filmov
tv
VBG or ABG? Which one to order?

Показать описание
the clinical value of VBG (venous blood gas) is discussed in this video, when can it be used as an alternative to ABG (arterial blood gas), how to interpret it and adjust for ABG, when not to use it, will provide you with some real-life clinical scenarios to make sure you understand this topic
Watch mechanical ventilation course here:
Watch ICU crash course here:
Watch IV fluids course:
Watch mechanical ventilation course here:
Watch ICU crash course here:
Watch IV fluids course:
VBG or ABG? Which one to order?
Respiratory Therapy ABG vs VBG How to tell the difference!
Blood Gas Interpretation Made Easy (Learn How To Interpret Blood Gases In 11 Minutes)
Understanding The Venous Blood Gas (VBG): Components, Sampling Sites, Physiology, Converting To ABG.
Respiratory Therapy - ABG vs VBG Breakdown
#icushort 51: Difference between ABG and VBG values
How to take blood for ABG (Arterial blood gas)
ABG - Arterial blood gas interpretation made simple in 8 minutes RN, LPN, LVN for NCLEX
Podcast 864: Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) vs Venous Blood Gas (VBG)
Respiratory System Anatomy | Arterial Blood Gas (Part 1)
Interpret an Arterial Blood gas report in 4 steps
Understanding Arterial Blood Gases
ABG Interpretation | Understanding Arterial Blood Gas Analysis - OSCE Guide | UKMLA | CPSA
How to read ABG’s?! | Quick and Simple Tutorial in under 5 minutes! #abgs #abg
ABG Interpretation (basic): Easy and Simple
ABGs Interpretation: Arterial Blood Gases & Acid-Base Imbalances (ROME & Tic-Tac-Toe Method)
Difference between ABG and VBG ? | ABG | VBG
How to check ABG or arterial blood gas || ABG Interpretation
Acid Base Disorders and ABG Interpretation | Introduction
ABG vs. VBG
How to properly handle a venous blood gas sample
Compensation | Blood Gas Interpretation | Arterial Blood Gases (Part 4)
Fundamentals of Arterial Blood Gases - Part 1
Blood Gases (O2, CO2 and ABG)
Комментарии
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:14:26
0:14:26
 0:11:26
0:11:26
 0:15:33
0:15:33
 0:09:51
0:09:51
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:01:02
0:01:02
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:02:33
0:02:33
 0:14:49
0:14:49
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:10:49
0:10:49
 0:10:29
0:10:29
 0:04:57
0:04:57
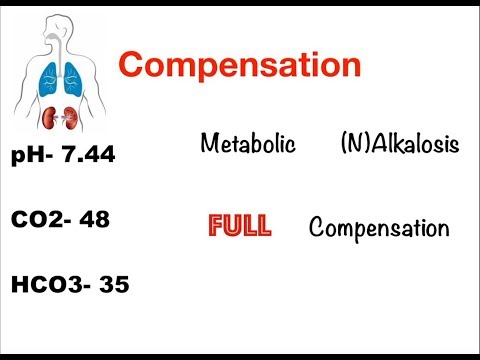 0:20:55
0:20:55
 0:25:35
0:25:35
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:58:08
0:58:08
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:07:30
0:07:30
 0:22:48
0:22:48
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:12:49
0:12:49