filmov
tv
SUM Function | Microsoft Excel | Functions #beginners #excel #functions #datascience #dataanalytics

Показать описание
The **SUM** function in Excel is one of the most commonly used functions. It adds up a range of numbers, making it a powerful tool for quick calculations. Here's a full description:
### 📝 **Syntax of the SUM function**:
```
=SUM(number1, [number2], ...)
```
- **number1**: The first number, cell reference, or range to be added.
- **number2** (optional): Additional numbers, cell references, or ranges you want to add. You can add up to 255 arguments (numbers, ranges, or references).
- **Range**: A group of cells, e.g., `A1:A10` (which means cells A1 through A10).
### 🧮 **How it works**:
The SUM function adds the values you provide in the arguments. These can be individual numbers, cell references (e.g., `A1`, `B2`), or ranges (e.g., `A1:A10`). You can mix these as well.
### **Examples**:
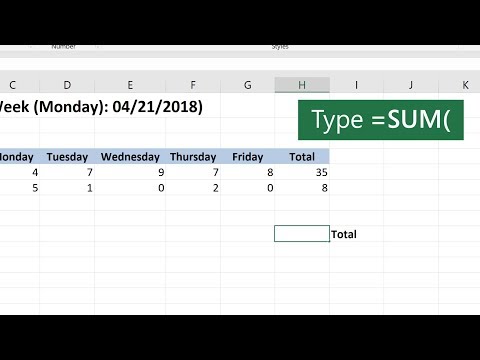
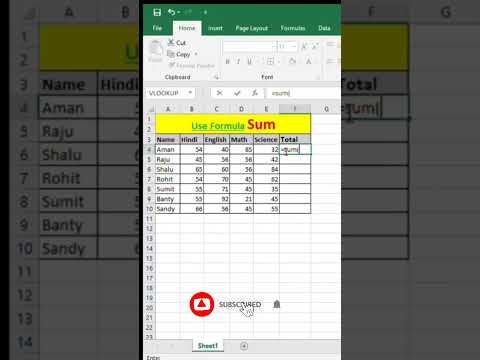
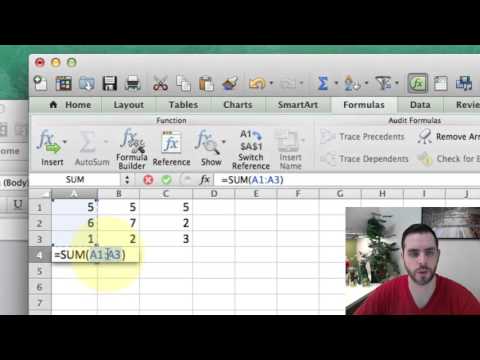
1. **Adding a Range**:
`=SUM(A1:A5)`
This adds all the numbers from cell A1 to A5.
2. **Adding Individual Cells**:
`=SUM(A1, A2, A3)`
This adds the numbers in cells A1, A2, and A3.
3. **Adding Numbers and Ranges**:
`=SUM(A1:A5, C1:C5)`
This adds the numbers in both ranges, from A1 to A5 and C1 to C5.
4. **Using Constants**:
`=SUM(10, 20, A1:A3)`
This adds the numbers 10 and 20 to the sum of the values in cells A1 to A3.
### 🚀 **Advanced Uses**:
- **Using SUM with other functions**:
You can combine the SUM function with other functions like **IF** or **AVERAGE** for more complex calculations.
This formula sums only the numbers greater than 10 in the range A1 to A5.
- **SUM with non-contiguous ranges**:
You can sum different ranges by separating them with commas.
Example: `=SUM(A1:A5, C1:C5)` adds all values in A1:A5 and C1:C5.
### 🌟 **Tips**:
1. **AutoSum**: In Excel, you can quickly use the **AutoSum** button (Σ) on the ribbon to add a column or row of numbers automatically.
2. **Ignore text**: The SUM function automatically ignores any non-numeric cells (e.g., text, empty cells) in the range.
### 🔧 **Why Use SUM**:
- **Efficiency**: Instead of adding numbers manually, the SUM function helps you quickly get the total.
- **Accuracy**: Reduces human error and is especially helpful with large datasets.
### 💡 **Example of a Use Case**:
If you're managing monthly expenses in an Excel sheet:
- Cells A1 to A12 have the expenses for each month.
- To find the total annual expense, you'd use the formula `=SUM(A1:A12)`, and Excel will give you the sum of all expenses for the year.
The **SUM** function is essential for budgeting, financial analysis, or any situation that involves summing large sets of numbers.
#excel #microsoft #datastructuresandalgorithmsinpython #datascience #addition #beginners
### 📝 **Syntax of the SUM function**:
```
=SUM(number1, [number2], ...)
```
- **number1**: The first number, cell reference, or range to be added.
- **number2** (optional): Additional numbers, cell references, or ranges you want to add. You can add up to 255 arguments (numbers, ranges, or references).
- **Range**: A group of cells, e.g., `A1:A10` (which means cells A1 through A10).
### 🧮 **How it works**:
The SUM function adds the values you provide in the arguments. These can be individual numbers, cell references (e.g., `A1`, `B2`), or ranges (e.g., `A1:A10`). You can mix these as well.
### **Examples**:
1. **Adding a Range**:
`=SUM(A1:A5)`
This adds all the numbers from cell A1 to A5.
2. **Adding Individual Cells**:
`=SUM(A1, A2, A3)`
This adds the numbers in cells A1, A2, and A3.
3. **Adding Numbers and Ranges**:
`=SUM(A1:A5, C1:C5)`
This adds the numbers in both ranges, from A1 to A5 and C1 to C5.
4. **Using Constants**:
`=SUM(10, 20, A1:A3)`
This adds the numbers 10 and 20 to the sum of the values in cells A1 to A3.
### 🚀 **Advanced Uses**:
- **Using SUM with other functions**:
You can combine the SUM function with other functions like **IF** or **AVERAGE** for more complex calculations.
This formula sums only the numbers greater than 10 in the range A1 to A5.
- **SUM with non-contiguous ranges**:
You can sum different ranges by separating them with commas.
Example: `=SUM(A1:A5, C1:C5)` adds all values in A1:A5 and C1:C5.
### 🌟 **Tips**:
1. **AutoSum**: In Excel, you can quickly use the **AutoSum** button (Σ) on the ribbon to add a column or row of numbers automatically.
2. **Ignore text**: The SUM function automatically ignores any non-numeric cells (e.g., text, empty cells) in the range.
### 🔧 **Why Use SUM**:
- **Efficiency**: Instead of adding numbers manually, the SUM function helps you quickly get the total.
- **Accuracy**: Reduces human error and is especially helpful with large datasets.
### 💡 **Example of a Use Case**:
If you're managing monthly expenses in an Excel sheet:
- Cells A1 to A12 have the expenses for each month.
- To find the total annual expense, you'd use the formula `=SUM(A1:A12)`, and Excel will give you the sum of all expenses for the year.
The **SUM** function is essential for budgeting, financial analysis, or any situation that involves summing large sets of numbers.
#excel #microsoft #datastructuresandalgorithmsinpython #datascience #addition #beginners
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:06:44
0:06:44
 0:16:45
0:16:45
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:02
0:01:02
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:00:52
0:00:52