filmov
tv
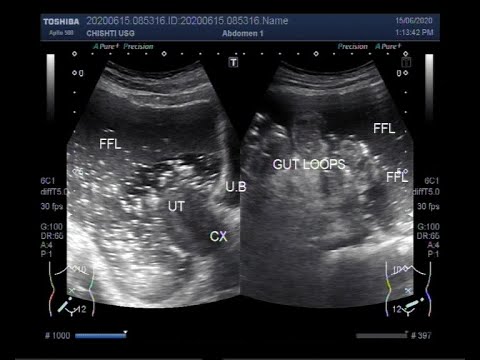
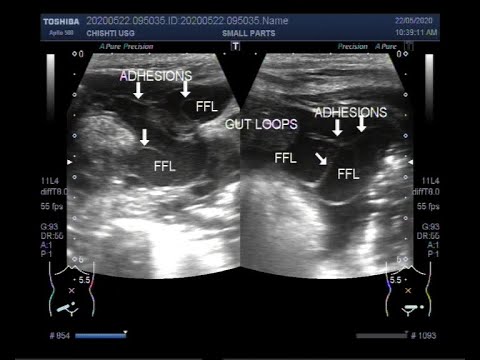
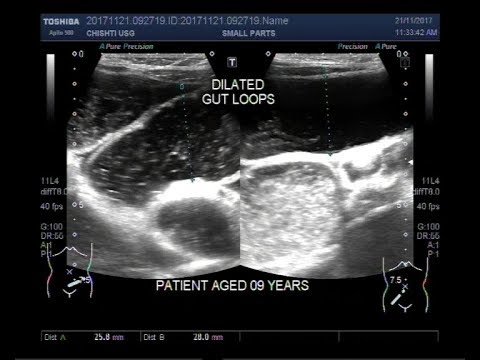
Ultrasound Video showing Intestinal Perforation.

Показать описание
This video shows Intestinal Perforation.
The classic presentation is sudden and severe abdominal pain, sometimes with localized peritonism or a rigid abdomen on examination.
Bowel perforation is an acute surgical emergency where there is a release of gastric or intestinal contents into the peritoneal space.
The primary symptoms of gastrointestinal perforation are severe abdominal pain and tenderness. The abdomen may also protrude or feel hard to the touch. If the hole is in a person's stomach or small intestine, the onset of pain is usually sudden, but if the hole is in the large bowel, the pain may come on gradually.
Constipation and fecal impaction can frequently be seen especially in elderly and debilitated patients. On the other hand, fecalomas rarely can cause colonic ischemia and stercoral perforation. Mainly older, weak, and bedridden patients are affected. The main trigger reason is chronic constipation.
History
Severe and generalized abdominal pain (upper)
Gradual and localized pain (lower)
Anorexia, nausea, and vomiting.
Examination
Rigid abdomen and generalized tenderness
Guarding and rebound
Bowel sounds range from quiet to absent
Pathophysiology
Gastric and duodenal ulceration
Infection (diverticulitis, appendicitis), ischemia and cancer
Blunt and penetrating trauma
Ingestion of corrosive materials
Iatrogenic causes (ERCP, colonoscopy, laparotomy, biopsy)
Role of imaging
Erect CXR
Very sensitive to even small amounts of gas within the peritoneal cavity
Seen as a crescent under the diaphragm
Summary Article: erect chest radiograph
If the perforation is suspected then an erect chest X-ray should be performed as well as an abdominal X-ray. This image shows a very large volume of gas under the diaphragm due to bowel perforation.
Gastrointestinal perforation (GP) occurs when a hole forms all the way through the stomach, large bowel, or small intestine. It can be due to a number of different diseases, including appendicitis and diverticulitis. It can also be the result of trauma, such as a knife wound or gunshot wound.
The classic presentation is sudden and severe abdominal pain, sometimes with localized peritonism or a rigid abdomen on examination.
Bowel perforation is an acute surgical emergency where there is a release of gastric or intestinal contents into the peritoneal space.
The primary symptoms of gastrointestinal perforation are severe abdominal pain and tenderness. The abdomen may also protrude or feel hard to the touch. If the hole is in a person's stomach or small intestine, the onset of pain is usually sudden, but if the hole is in the large bowel, the pain may come on gradually.
Constipation and fecal impaction can frequently be seen especially in elderly and debilitated patients. On the other hand, fecalomas rarely can cause colonic ischemia and stercoral perforation. Mainly older, weak, and bedridden patients are affected. The main trigger reason is chronic constipation.
History
Severe and generalized abdominal pain (upper)
Gradual and localized pain (lower)
Anorexia, nausea, and vomiting.
Examination
Rigid abdomen and generalized tenderness
Guarding and rebound
Bowel sounds range from quiet to absent
Pathophysiology
Gastric and duodenal ulceration
Infection (diverticulitis, appendicitis), ischemia and cancer
Blunt and penetrating trauma
Ingestion of corrosive materials
Iatrogenic causes (ERCP, colonoscopy, laparotomy, biopsy)
Role of imaging
Erect CXR
Very sensitive to even small amounts of gas within the peritoneal cavity
Seen as a crescent under the diaphragm
Summary Article: erect chest radiograph
If the perforation is suspected then an erect chest X-ray should be performed as well as an abdominal X-ray. This image shows a very large volume of gas under the diaphragm due to bowel perforation.
Gastrointestinal perforation (GP) occurs when a hole forms all the way through the stomach, large bowel, or small intestine. It can be due to a number of different diseases, including appendicitis and diverticulitis. It can also be the result of trauma, such as a knife wound or gunshot wound.
Комментарии
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:08:14
0:08:14
 0:10:51
0:10:51
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:08:03
0:08:03
 0:07:31
0:07:31
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:09:41
0:09:41
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:03:32
0:03:32
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:07:25
0:07:25
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:05:47
0:05:47