filmov
tv
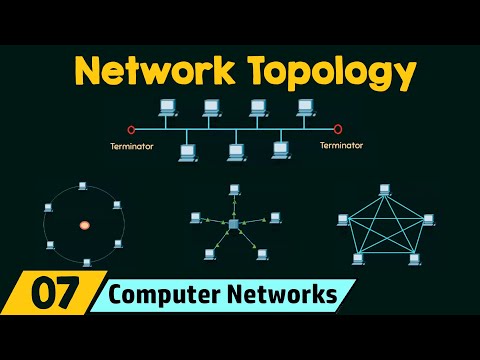
Network Topology Map – Path Analysis & Generic Tools

Показать описание
A firewall topology map provides a detailed view of your entire network, and provides centralized firewall management. Highly scalable, Tufin's network topology solution provides out of the box support for technologies like - NAT, VPN, VPS Peering and more. Our topology map is fully interactive and allows for better firewall change automation.
Download UVexplorer Now:
Transcript:
Thank you for watching this session on Network
Topology Map – Path Analysis and Generic Tools.
In this session, we will talk about the path analysis
and generic tools of U V explorer in the topology map.
The topology map is a highly scalable solution
supporting thousands of firewalls,
routers and switches.
It provides centralized visibility and control across
multiple vendors with out-of-the-box support for
advanced network technologies, including SNMP, SSH,
WMI and more, both on-prem and in the cloud.
Topology intelligence uses their routing and security
information from the devices in order to build the
interactive map for network troubleshooting and for
suggesting accurate path for change automation.
Based on the information received from the devices,
this map shows the connectivity among the different
units and the technology they use.
Let’s delve deeper into the core
benefits of network topology:
The first use case that I'm going to
show you is for visibility.
I can search for one of the devices that I have in my
network, for example, my Cisco 3560 switch.
This device appears on the map with its subnets, as
well as the routes, interfaces, and bridge ports
associated with it.
We can use the Path Analysis to perform
troubleshooting in the network.
I can add source or target and find the relevant path.
Let's test this Path Analysis tool together.
I want to check if I have a connection between one of
my switches to another switch.
By clicking on the Ping button, it will test the full
path between the source to the destination.
In the first row, which is related to this Cisco
switch, I can see the ping status and interface status.
This device is marked with a red arrow.
It means that U V explorer is unable to communicate
with the device.
In the topology map, it's really important to have all
the devices from the network in order to avoid a
broken path between the source and the destination,
like in this example, where the path is not completed.
In some cases, users cannot see all their devices with
due to lack of access to a device, credential issue,
or an unsupported device.
This is where the generic devices tool comes in.
Using the generic device, you can add the interface
and routing information from the devices that U V
explorer doesn't monitor.
Let's demonstrate adding a generic device.
I can click on the Manual Devices option on the top
bar and add the generic device.
I can enter the device name, I P address and the
interfaces it connects to.
After adding a generic device, the topology will
automatically recalculate to include the generic
device in the topology in order to complete the
connection when the path is broken.
Now you can see the new device in the network.
You can also use other generic tools in the topology
map, like adding a generic route or adding a generic
interface if needed.
In summary, the topology map is the
basis of two things.
By using a dynamic map that updates according to the
user's network, we can, first of all, reduce the time
it takes to carry out network troubleshooting, and
also the user can leverage the accuracy of the
topology map for automating changes across the entire
on-prem, SDN, and cloud networks in
minutes instead of days.
I hope this has been informative for you, and I would
like to thank you for viewing.
For more information on network topology map, path
Download UVexplorer Now:
Transcript:
Thank you for watching this session on Network
Topology Map – Path Analysis and Generic Tools.
In this session, we will talk about the path analysis
and generic tools of U V explorer in the topology map.
The topology map is a highly scalable solution
supporting thousands of firewalls,
routers and switches.
It provides centralized visibility and control across
multiple vendors with out-of-the-box support for
advanced network technologies, including SNMP, SSH,
WMI and more, both on-prem and in the cloud.
Topology intelligence uses their routing and security
information from the devices in order to build the
interactive map for network troubleshooting and for
suggesting accurate path for change automation.
Based on the information received from the devices,
this map shows the connectivity among the different
units and the technology they use.
Let’s delve deeper into the core
benefits of network topology:
The first use case that I'm going to
show you is for visibility.
I can search for one of the devices that I have in my
network, for example, my Cisco 3560 switch.
This device appears on the map with its subnets, as
well as the routes, interfaces, and bridge ports
associated with it.
We can use the Path Analysis to perform
troubleshooting in the network.
I can add source or target and find the relevant path.
Let's test this Path Analysis tool together.
I want to check if I have a connection between one of
my switches to another switch.
By clicking on the Ping button, it will test the full
path between the source to the destination.
In the first row, which is related to this Cisco
switch, I can see the ping status and interface status.
This device is marked with a red arrow.
It means that U V explorer is unable to communicate
with the device.
In the topology map, it's really important to have all
the devices from the network in order to avoid a
broken path between the source and the destination,
like in this example, where the path is not completed.
In some cases, users cannot see all their devices with
due to lack of access to a device, credential issue,
or an unsupported device.
This is where the generic devices tool comes in.
Using the generic device, you can add the interface
and routing information from the devices that U V
explorer doesn't monitor.
Let's demonstrate adding a generic device.
I can click on the Manual Devices option on the top
bar and add the generic device.
I can enter the device name, I P address and the
interfaces it connects to.
After adding a generic device, the topology will
automatically recalculate to include the generic
device in the topology in order to complete the
connection when the path is broken.
Now you can see the new device in the network.
You can also use other generic tools in the topology
map, like adding a generic route or adding a generic
interface if needed.
In summary, the topology map is the
basis of two things.
By using a dynamic map that updates according to the
user's network, we can, first of all, reduce the time
it takes to carry out network troubleshooting, and
also the user can leverage the accuracy of the
topology map for automating changes across the entire
on-prem, SDN, and cloud networks in
minutes instead of days.
I hope this has been informative for you, and I would
like to thank you for viewing.
For more information on network topology map, path
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:06:11
0:06:11
 0:08:58
0:08:58
 0:02:32
0:02:32
 0:05:55
0:05:55
 0:42:08
0:42:08
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:13:36
0:13:36
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:16:24
0:16:24
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:42:55
0:42:55
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:06:42
0:06:42
 0:14:30
0:14:30
 0:02:46
0:02:46
 0:02:31
0:02:31
 0:01:54
0:01:54