filmov
tv
Complement System Made Easy- Immunology- Classical Alternate & Lectin pathway

Показать описание
GET LECTURE HANDOUTS and other DOWNLOADABLE CONTENT FROM THIS VIDEO
SUPPORT US ON PATREON OR JOIN HERE ON YOUTUBE.
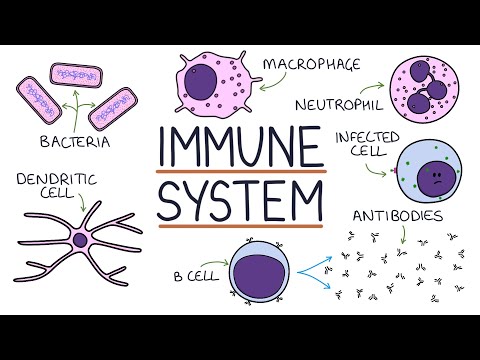
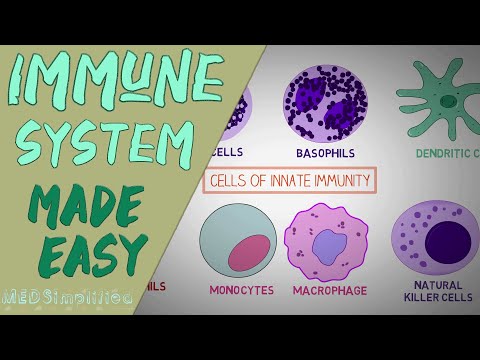
The complement system is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promotes inflammation, and attacks the pathogen's plasma membrane. It is part of the innate immune system,[1] which is not adaptable and does not change over the course of an individual's lifetime. It can be recruited and brought into action by the adaptive immune system.
The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, in general synthesized by the liver, and normally circulating as inactive precursors (pro-proteins). When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end result of this complement activation or complement fixation cascade is stimulation of phagocytes to clear foreign and damaged material, proxy inflammation to attract additional phagocytes, and activation of the cell-killing membrane attack complex. Over 30 proteins and protein fragments make up the complement system, including serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors. They account for about 10% of the globulin fraction of blood serum and can serve as opsonins.[citation needed]
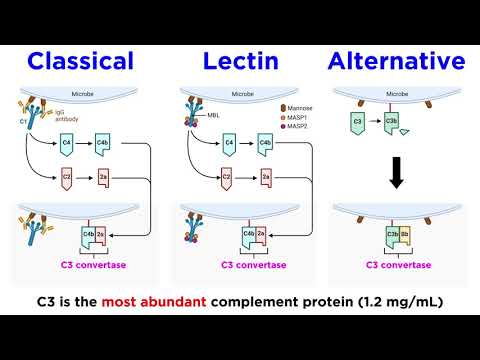
Three biochemical pathways activate the complement system: the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, and the lectin pathway.
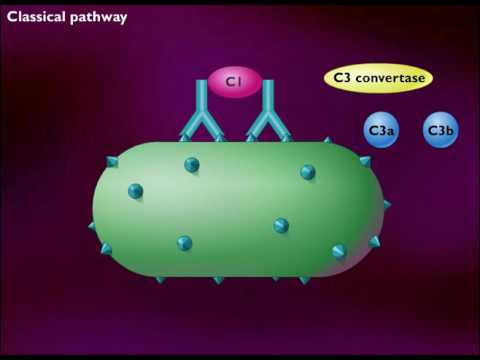
Most of the proteins and glycoproteins that constitute the complement system are synthesized by hepatocytes. But significant amounts are also produced by tissue macrophages, blood monocytes, and epithelial cells of the genitourinal tract and gastrointestinal tract. The three pathways of activation all generate homologous variants of the protease C3-convertase. The classical complement pathway typically requires antigen—antibody complexes (immune complexes) for activation (specific immune response), whereas the alternative pathway can be activated by C3 hydrolysis, foreign material, pathogens, or damaged cells. The mannose-binding lectin pathway can be activated by C3 hydrolysis or antigens without the presence of antibodies (non-specific immune response). In all three pathways, C3-convertase cleaves and activates component C3, creating C3a and C3b, and causes a cascade of further cleavage and activation events. C3b binds to the surface of pathogens, leading to greater internalization by phagocytic cells by opsonization.
In the alternative pathway, C3b binds to Factor B. Factor D releases Factor Ba from Factor B bound to C3b. The complex of C3b(2)Bb is a protease which cleaves C5 into C5b and C5a. C5 convertase is also formed by the Classical Pathway when C3b binds C4b and C2a. C5a is an important chemotactic protein, helping recruit inflammatory cells. C3a is the precursor of an important cytokine (adipokine) named ASP (although this is not universally accepted [6]) and is usually rapidly cleaved by carboxypeptidase B. Both C3a and C5a have anaphylatoxin activity, directly triggering degranulation of mast cells as well as increasing vascular permeability and smooth muscle contraction.[6] C5b initiates the membrane attack pathway, which results in the membrane attack complex (MAC), consisting of C5b, C6, C7, C8, and polymeric C9.[7] MAC is the cytolytic endproduct of the complement cascade; it forms a transmembrane channel, which causes osmotic lysis of the target cell. Kupffer cells and other macrophage cell types help clear complement-coated pathogens. As part of the innate immune system, elements of the complement cascade can be found in species earlier than vertebrates; most recently in the protostome horseshoe crab species, putting the origins of the system back further than was previously thought.
-~-~~-~~~-~~-~-
CHECK OUT NEWEST VIDEO: "Nucleic acids - DNA and RNA structure "
-~-~~-~~~-~~-~-
SUPPORT US ON PATREON OR JOIN HERE ON YOUTUBE.
The complement system is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promotes inflammation, and attacks the pathogen's plasma membrane. It is part of the innate immune system,[1] which is not adaptable and does not change over the course of an individual's lifetime. It can be recruited and brought into action by the adaptive immune system.
The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, in general synthesized by the liver, and normally circulating as inactive precursors (pro-proteins). When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end result of this complement activation or complement fixation cascade is stimulation of phagocytes to clear foreign and damaged material, proxy inflammation to attract additional phagocytes, and activation of the cell-killing membrane attack complex. Over 30 proteins and protein fragments make up the complement system, including serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors. They account for about 10% of the globulin fraction of blood serum and can serve as opsonins.[citation needed]
Three biochemical pathways activate the complement system: the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, and the lectin pathway.
Most of the proteins and glycoproteins that constitute the complement system are synthesized by hepatocytes. But significant amounts are also produced by tissue macrophages, blood monocytes, and epithelial cells of the genitourinal tract and gastrointestinal tract. The three pathways of activation all generate homologous variants of the protease C3-convertase. The classical complement pathway typically requires antigen—antibody complexes (immune complexes) for activation (specific immune response), whereas the alternative pathway can be activated by C3 hydrolysis, foreign material, pathogens, or damaged cells. The mannose-binding lectin pathway can be activated by C3 hydrolysis or antigens without the presence of antibodies (non-specific immune response). In all three pathways, C3-convertase cleaves and activates component C3, creating C3a and C3b, and causes a cascade of further cleavage and activation events. C3b binds to the surface of pathogens, leading to greater internalization by phagocytic cells by opsonization.
In the alternative pathway, C3b binds to Factor B. Factor D releases Factor Ba from Factor B bound to C3b. The complex of C3b(2)Bb is a protease which cleaves C5 into C5b and C5a. C5 convertase is also formed by the Classical Pathway when C3b binds C4b and C2a. C5a is an important chemotactic protein, helping recruit inflammatory cells. C3a is the precursor of an important cytokine (adipokine) named ASP (although this is not universally accepted [6]) and is usually rapidly cleaved by carboxypeptidase B. Both C3a and C5a have anaphylatoxin activity, directly triggering degranulation of mast cells as well as increasing vascular permeability and smooth muscle contraction.[6] C5b initiates the membrane attack pathway, which results in the membrane attack complex (MAC), consisting of C5b, C6, C7, C8, and polymeric C9.[7] MAC is the cytolytic endproduct of the complement cascade; it forms a transmembrane channel, which causes osmotic lysis of the target cell. Kupffer cells and other macrophage cell types help clear complement-coated pathogens. As part of the innate immune system, elements of the complement cascade can be found in species earlier than vertebrates; most recently in the protostome horseshoe crab species, putting the origins of the system back further than was previously thought.
-~-~~-~~~-~~-~-
CHECK OUT NEWEST VIDEO: "Nucleic acids - DNA and RNA structure "
-~-~~-~~~-~~-~-
Комментарии
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:19:09
0:19:09
 0:14:49
0:14:49
 0:27:59
0:27:59
 0:02:56
0:02:56
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:11:51
0:11:51
 0:23:56
0:23:56
 0:15:17
0:15:17
 0:25:09
0:25:09
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 2:37:19
2:37:19
 0:05:32
0:05:32
 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:15:24
0:15:24
 0:05:08
0:05:08
 0:07:35
0:07:35
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:19:24
0:19:24
 0:10:30
0:10:30
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:17:31
0:17:31