filmov
tv
Higher Order Modulation Explained, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM

Показать описание
Whether it’s for long haul telecommunications or for data centers, information is sent by shooting laser light down fiber optic cables using transmitters and receivers. This light is encoded in amplitude and phase using Mach–Zehnder modulators. Winston Way, PhD, Electrical Engineering, and Chief Technology Officer at NeoPhotonics, shares his expertise as he covers QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM, symbol rate, baud rate and polarization. Let us know if you want more of these videos. Winston is interviewed by John Houghton, CEO, MobileCast Media.
Higher Order Modulation Explained, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM
Understanding Phase Shift Keying
Understanding APSK and QAM
Inside Wireless: QAM modulation (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation)
Inside Wireless: QAM modulation II - The Modulator
QPSK Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (Basics, Modulator, Waveforms, Demodulator & Applications)
How are Data Rate and Bandwidth Related? ('a super clear explanation!')
Modulation & QAM Basics
Quadrature Amplitude Modlation (QAM): Explained
Digital modulation: ASK, FSK, and PSK
6.7 BPSK VS QPSK
Module 4: Phase Shift Key (PSK)
3 Modulation
Understanding Modulation! | ICT #7
#170: Basics of IQ Signals and IQ modulation & demodulation - A tutorial
What is a Constellation Diagram?
[13] QPSK and QAM-M modulation
Engage Students With Experiential Learning of QPSK
Module 4: Digital Modulation
Lec 38: Biasing of MZM: QPSK and 16 QAM Generation
GnuRadio Tutorial | Digital Modulation BPSK, QPSK, & 16 QAM | Adaptive Modulation and Coding for...
#In mobiles,which Digital modulation scheme is used? QPSK or MSK ? and why ?
(English) Offset QPSK, Quadrature Amplitude Modulation QAM
BPSK,DPSK,QAM,QPSK
Комментарии
 0:40:00
0:40:00
 0:08:24
0:08:24
 0:10:17
0:10:17
 0:03:10
0:03:10
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:11:36
0:11:36
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:10:16
0:10:16
 0:24:59
0:24:59
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:11:17
0:11:17
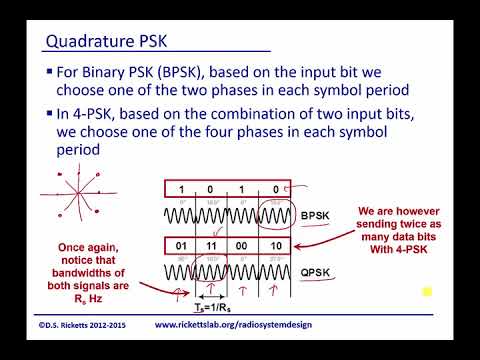 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:11:44
0:11:44
 0:07:26
0:07:26
 0:19:00
0:19:00
 0:11:30
0:11:30
![[13] QPSK and](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/sCImEN3msY8/hqdefault.jpg) 1:21:58
1:21:58
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:10:55
0:10:55
 0:18:01
0:18:01
 0:12:03
0:12:03
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:43:56
0:43:56
 0:16:42
0:16:42