filmov
tv
The Weird World of Protista (Part 4) #neet #biology #shorts

Показать описание
The Weird World of Protista (Part 4) #neet #biology #shorts
Protista, Biology, Neet, Shorts, microbial diversity, microbiology, protista characteristics, protista classification, eukaryotic microorganisms, protista biology, algal groups, cell membrane, biology, single-celled organisms, aquatic protists, protista, protista kingdom, eukaryotic life, protist diversity, biological classification neet, microorganism study, biological classification class 11, protista science, biological classification, eukaryotic organisms, protists examples
he fungi constitute a unique kingdom of heterotrophic organisms. They
show a great diversity in morphology and habitat. You must have seen
fungi on a moist bread and rotten fruits. The common mushroom you eat
and toadstools are also fungi. White spots seen on mustard leaves are due
to a parasitic fungus. Some unicellular fungi, e.g., yeast are used to make
bread and beer. Other fungi cause diseases in plants and animals; wheat
rust-causing Puccinia is an important example. Some are the source of
antibiotics, e.g., Penicillium. Fungi are cosmopolitan and occur in air, water,
soil and on animals and plants. They prefer to grow in warm and humid
places. Have you ever wondered why we keep food in the refrigerator ? Yes,
it is to prevent food from going bad due to bacterial or fungal infections.
With the exception of yeasts which are unicellular, fungi are
filamentous. Their bodies consist of long, slender thread-like structures
called hyphae. The network of hyphae is known as mycelium. Some hyphae
are continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm – these are
called coenocytic hyphae. Others have septae or cross walls in their
hyphae. The cell walls of fungi are composed of chitin and polysaccharides.
Most fungi are heterotrophic and absorb soluble organic matter from
dead substrates and hence are called saprophytes. Those that depend
on living plants and animals are called parasites. They can also live as
symbionts – in association with algae as lichens and with roots of higher
plants as mycorrhiza.
Reproduction in fungi can take place by vegetative means –
fragmentation, fission and budding. Asexual reproduction is by spores
Protista, Biology, Neet, Shorts, microbial diversity, microbiology, protista characteristics, protista classification, eukaryotic microorganisms, protista biology, algal groups, cell membrane, biology, single-celled organisms, aquatic protists, protista, protista kingdom, eukaryotic life, protist diversity, biological classification neet, microorganism study, biological classification class 11, protista science, biological classification, eukaryotic organisms, protists examples
he fungi constitute a unique kingdom of heterotrophic organisms. They
show a great diversity in morphology and habitat. You must have seen
fungi on a moist bread and rotten fruits. The common mushroom you eat
and toadstools are also fungi. White spots seen on mustard leaves are due
to a parasitic fungus. Some unicellular fungi, e.g., yeast are used to make
bread and beer. Other fungi cause diseases in plants and animals; wheat
rust-causing Puccinia is an important example. Some are the source of
antibiotics, e.g., Penicillium. Fungi are cosmopolitan and occur in air, water,
soil and on animals and plants. They prefer to grow in warm and humid
places. Have you ever wondered why we keep food in the refrigerator ? Yes,
it is to prevent food from going bad due to bacterial or fungal infections.
With the exception of yeasts which are unicellular, fungi are
filamentous. Their bodies consist of long, slender thread-like structures
called hyphae. The network of hyphae is known as mycelium. Some hyphae
are continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm – these are
called coenocytic hyphae. Others have septae or cross walls in their
hyphae. The cell walls of fungi are composed of chitin and polysaccharides.
Most fungi are heterotrophic and absorb soluble organic matter from
dead substrates and hence are called saprophytes. Those that depend
on living plants and animals are called parasites. They can also live as
symbionts – in association with algae as lichens and with roots of higher
plants as mycorrhiza.
Reproduction in fungi can take place by vegetative means –
fragmentation, fission and budding. Asexual reproduction is by spores
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:12:17
0:12:17
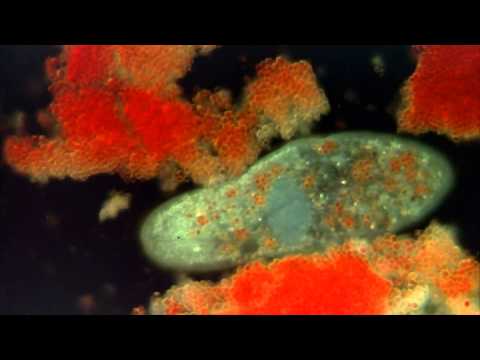 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:02:20
0:02:20
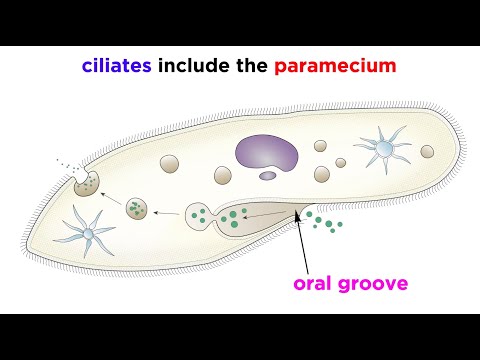 0:07:14
0:07:14
 0:07:09
0:07:09
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:02:56
0:02:56
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:17:10
0:17:10
 0:17:47
0:17:47
 1:15:04
1:15:04
 0:08:17
0:08:17
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:05:43
0:05:43
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:24:22
0:24:22
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:10:42
0:10:42
 0:30:22
0:30:22