filmov
tv
The Gluteus Medius Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim

Показать описание
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video teaches the anatomy of the Gluteus Medius muscle with simple images, this video also provides you with all you need to know about this muscle, its innervation, action, and function. Animation of the gluteus medius video .gluteus medius anatomy, gluteus medius pain and gluteus medius stretch, gluteus medius gait.
The gluteus medius muscle is a favorite item which appears on exam.
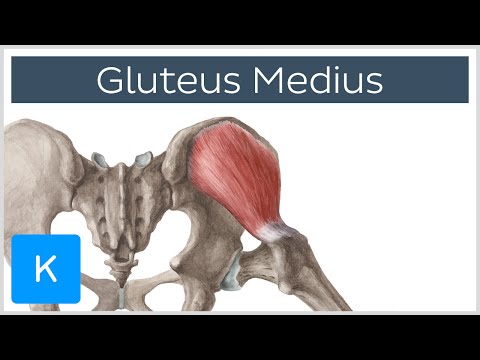
Origin: it arises from the dorsal ilium inferior to the iliac crest from the posterior gluteal line to the anterior gluteal line.
The gluteus medius muscle from the middle layer of the gluteal muscles.
Insertion: it inserts into the lateral aspect of the greater trochanter of the proximal femur.
The caudal portion of the gluteus medius tendon is close to the piriformis muscle.
The gluteus medius muscle covers the entire gluteus minimus muscle.
Remember: the gluteus medius muscle runs from the ilium to the greater trochanter of the proximal femur.
The gluteus medius muscle is supplied by the superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1 predominantly L5).
The blood supply comes from the superior gluteal artery which runs above the piriformis muscle.
This artery may become injured due to acetabular fractures either due to the trauma or by the surgery.
This may lead to compromise of the abductor muscles.
Function: Hip abduction: the gluteus medius muscle is the most powerful abductor of the hip joint.
What muscles abduct the hip? Gluteus medius muscle and Gluteus minimus muscle
Gluteus medius muscle: the abductor muscles play an important role in stabilization of the pelvis, the anterior fibers of the gluteus medius muscle provide some internal rotation of the hip and the posterior fibers provide some external rotation of the hip, there is many clinical situations that involve the gluteus medius muscle.
The superior gluteal nerve may be injures due to the Watson- Jones or lateral approach to the hip if the incision extends more than 5 cm above the acetabulum, surgeons like the lateral approach (Hardinge approach) better compared to the posterior approach to the hip because the rate of hip dislocation is less, the superior gluteal nerve will limit the proximal extent of the gluteus medius split.
The superior gluteal nerve is approximately 5 cm proximal from the tip of the greater trochanter.
If you split the gluteus medius muscle about this point, then you run the risk of injuring the superior gluteal nerve and compromise the muscle function.
If injury occurs to the gluteus to the gluteus medius muscle, there will be weakness of hip abduction.
Weakness of the muscle could be seen early after total hip replacement.
The patient will be sent to therapy to regain the strength of the muscle.
Occasionally there is an occult injury or rupture of the muscle itself that goes unrecognized.
Injury to the muscle may sometimes be mistaken for trochanteric bursitis but it is really an occult rupture of the tendon.
MRI may be needed to check for a rupture.
MRI is good even if metal is present around the hip.
Injury may or may not result from surgery I this area.
If there is gluteus medius muscle weakness, the trendelenburg gait may occur.
Become a friend on facebook:
Follow me on twitter:
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
The gluteus medius muscle is a favorite item which appears on exam.
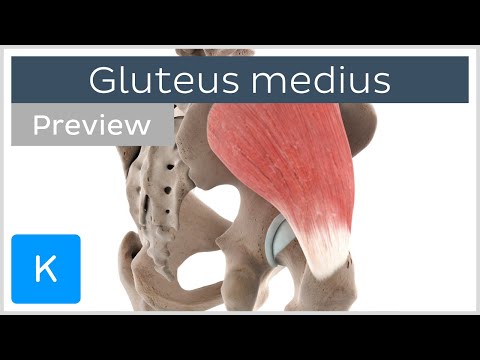
Origin: it arises from the dorsal ilium inferior to the iliac crest from the posterior gluteal line to the anterior gluteal line.
The gluteus medius muscle from the middle layer of the gluteal muscles.
Insertion: it inserts into the lateral aspect of the greater trochanter of the proximal femur.
The caudal portion of the gluteus medius tendon is close to the piriformis muscle.
The gluteus medius muscle covers the entire gluteus minimus muscle.
Remember: the gluteus medius muscle runs from the ilium to the greater trochanter of the proximal femur.
The gluteus medius muscle is supplied by the superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1 predominantly L5).
The blood supply comes from the superior gluteal artery which runs above the piriformis muscle.
This artery may become injured due to acetabular fractures either due to the trauma or by the surgery.
This may lead to compromise of the abductor muscles.
Function: Hip abduction: the gluteus medius muscle is the most powerful abductor of the hip joint.
What muscles abduct the hip? Gluteus medius muscle and Gluteus minimus muscle
Gluteus medius muscle: the abductor muscles play an important role in stabilization of the pelvis, the anterior fibers of the gluteus medius muscle provide some internal rotation of the hip and the posterior fibers provide some external rotation of the hip, there is many clinical situations that involve the gluteus medius muscle.
The superior gluteal nerve may be injures due to the Watson- Jones or lateral approach to the hip if the incision extends more than 5 cm above the acetabulum, surgeons like the lateral approach (Hardinge approach) better compared to the posterior approach to the hip because the rate of hip dislocation is less, the superior gluteal nerve will limit the proximal extent of the gluteus medius split.
The superior gluteal nerve is approximately 5 cm proximal from the tip of the greater trochanter.
If you split the gluteus medius muscle about this point, then you run the risk of injuring the superior gluteal nerve and compromise the muscle function.
If injury occurs to the gluteus to the gluteus medius muscle, there will be weakness of hip abduction.
Weakness of the muscle could be seen early after total hip replacement.
The patient will be sent to therapy to regain the strength of the muscle.
Occasionally there is an occult injury or rupture of the muscle itself that goes unrecognized.
Injury to the muscle may sometimes be mistaken for trochanteric bursitis but it is really an occult rupture of the tendon.
MRI may be needed to check for a rupture.
MRI is good even if metal is present around the hip.
Injury may or may not result from surgery I this area.
If there is gluteus medius muscle weakness, the trendelenburg gait may occur.
Become a friend on facebook:
Follow me on twitter:
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
Комментарии
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:01:06
0:01:06
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:31:56
0:31:56
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:06:25
0:06:25
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:04:26
0:04:26