filmov
tv
Spanning Tree Protocol - STP in Computer Networks

Показать описание
Spanning Tree Protocol - STP in Computer Networks is explained with the following timecodes:
0:00 - Spanning Tree Protocol - STP - Computer Network
0:50 - Basics of Spanning Tree Protocol
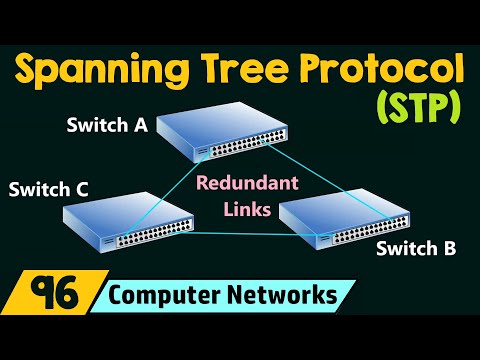
2:24 - Redundant Link, Redundant Channel, Redundant Cable
7:17 - Spanning Tree
8:09 - Spanning Tree Algorithm
11:38 - Example of Creation of Spanning Tree
15:38 - History of Spanning Tree Algorithm
The following points are covered in this video:
0. Computer Network
1. Network device
2. Spanning Tree Protocol - STP
3. Basics of Spanning Tree Protocol
4. Redundant Link, Redundant Channel, Redundant Cable
5. Spanning Tree
6. Spanning Tree Algorithm
7. Example of Creation of Spanning Tree
8. History of Spanning Tree Algorithm
Chapter-wise detailed Syllabus of the Computer Network Course is as follows:
Computer Network Basics, Types of Data Communication in Computer Network, Types of Casting in Computer Network, Peer to Peer Network Vs Client Server Network, Types of Computer Network, Topologies of Computer Network.
Basics of OSI Model, OSI Model Details, Comparison of TCP and UDP, Comparison of OSI Model and TCP/IP Model, Transmission Medium in Computer Network, IP Address, MAC Address and Port Address.
Data Link Layer Basics, Transmission Delay & Propagation Delay, Stop & Wait ARQ Protocol, Capacity of Channel in Computer Network, Sliding Window Protocol, Go Back N ARQ Protocol, Selective Repeat ARQ Protocol, Comparison of Sliding Window Protocol, Go Back N ARQ Protocol and Selective Repeat ARQ Protocol, Media Access Protocols, Channelization Protocols: FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, Polling Protocol, Reservation Protocol, Token Passing Protocol, Pure ALOHA, Slotted ALOHA, CSMA - Carrier Sense Multiple Access, CSMA/CD, Back off Algorithm for CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA.
VRC - Vertical Redundancy Check & LRP - Longitudinal Redundancy Parity, Checksum, CRC - Cyclic Redundancy Check, Hamming Code for Error Correction and Error Detection, Minimum Hamming Distance, Error Detection Capabilities & Error Correction Capabilities.
Framing, Ethernet LAN Protocol - IEEE 802.3, Wireless LAN Protocol - IEEE 802.11, Token Ring LAN Protocol - IEEE 802.5, Examples on CSMA Protocols, Examples on Flow Control Protocols.
Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Router and Brouter, Comparison of Repeater Hub Bridge Switch Router and Brouter, Network Segment, Collision Domain & Broadcast Domain, Spanning Tree Protocol.
Network Layer Basics, logical Addressing, Classful Addressing of IP Address, Subnetting, Classes Inter-Domain Routing - CIDR, Subnet Masking, Supernetting, IPV4 Frame Format, Fragmentation, IPV4 Broadcasting, Localhost and Loopback, ARP, RARP, BOOTP , DHCP, Public IP and Privet IP, NAT - Network Address Translation, ICMP, Routing, Non Adaptive Routing, Distance Vector Routing, Link State Routing, Circuit Switching, Packet Switching and Message Switching, IPV6, IPV6 Casting, IPV6 Frame Format.
Transport Layer Basics, TCP Frame Format, Port Number & Network Socket, Sequence Number & Acknowledgment Number in TCP, Wrap Around Time and Life Time in TCP, Header Length and Checksum in TCP, TCP Connections, PSH URG RST Urgent Pointer and Option Field in TCP, Flow Control in TCP Protocol, Sliding Window Protocol in TCP, Retransmission in TCP, Congestion Control in TCP, Timers in TCP, Basic Algorithm for Timeout Timer in TCP, Jacobson's Algorithm for Timeout Timer in TCP, Karn's Modification of Timeout Timer in TCP, Silly Window Syndrome and It's Solution in TCP, Congestion Control using Traffic Shaping in TCP, Leaky Bucket Algorithm, Token Bucket Algorithm, UDP - User Datagram Protocol, UDP Segment Header, UDP Frame Format.
Application Layer Basics, DNS - Domain Name System, SMTP POP and IMAP, HTTP/HTTPs , FTP SFTP and TFTP - File Transfer Protocols.
Engineering Funda channel is all about Engineering and Technology. Here this video is a part of Computer Network.
#SpanningTreeProtocol #STP #ComputerNetwork #EngineeringFunda
0:00 - Spanning Tree Protocol - STP - Computer Network
0:50 - Basics of Spanning Tree Protocol
2:24 - Redundant Link, Redundant Channel, Redundant Cable
7:17 - Spanning Tree
8:09 - Spanning Tree Algorithm
11:38 - Example of Creation of Spanning Tree
15:38 - History of Spanning Tree Algorithm
The following points are covered in this video:
0. Computer Network
1. Network device
2. Spanning Tree Protocol - STP
3. Basics of Spanning Tree Protocol
4. Redundant Link, Redundant Channel, Redundant Cable
5. Spanning Tree
6. Spanning Tree Algorithm
7. Example of Creation of Spanning Tree
8. History of Spanning Tree Algorithm
Chapter-wise detailed Syllabus of the Computer Network Course is as follows:
Computer Network Basics, Types of Data Communication in Computer Network, Types of Casting in Computer Network, Peer to Peer Network Vs Client Server Network, Types of Computer Network, Topologies of Computer Network.
Basics of OSI Model, OSI Model Details, Comparison of TCP and UDP, Comparison of OSI Model and TCP/IP Model, Transmission Medium in Computer Network, IP Address, MAC Address and Port Address.
Data Link Layer Basics, Transmission Delay & Propagation Delay, Stop & Wait ARQ Protocol, Capacity of Channel in Computer Network, Sliding Window Protocol, Go Back N ARQ Protocol, Selective Repeat ARQ Protocol, Comparison of Sliding Window Protocol, Go Back N ARQ Protocol and Selective Repeat ARQ Protocol, Media Access Protocols, Channelization Protocols: FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, Polling Protocol, Reservation Protocol, Token Passing Protocol, Pure ALOHA, Slotted ALOHA, CSMA - Carrier Sense Multiple Access, CSMA/CD, Back off Algorithm for CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA.
VRC - Vertical Redundancy Check & LRP - Longitudinal Redundancy Parity, Checksum, CRC - Cyclic Redundancy Check, Hamming Code for Error Correction and Error Detection, Minimum Hamming Distance, Error Detection Capabilities & Error Correction Capabilities.
Framing, Ethernet LAN Protocol - IEEE 802.3, Wireless LAN Protocol - IEEE 802.11, Token Ring LAN Protocol - IEEE 802.5, Examples on CSMA Protocols, Examples on Flow Control Protocols.
Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Router and Brouter, Comparison of Repeater Hub Bridge Switch Router and Brouter, Network Segment, Collision Domain & Broadcast Domain, Spanning Tree Protocol.
Network Layer Basics, logical Addressing, Classful Addressing of IP Address, Subnetting, Classes Inter-Domain Routing - CIDR, Subnet Masking, Supernetting, IPV4 Frame Format, Fragmentation, IPV4 Broadcasting, Localhost and Loopback, ARP, RARP, BOOTP , DHCP, Public IP and Privet IP, NAT - Network Address Translation, ICMP, Routing, Non Adaptive Routing, Distance Vector Routing, Link State Routing, Circuit Switching, Packet Switching and Message Switching, IPV6, IPV6 Casting, IPV6 Frame Format.
Transport Layer Basics, TCP Frame Format, Port Number & Network Socket, Sequence Number & Acknowledgment Number in TCP, Wrap Around Time and Life Time in TCP, Header Length and Checksum in TCP, TCP Connections, PSH URG RST Urgent Pointer and Option Field in TCP, Flow Control in TCP Protocol, Sliding Window Protocol in TCP, Retransmission in TCP, Congestion Control in TCP, Timers in TCP, Basic Algorithm for Timeout Timer in TCP, Jacobson's Algorithm for Timeout Timer in TCP, Karn's Modification of Timeout Timer in TCP, Silly Window Syndrome and It's Solution in TCP, Congestion Control using Traffic Shaping in TCP, Leaky Bucket Algorithm, Token Bucket Algorithm, UDP - User Datagram Protocol, UDP Segment Header, UDP Frame Format.
Application Layer Basics, DNS - Domain Name System, SMTP POP and IMAP, HTTP/HTTPs , FTP SFTP and TFTP - File Transfer Protocols.
Engineering Funda channel is all about Engineering and Technology. Here this video is a part of Computer Network.
#SpanningTreeProtocol #STP #ComputerNetwork #EngineeringFunda
Комментарии
 0:20:12
0:20:12
 0:19:55
0:19:55
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 2:02:10
2:02:10
 1:04:52
1:04:52
 0:10:12
0:10:12
 0:19:12
0:19:12
 0:17:00
0:17:00
 0:10:27
0:10:27
 0:19:18
0:19:18
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:15:13
0:15:13
 0:19:46
0:19:46
 0:10:58
0:10:58
 0:20:55
0:20:55
![[Hindi] STP -](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aIG38PMoSBA/hqdefault.jpg) 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:12:57
0:12:57
 0:15:22
0:15:22
 0:16:42
0:16:42
 0:06:18
0:06:18
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 0:42:18
0:42:18
 0:06:56
0:06:56