filmov
tv
Lecture 19: Microprogrammed Control Organization

Показать описание
#ComponentsofMCU #TypesofControlUnit
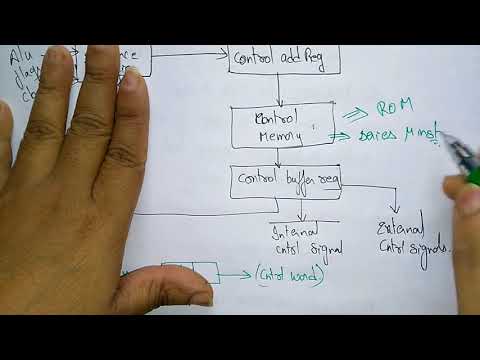
The general configuration of a microprogrammed control unit is demonstrated above. The control memory is assumed to be a ROM, within which all control information is permanently stored. The control memory address register specifies the address of the microinstruction, and the control data register holds the microinstruction read from memory. The microinstruction contains a control word that specifies one or more microoperations for the data processor. Once these operations are executed, the control must determine the nest address. The location of the next
microinstruction may be the one next in sequence, or it may be located somewhere else in the control memory. For this reason it is necessary to use some bits of the present microinstruction to control the generation of the address of the next microinstruction. The next address may also be a
function of external input conditions. While the microoperations are being executed, the next address is computer in the next address generator circuit and then transferred into the control address register to read the next microinstruction. Thus a microinstruction contains bits for initiating microoperations in the data processor part and bits that determine the address sequence for the control memory.
The next address generator is sometimes called a microprogram sequencer, as it determines the address sequence that is read from control memory. ;the address of the next microinstruction can be specified in several ways, depending on the sequencer inputs. Typical functions of a microprogram sequencer are incrementing the control address register by one, loading into the control address register an address from control memory, transferring an external address, or loading an initial address to start the control operations.
The control data register holds the present microinstruction while the next address is computed and read from memory; the data register is sometimes called a pipeline register. It allows the execution of the microoperations specified by the control word simultaneously with the generation of the next microinstruction. This configuration requires a two-phase clock., with
one clock applied to the address register and the other to the data register.
The general configuration of a microprogrammed control unit is demonstrated above. The control memory is assumed to be a ROM, within which all control information is permanently stored. The control memory address register specifies the address of the microinstruction, and the control data register holds the microinstruction read from memory. The microinstruction contains a control word that specifies one or more microoperations for the data processor. Once these operations are executed, the control must determine the nest address. The location of the next
microinstruction may be the one next in sequence, or it may be located somewhere else in the control memory. For this reason it is necessary to use some bits of the present microinstruction to control the generation of the address of the next microinstruction. The next address may also be a
function of external input conditions. While the microoperations are being executed, the next address is computer in the next address generator circuit and then transferred into the control address register to read the next microinstruction. Thus a microinstruction contains bits for initiating microoperations in the data processor part and bits that determine the address sequence for the control memory.
The next address generator is sometimes called a microprogram sequencer, as it determines the address sequence that is read from control memory. ;the address of the next microinstruction can be specified in several ways, depending on the sequencer inputs. Typical functions of a microprogram sequencer are incrementing the control address register by one, loading into the control address register an address from control memory, transferring an external address, or loading an initial address to start the control operations.
The control data register holds the present microinstruction while the next address is computed and read from memory; the data register is sometimes called a pipeline register. It allows the execution of the microoperations specified by the control word simultaneously with the generation of the next microinstruction. This configuration requires a two-phase clock., with
one clock applied to the address register and the other to the data register.
 0:06:10
0:06:10
 0:07:37
0:07:37
 0:27:37
0:27:37
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:07:35
0:07:35
 1:11:05
1:11:05
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:13:24
0:13:24
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:15:05
0:15:05
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:17:45
0:17:45
 0:09:23
0:09:23
 1:08:42
1:08:42
 0:18:58
0:18:58
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:32:57
0:32:57
 0:13:31
0:13:31
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:06:54
0:06:54
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:12:14
0:12:14