filmov
tv
Collision Domain vs Broadcast Domain - CCNA

Показать описание
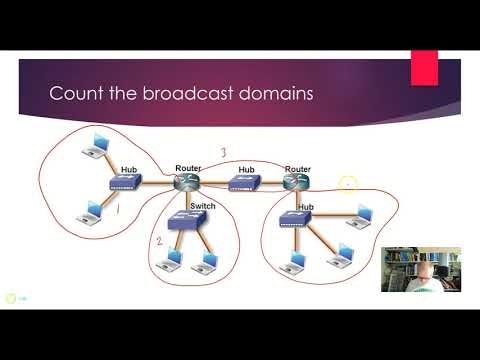
You have learned what a broadcast domain is:
A broadcast domain is a collection of devices that receive broadcast traffic from each other.
Switches will forward broadcast traffic to all interfaces, except the one where it originated from.
A lot of broadcast traffic might impact your network performance so reducing the size of the broadcast domain is something to consider.
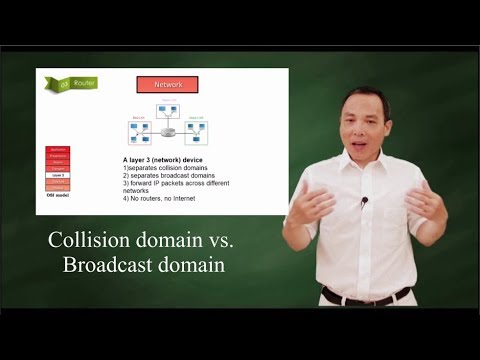
Routers do not forward broadcast traffic, they break broadcast domains.
VLANs on switches also allow you to break broadcast domains.
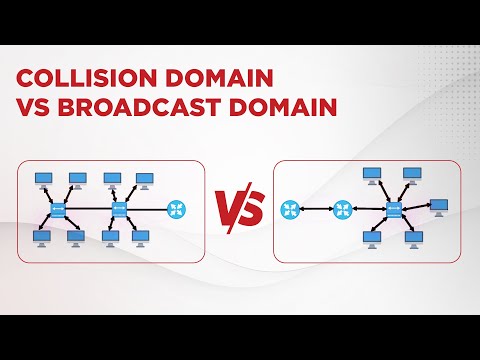
Collision Domain:
The hub is a simple repeater, we can get collisions when it attempts to send two frames to one interface.
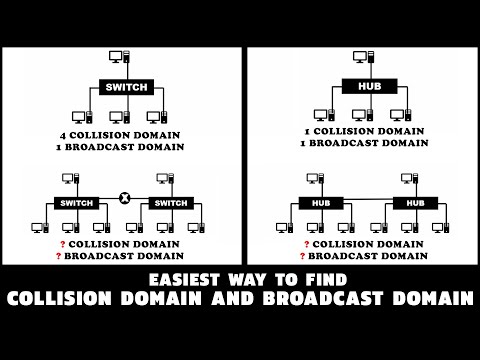
Everything that is connected to a hub is a single collision domain.
Because of these collisions, we have to use half duplex. We can’t send and transmit at the same time. CSMA/CD is the protocol that is used to detect collisions and to re-transmit frames.
The bridge, a predecessor of our switch breaks up the collision domain since it has some intelligence. It learns MAC addresses and only forwards Ethernet frames to interfaces where we need them. It is also able to store Ethernet frames in memory so that it can queue them.
The switch is our bridge on steroids. It has more interfaces and is faster. Each interface on a switch is considered a collision domain.
Switch interfaces run in full duplex, we can transmit and receive at the same time. No collisions occur in a switched network unless you have defective interfaces or network cards.
Because we can’t get collisions in a switched network, CSMA/CD is disabled by default.
A broadcast domain is a collection of devices that receive broadcast traffic from each other.
Switches will forward broadcast traffic to all interfaces, except the one where it originated from.
A lot of broadcast traffic might impact your network performance so reducing the size of the broadcast domain is something to consider.
Routers do not forward broadcast traffic, they break broadcast domains.
VLANs on switches also allow you to break broadcast domains.
Collision Domain:
The hub is a simple repeater, we can get collisions when it attempts to send two frames to one interface.
Everything that is connected to a hub is a single collision domain.
Because of these collisions, we have to use half duplex. We can’t send and transmit at the same time. CSMA/CD is the protocol that is used to detect collisions and to re-transmit frames.
The bridge, a predecessor of our switch breaks up the collision domain since it has some intelligence. It learns MAC addresses and only forwards Ethernet frames to interfaces where we need them. It is also able to store Ethernet frames in memory so that it can queue them.
The switch is our bridge on steroids. It has more interfaces and is faster. Each interface on a switch is considered a collision domain.
Switch interfaces run in full duplex, we can transmit and receive at the same time. No collisions occur in a switched network unless you have defective interfaces or network cards.
Because we can’t get collisions in a switched network, CSMA/CD is disabled by default.
Комментарии
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:05:25
0:05:25
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:05:18
0:05:18
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:14:36
0:14:36
 0:13:52
0:13:52
 0:10:39
0:10:39
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:06:18
0:06:18
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:07:30
0:07:30
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:01:55
0:01:55
 0:00:26
0:00:26