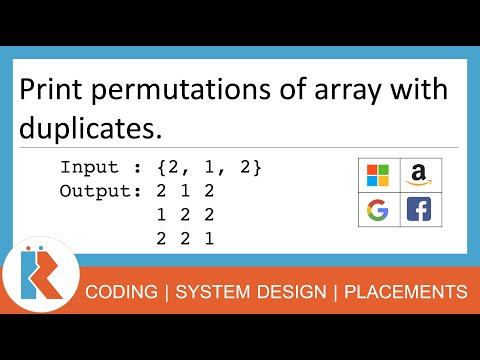
Print Permutations of an array with duplicate elements

Показать описание
Given an array with duplicate elements. Print all the unique permutations of elements of the array. In part-1 of this problem we discussed the solution where there are no duplicates in the array.
Covers Following Leetcode Problems:
-----------------------------------------------------
Join our 30-days online course to prepare for coding interviews of companies like Google, Amazon, Facebook, Microsoft, etc.
We have our office in Greater Noida (India) where we run courses for students to prepare them for placements in Top IT companies. For Placement Preparation and Industrial Training call us.
Call: +91-8377803450
Call us to conduct a workshop in your college campus.
Buy our books and prepare for coding interviews on your own.
For detailed discussions on Interview Questions visit:
Covers Following Leetcode Problems:
-----------------------------------------------------
Join our 30-days online course to prepare for coding interviews of companies like Google, Amazon, Facebook, Microsoft, etc.
We have our office in Greater Noida (India) where we run courses for students to prepare them for placements in Top IT companies. For Placement Preparation and Industrial Training call us.
Call: +91-8377803450
Call us to conduct a workshop in your college campus.
Buy our books and prepare for coding interviews on your own.
For detailed discussions on Interview Questions visit:
L12. Print all Permutations of a String/Array | Recursion | Approach - 1
Backtracking: Permutations - Leetcode 46 - Python
Print Permutations of elements of an array with no duplicates
Permutation - Return all possible permutations | C++ Placement Course | Lecture 17
L13. Print all Permutations of a String/Array | Recursion | Approach - 2
String permutation algorithm | All permutations of a string
Permutations (LeetCode 46) | Full solution with backtracking examples | Interview | Study Algorithms
Print Permutations of an array with duplicate elements
Recursion - Permutations (Theory + Code + Tips)
Print all the Permutations of the given Array (Iterative Method) | Love Babbar DSA Sheet | Amazon🔥...
Leetcode 46. Permutations : Introduction to backtracking
Next Permutation - Intuition in Detail 🔥 | Brute to Optimal
Lecture39: Permutations of a String || C++ Placement Course
Permutations | Live Coding with Explanation | Leetcode #46
Next Permutation | Leetcode #31
String Permutation Algorithm
4. Recursion | Permutations of an Array
Array : Print out all permutations of an Array
POTD- 17/01/2024 | All Unique Permutations of an Array | Problem of the Day | GeeksforGeeks
Ep9- Find all the UNIQUE permutations of an array | Recursion | DSA series | Codes in description.
Print combinations of r elements in an array of size n
How To Permute A String - Generate All Permutations Of A String
Print Permutations - Solution | Recursion | Data Structures and Algorithms in JAVA
All possible permutations | Decoding Recursion | Nishant Chahar | Ep-8
Комментарии
 0:19:07
0:19:07
 0:09:43
0:09:43
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:14:39
0:14:39
 0:18:14
0:18:14
 0:14:59
0:14:59
 0:16:55
0:16:55
 0:15:24
0:15:24
 0:25:22
0:25:22
 0:14:03
0:14:03
 0:10:06
0:10:06
 0:28:15
0:28:15
 0:21:50
0:21:50
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:19:12
0:19:12
 0:25:09
0:25:09
 0:12:10
0:12:10
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:20:38
0:20:38
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:14:09
0:14:09
 0:28:37
0:28:37
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:11:21
0:11:21