filmov
tv
Alpha vs Beta Decay and Gamma Decay (Radiologic Technologist)

Показать описание
Alpha vs Beta decay cover the initial nuclear decay modes, and after the initial decay if the nucleus is in an unstable state (i.e. an excited state) it will decay to a more stable state (i.e. a ground state). When the nucleus decays from the excited state to the ground state it is via a gamma decay.
In this video we focus on these methods of nuclear decay.
Chapters
00:00. Intro radioactive decay
00:42. Nucleus review
02:22. Alpha decay
04:00. Beta decay
04:48. What is measured in a PET scan
07:30. Gamma decay
08:40. What is measured in a SPECT scan
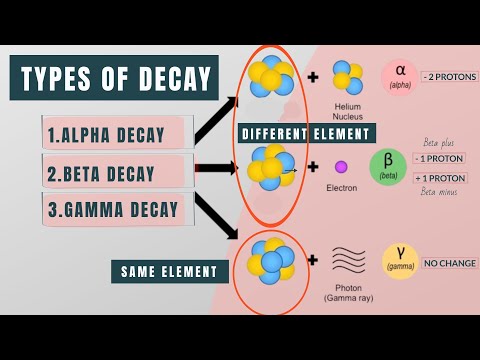
In these decays what leaves the nucleus:
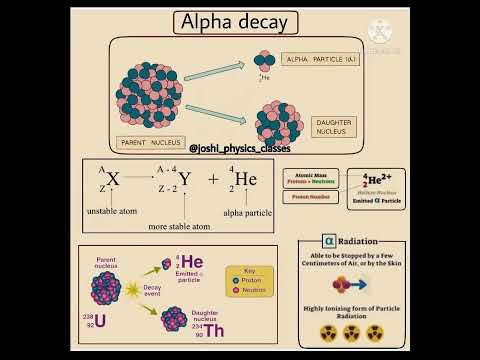
Alpha Decay- a helium nucleus leaves the nucleus
Beta + : a positron leaves the nucleus (this is the mechanism used in PET scanning)
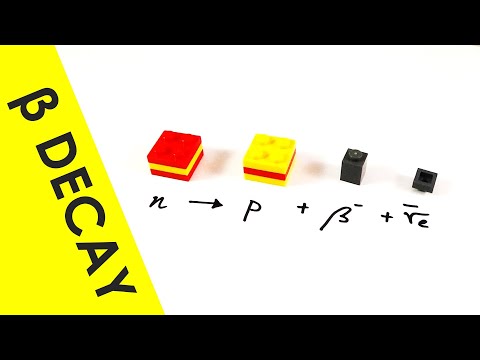
Beta -: an electron leaves the nucleus
The number of protons is denoted as Z, and the combined number of protons and neutrons is Z+N, where N is the number of neutrons.
In these decays the result on the nucleus:
Alpha Decay: a helium nucleus leaves the nucleus (i.e. 2 protons and 2 neutrons), the nucleus would then have two fewer protons: Z_new=Z-2 , and the atomic number is four less Atomic#_new=Atomic#-4
Beta + decay: a positron leaves the nucleus, via a conversion from a proton to a neutron
Beta - decay: an electron leaves the nucleus, via a conversion of a neutron from a proton.
Gamma decay- after an alpha or beta decay there can then be a gamma ray emitted in order for the nucleus to enter a more stable state. Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation, just like light and x-rays. Gamma rays are distinguished from x-rays by their means of production. X-rays from an x-ray tube and gamma rays from natural decay processes.
In this video we focus on these methods of nuclear decay.
Chapters
00:00. Intro radioactive decay
00:42. Nucleus review
02:22. Alpha decay
04:00. Beta decay
04:48. What is measured in a PET scan
07:30. Gamma decay
08:40. What is measured in a SPECT scan
In these decays what leaves the nucleus:
Alpha Decay- a helium nucleus leaves the nucleus
Beta + : a positron leaves the nucleus (this is the mechanism used in PET scanning)
Beta -: an electron leaves the nucleus
The number of protons is denoted as Z, and the combined number of protons and neutrons is Z+N, where N is the number of neutrons.
In these decays the result on the nucleus:
Alpha Decay: a helium nucleus leaves the nucleus (i.e. 2 protons and 2 neutrons), the nucleus would then have two fewer protons: Z_new=Z-2 , and the atomic number is four less Atomic#_new=Atomic#-4
Beta + decay: a positron leaves the nucleus, via a conversion from a proton to a neutron
Beta - decay: an electron leaves the nucleus, via a conversion of a neutron from a proton.
Gamma decay- after an alpha or beta decay there can then be a gamma ray emitted in order for the nucleus to enter a more stable state. Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation, just like light and x-rays. Gamma rays are distinguished from x-rays by their means of production. X-rays from an x-ray tube and gamma rays from natural decay processes.
Комментарии
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:09:09
0:09:09
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:17:06
0:17:06
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:11:48
0:11:48
 0:00:42
0:00:42
 0:14:12
0:14:12
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:12:35
0:12:35
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:14:10
0:14:10
 0:08:37
0:08:37
 0:26:04
0:26:04
 0:07:37
0:07:37
 0:00:06
0:00:06