filmov
tv
Anterior view of the brainstem | Neuroanatomy Diagram

Показать описание
#brainstem #neuroanatomy #brain
Today we will draw the anatomical features present on the anterior aspect of the brainstem.
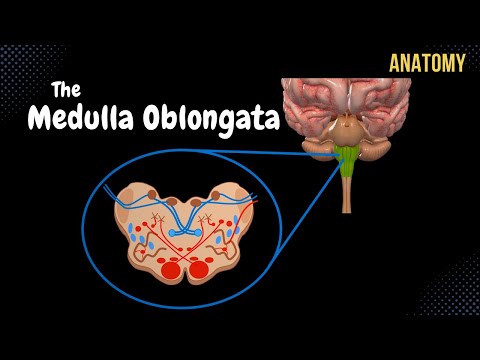
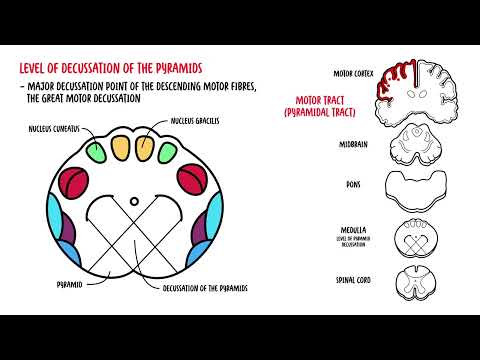
The bottom part of the brainstem is the medulla which is boundered superiorly by the pontomedullary sulcus and inferiorly by the pyramidal decussation.
On the midline we have the anterior median fissure. On each side of this fissure is a proeminence called Pyramid.
Lateral to the pyramid is a proeminent oval structure called Olive.
Between Pyramid and Olive is the preolivary sulcus. At this level the Hypoglossal nerve or the 12th cranial nerve originates from the medulla.
Behind Olive is the retrolivary sulcus. At this level, from above downwards originates the glossopharyngeal nerve or the 9th cranial nerve, The vagus nerve or the 10th cranial nerve and the cranial root of accessory nerve or 11th cranial nerve.
The middle portion of the brainstem is represented by the pons which is boundered superiorly by the pontomesencephalic sulcus and inferiorly by the already indicated pontomedullary sulcus. On the midline the pons features a groove for the basilar artery. Laterally , marking the limit between pons and middle cerebellar peduncle is the apparent origin of the trigeminal nerve or the 5th cranial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is comprised of a lateraly large sensory root and a medialy smaller motor root.
Beween Pons and Medulla, at the level of Pontomedullary suclus, emerge three cranial nerves. From medial to lateral we have the abducens or the 6th cranial nerve, the facial or 7th cranial nerve and vestobulocochlear or 8th cranial nerve.
The top part of the brainstem is the midbrain. The midbrain is boundered superiorly by the optic chiasm and optic tracts. Inferiorly is boundered by the pontomesencephalic sulcus.
The ventral surface of the midbrain presents two cerebral peduncles which emerge from the cerebral hemispheres and converge downward to enter the pons.
Between cerebral peduncles, optic chiasm and optic tracts is present a space called the interpeducular fossa. At this level from above downward we find the Pituitary stalk, the two mammillary bodies and the posterior perforated substance.
The oculomotor nerve or the 3rd cranial nerve is emerging at a groove on the lateral wall of the interpeduncular fossa.
On the lateral surface of the cerebral peduncles close to the pontomesencephalic sulcus is the trochlear nerve or the 4th cranial nerve which is the only cranial nerve that exits the brainstem through its posterior surface.
Today we will draw the anatomical features present on the anterior aspect of the brainstem.
The bottom part of the brainstem is the medulla which is boundered superiorly by the pontomedullary sulcus and inferiorly by the pyramidal decussation.
On the midline we have the anterior median fissure. On each side of this fissure is a proeminence called Pyramid.
Lateral to the pyramid is a proeminent oval structure called Olive.
Between Pyramid and Olive is the preolivary sulcus. At this level the Hypoglossal nerve or the 12th cranial nerve originates from the medulla.
Behind Olive is the retrolivary sulcus. At this level, from above downwards originates the glossopharyngeal nerve or the 9th cranial nerve, The vagus nerve or the 10th cranial nerve and the cranial root of accessory nerve or 11th cranial nerve.
The middle portion of the brainstem is represented by the pons which is boundered superiorly by the pontomesencephalic sulcus and inferiorly by the already indicated pontomedullary sulcus. On the midline the pons features a groove for the basilar artery. Laterally , marking the limit between pons and middle cerebellar peduncle is the apparent origin of the trigeminal nerve or the 5th cranial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is comprised of a lateraly large sensory root and a medialy smaller motor root.
Beween Pons and Medulla, at the level of Pontomedullary suclus, emerge three cranial nerves. From medial to lateral we have the abducens or the 6th cranial nerve, the facial or 7th cranial nerve and vestobulocochlear or 8th cranial nerve.
The top part of the brainstem is the midbrain. The midbrain is boundered superiorly by the optic chiasm and optic tracts. Inferiorly is boundered by the pontomesencephalic sulcus.
The ventral surface of the midbrain presents two cerebral peduncles which emerge from the cerebral hemispheres and converge downward to enter the pons.
Between cerebral peduncles, optic chiasm and optic tracts is present a space called the interpeducular fossa. At this level from above downward we find the Pituitary stalk, the two mammillary bodies and the posterior perforated substance.
The oculomotor nerve or the 3rd cranial nerve is emerging at a groove on the lateral wall of the interpeduncular fossa.
On the lateral surface of the cerebral peduncles close to the pontomesencephalic sulcus is the trochlear nerve or the 4th cranial nerve which is the only cranial nerve that exits the brainstem through its posterior surface.
Комментарии
 0:03:37
0:03:37
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:15:00
0:15:00
 0:10:43
0:10:43
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:16:46
0:16:46
 0:11:38
0:11:38
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:16:52
0:16:52
 0:09:11
0:09:11
 0:53:21
0:53:21
 0:09:35
0:09:35
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:19:42
0:19:42
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:11:58
0:11:58