filmov
tv
How to Implement Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Solutions and Cryptography

Показать описание
CBT Nuggets trainer Bob Salmans covers encryption. Bob uses visuals to explain what encryption is, how it’s done with private and public key pairs, and what the Public Key Infrastructure has to do with it. If you’ve got questions about symmetric or asymmetric encryption methods, this video helps clarify the process.
Encryption is converting plain text into unreadable data called cipher text. Encryption protects data against unauthorized viewing (referred to as Confidentiality in the C-I-A triad). Encryption also protects data against unauthorized manipulation or alteration (also referred to as Integrity in the CIA triad).
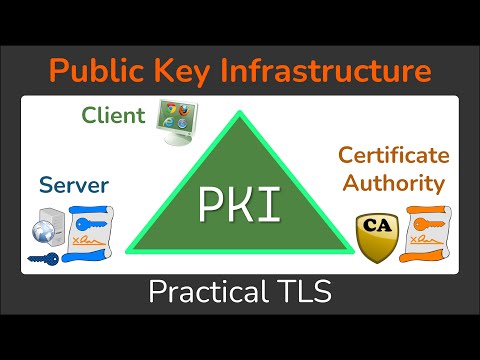
Symmetric encryption is one of the two types of encryption schemes. Symmetric encryption uses the same key (called a “secret key”) to encrypt and decrypt the data. Examples of this are 3DES and AES. Asymmetric encryption is the other major type of encryption, it uses two different keys. In asymmetric encryption, one key encrypts, and the other decrypts. It also relies on a public key which is shared, and a private key which must be kept secure and not shared. The keys are stored and distributed by the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). Examples of asymmetric encryption are RSA, ECC and Diffie Hellman.
The most important part of PKI and asymmetric encryption is the pairing of the private key with the public key. When encrypting messages via PKI, the sender uses the public key to encrypt the message and the private key is used to decrypt the message. It’s also possible to encrypt a message with the private key and have the public key decrypt it.
0:00 – Introduction how to implement PKI solutions and cryptography
0:20 – The definition of encryption and its use in cryptography
1:25 – Symmetric encryption is one of the two major types of encryption schemes
3:10 – How asymmetric encryption differs from symmetric encryption
5:05 – Using a public key and a private key pair to encrypt and decrypt messages
-----------------
Connect with CBT Nuggets for the latest in IT training:
#encryption #pki #cryptography #ittraining #cbtnuggets
Encryption is converting plain text into unreadable data called cipher text. Encryption protects data against unauthorized viewing (referred to as Confidentiality in the C-I-A triad). Encryption also protects data against unauthorized manipulation or alteration (also referred to as Integrity in the CIA triad).
Symmetric encryption is one of the two types of encryption schemes. Symmetric encryption uses the same key (called a “secret key”) to encrypt and decrypt the data. Examples of this are 3DES and AES. Asymmetric encryption is the other major type of encryption, it uses two different keys. In asymmetric encryption, one key encrypts, and the other decrypts. It also relies on a public key which is shared, and a private key which must be kept secure and not shared. The keys are stored and distributed by the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). Examples of asymmetric encryption are RSA, ECC and Diffie Hellman.
The most important part of PKI and asymmetric encryption is the pairing of the private key with the public key. When encrypting messages via PKI, the sender uses the public key to encrypt the message and the private key is used to decrypt the message. It’s also possible to encrypt a message with the private key and have the public key decrypt it.
0:00 – Introduction how to implement PKI solutions and cryptography
0:20 – The definition of encryption and its use in cryptography
1:25 – Symmetric encryption is one of the two major types of encryption schemes
3:10 – How asymmetric encryption differs from symmetric encryption
5:05 – Using a public key and a private key pair to encrypt and decrypt messages
-----------------
Connect with CBT Nuggets for the latest in IT training:
#encryption #pki #cryptography #ittraining #cbtnuggets
Комментарии
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:07:16
0:07:16
 0:12:33
0:12:33
 0:09:22
0:09:22
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:24:24
0:24:24
 0:10:12
0:10:12
 0:18:46
0:18:46
 1:01:51
1:01:51
 0:19:05
0:19:05
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:22:37
0:22:37
 0:04:59
0:04:59
 0:15:46
0:15:46
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:12:42
0:12:42
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:09:08
0:09:08
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:13:40
0:13:40