filmov
tv
Sudden Abdominal Pain 🪨 Gallbladder stone - Cholelithiasis

Показать описание
Join this channel and become an insider member.
Subscribe for free to see our next release.
Click the bell 🔔 to be notified about our new content.
#shorts
Gallbladder stones, or gallstones, are a common condition affecting millions worldwide. These stones form in the gallbladder, a small organ beneath the liver that plays a critical role in digestion by storing and releasing bile, which helps break down fats.
What are Gallstones?
Gallstones are hard, pebble-like deposits that form in the gallbladder.
They can range from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. There are two main types of gallstones:
Cholesterol Stones: These are the most common type, formed when the bile has too much cholesterol.
Pigment Stones: These are made up of bilirubin, a substance produced when red blood cells break down, and they are more common in people with liver disease or certain blood disorders.
Brown Stones: Mixed stones of bilirubin, fatty substances, and cholesterol typically form in bile ducts and are linked to infections and bile flow issues.
Causes of Gallstones
The exact cause of gallstone formation is not always clear, but several factors can contribute to their development:
Excess Cholesterol: When the liver produces more cholesterol than bile can dissolve, the excess may crystallize into stones.
Bile Imbalance: An imbalance in bile composition can lead to the formation of pigment stones.
Gallbladder Dysfunction: If the gallbladder doesn't empty properly or often enough, the bile becomes concentrated and may lead to stone formation.
Genetics: A family history of gallstones increases the risk.
Obesity: Being overweight is a significant risk factor due to increased cholesterol levels in bile.
Diet: High-fat, high-cholesterol diets and rapid weight loss may contribute to gallstone formation.
Other Factors: Pregnancy, age, and conditions like diabetes or liver cirrhosis can increase the risk.
Symptoms of Gallstones
Gallstones often don't cause symptoms and may be discovered incidentally during medical imaging. However, when symptoms do appear, they can be quite painful. The common symptoms include:
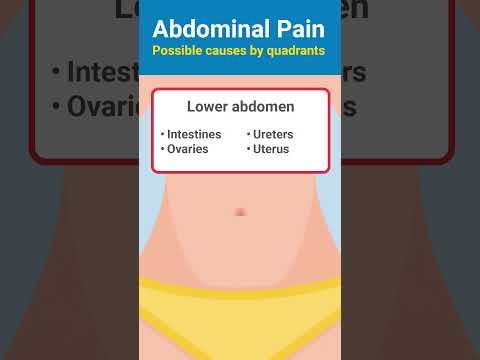
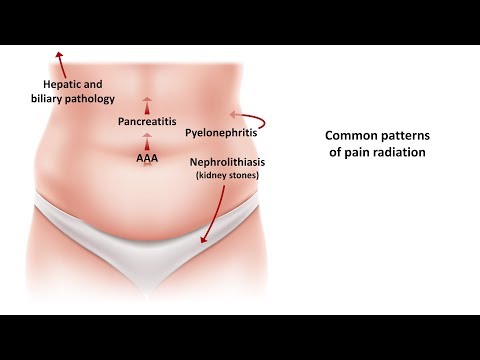
Biliary Colic: A sharp, intense pain in the upper right abdomen or center of the stomach, often occurring after a meal. The pain may radiate to the back or right shoulder blade and last several hours.
Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms often accompany gallstone-related pain.
Jaundice: A yellowing of the skin and eyes occurs if a stone blocks the bile duct.
Fever and Chills: These may indicate an infection of the gallbladder or bile ducts.
Complications of Gallstones
Untreated gallstones can lead to several complications, including:
Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder can cause severe pain and fever.
Pancreatitis: Gallstones can block the pancreatic duct, leading to inflammation of the pancreas, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Bile Duct Infection: A blocked bile duct can lead to an infection, which may require immediate treatment.
Gallbladder Cancer: Although rare, long-term inflammation caused by gallstones increases the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Diagnosis of Gallstones
Diagnosis begins with a thorough medical history and physical exam. If gallstones are suspected, several diagnostic tests may be used:
Ultrasound: This is the most common and non-invasive method for detecting gallstones. It provides clear images of the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
CT Scan: This imaging test can provide more detailed pictures and is often used if complications are suspected.
Blood Tests: These can check for signs of infection, inflammation, or bile duct obstruction.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A specialized procedure that combines endoscopy and X-rays to locate and potentially remove stones from the bile duct.
We ran out of space, the following sections are available on the community wall of our channel members:
Treatment of Gallstones
Prevention of Gallstones
For more free resources, you can find us:
Pinterest: MedicalArtsOfficial
Facebook MedicalArtsOfficial
Instagram MedicalArtsOfficial
TikTok MedicalArts
Keywords:
#cholelithiasis #gallbladderstones
This video is for entertainment and educational purposes only!!
Medical Arts Official, 2024
@MedicalArts
Subscribe for free to see our next release.
Click the bell 🔔 to be notified about our new content.
#shorts
Gallbladder stones, or gallstones, are a common condition affecting millions worldwide. These stones form in the gallbladder, a small organ beneath the liver that plays a critical role in digestion by storing and releasing bile, which helps break down fats.
What are Gallstones?
Gallstones are hard, pebble-like deposits that form in the gallbladder.
They can range from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. There are two main types of gallstones:
Cholesterol Stones: These are the most common type, formed when the bile has too much cholesterol.
Pigment Stones: These are made up of bilirubin, a substance produced when red blood cells break down, and they are more common in people with liver disease or certain blood disorders.
Brown Stones: Mixed stones of bilirubin, fatty substances, and cholesterol typically form in bile ducts and are linked to infections and bile flow issues.
Causes of Gallstones
The exact cause of gallstone formation is not always clear, but several factors can contribute to their development:
Excess Cholesterol: When the liver produces more cholesterol than bile can dissolve, the excess may crystallize into stones.
Bile Imbalance: An imbalance in bile composition can lead to the formation of pigment stones.
Gallbladder Dysfunction: If the gallbladder doesn't empty properly or often enough, the bile becomes concentrated and may lead to stone formation.
Genetics: A family history of gallstones increases the risk.
Obesity: Being overweight is a significant risk factor due to increased cholesterol levels in bile.
Diet: High-fat, high-cholesterol diets and rapid weight loss may contribute to gallstone formation.
Other Factors: Pregnancy, age, and conditions like diabetes or liver cirrhosis can increase the risk.
Symptoms of Gallstones
Gallstones often don't cause symptoms and may be discovered incidentally during medical imaging. However, when symptoms do appear, they can be quite painful. The common symptoms include:
Biliary Colic: A sharp, intense pain in the upper right abdomen or center of the stomach, often occurring after a meal. The pain may radiate to the back or right shoulder blade and last several hours.
Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms often accompany gallstone-related pain.
Jaundice: A yellowing of the skin and eyes occurs if a stone blocks the bile duct.
Fever and Chills: These may indicate an infection of the gallbladder or bile ducts.
Complications of Gallstones
Untreated gallstones can lead to several complications, including:
Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder can cause severe pain and fever.
Pancreatitis: Gallstones can block the pancreatic duct, leading to inflammation of the pancreas, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Bile Duct Infection: A blocked bile duct can lead to an infection, which may require immediate treatment.
Gallbladder Cancer: Although rare, long-term inflammation caused by gallstones increases the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Diagnosis of Gallstones
Diagnosis begins with a thorough medical history and physical exam. If gallstones are suspected, several diagnostic tests may be used:
Ultrasound: This is the most common and non-invasive method for detecting gallstones. It provides clear images of the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
CT Scan: This imaging test can provide more detailed pictures and is often used if complications are suspected.
Blood Tests: These can check for signs of infection, inflammation, or bile duct obstruction.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A specialized procedure that combines endoscopy and X-rays to locate and potentially remove stones from the bile duct.
We ran out of space, the following sections are available on the community wall of our channel members:
Treatment of Gallstones
Prevention of Gallstones
For more free resources, you can find us:
Pinterest: MedicalArtsOfficial
Facebook MedicalArtsOfficial
Instagram MedicalArtsOfficial
TikTok MedicalArts
Keywords:
#cholelithiasis #gallbladderstones
This video is for entertainment and educational purposes only!!
Medical Arts Official, 2024
@MedicalArts
Комментарии
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:09:52
0:09:52
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:25:26
0:25:26
 0:02:29
0:02:29
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:09:24
0:09:24
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:01:52
0:01:52
 0:00:46
0:00:46