filmov
tv
Binomial Nomenclature & Virus || CH 02 || Biodiversity || Grade 9 || National Foundation Islamabad

Показать описание
Binomial Nomenclature & Virus || CH 02 || Biodiversity || Grade 9 || National Foundation Islamabad #biologyclass
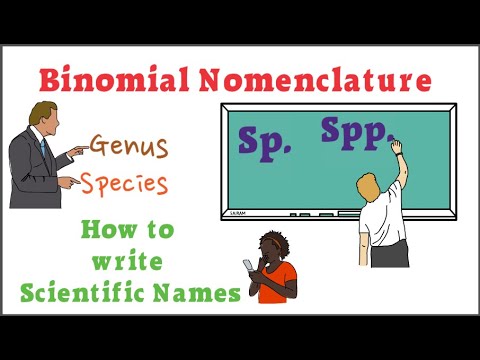
2.7 BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE
Fig 2.4: Infertile mule
Carolus Linnaeus introduced a naming system to give each organism a name consisting of two Latin names. The first name is genus name and the second name represents the particular species. The genus name begins with a capital letter but the species name begins with a small letter. Since each name has two parts so it is called binomial nomenclature, e.g., biological name of human beings is Homo sapiens. Our genus name is Homo and specie name is sapiens. A genus may have many species e.g., all cats belong to genus Felis including lion.
Importance of Binomial Nomenclature
Why do organisms need to be given a scientific name in Latin? Why can't we just use common
names for organisms? A common name will vary from country to country just because different
countries use different languages. Hence there was a need for a universal language such as
Latin. Even those who speak the same language sometime use different common name for the
same organisms. Example: Brinjal is Baigun in Urdu, Bataoon in Punjabi, Vagton in Sindhi. Is it
not confusing? Its biological name is Solanum melangena. Find out the Punjabi, Sindhi, Pushto
or other local names or German, French, Spanish, Arabic, Russian, Chinese names of the
following organisms which will show the importance of biological name.
1. Potato -
Solanum tuberosum
2. Rice
Oryza sativa
26
Chapter 2: Biodiversity
A scientific name has the advantage of standing for a single kind of animal, plant or microorganism all over the world.
2.8 COMPLICATIONS OF CLASSIFYING VIRUSES
Viruses show characteristics of both living and nonliving things. The living characteristics of viruses are:
1. They occur in different varieties.
2. They have their own genetic material in the form of either RNA or DNA.
3. They reproduce using the material of the host cell they infect.
4. They enter the cells of living organisms and cause diseases.
The non-living characteristics of viruses are:
1. They lack cellular structure and enzyme system.
2. They can be crystallized and store in bottle.
3. They do not respire.
4. Viruses behave
as non-living, inert infectious particles outside the host.
Viruses are at the borderline of living and non-living. So, they are not included in any domain
and kingdom under modern classification.
Prions are composed of proteins only. Viroids are composed of circular RNA only. Both causes infectious diseases in certain plants. Both are acellular particles. They are not included in any kingdom system. Funda of clas
2.7 BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE
Fig 2.4: Infertile mule
Carolus Linnaeus introduced a naming system to give each organism a name consisting of two Latin names. The first name is genus name and the second name represents the particular species. The genus name begins with a capital letter but the species name begins with a small letter. Since each name has two parts so it is called binomial nomenclature, e.g., biological name of human beings is Homo sapiens. Our genus name is Homo and specie name is sapiens. A genus may have many species e.g., all cats belong to genus Felis including lion.
Importance of Binomial Nomenclature
Why do organisms need to be given a scientific name in Latin? Why can't we just use common
names for organisms? A common name will vary from country to country just because different
countries use different languages. Hence there was a need for a universal language such as
Latin. Even those who speak the same language sometime use different common name for the
same organisms. Example: Brinjal is Baigun in Urdu, Bataoon in Punjabi, Vagton in Sindhi. Is it
not confusing? Its biological name is Solanum melangena. Find out the Punjabi, Sindhi, Pushto
or other local names or German, French, Spanish, Arabic, Russian, Chinese names of the
following organisms which will show the importance of biological name.
1. Potato -
Solanum tuberosum
2. Rice
Oryza sativa
26
Chapter 2: Biodiversity
A scientific name has the advantage of standing for a single kind of animal, plant or microorganism all over the world.
2.8 COMPLICATIONS OF CLASSIFYING VIRUSES
Viruses show characteristics of both living and nonliving things. The living characteristics of viruses are:
1. They occur in different varieties.
2. They have their own genetic material in the form of either RNA or DNA.
3. They reproduce using the material of the host cell they infect.
4. They enter the cells of living organisms and cause diseases.
The non-living characteristics of viruses are:
1. They lack cellular structure and enzyme system.
2. They can be crystallized and store in bottle.
3. They do not respire.
4. Viruses behave
as non-living, inert infectious particles outside the host.
Viruses are at the borderline of living and non-living. So, they are not included in any domain
and kingdom under modern classification.
Prions are composed of proteins only. Viroids are composed of circular RNA only. Both causes infectious diseases in certain plants. Both are acellular particles. They are not included in any kingdom system. Funda of clas
Комментарии
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:24:47
0:24:47
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:06:30
0:06:30
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:10:49
0:10:49
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:10:41
0:10:41
 0:25:17
0:25:17
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:12:56
0:12:56
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:05:33
0:05:33
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:34:23
0:34:23
 0:16:02
0:16:02
 0:08:32
0:08:32
 0:48:21
0:48:21
 0:15:20
0:15:20
 0:13:55
0:13:55
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:18:06
0:18:06