filmov
tv
Regulation of the Cell Cycle: A Cyclin-Dependent Kinases and Cyclin-CDK Complexes Review

Показать описание
Question: What are Cyclin-dependent kinases?
Answer: Cyclin-dependent kinases are constitutively expressed but inactive when not bound to cyclin.Question: What are Cyclin-CDK Complexes?
Answer: Cyclin-CDK Complexes are formed when Cyclins, which are phase-specific regulatory proteins, activate CDKs when stimulated by growth factors. The complex can then phosphorylate other proteins to coordinate cell cycle progression.Question: How does the cyclin-CDK complex coordinate cell cycle progression?
Answer: The cyclin-CDK complex coordinates cell cycle progression by phosphorylating other proteins, such as Rb, when it is activated.Question: Why is it important that the cyclin-CDK complex be activated/inactivated at appropriate times for cell cycle to progress?
Answer: The cyclin-CDK complex must be activated and inactivated at appropriate times for the cell cycle to progress. If the complex is not activated and inactivated at the right times, it can lead to errors in the cell cycle, which can lead to cell death or even cancer. Question: How do Cyclins activate CDKs?
Answer: Cyclins activate CDKs when they are stimulated by growth factors.Question: What are the specific functions of Cyclin-CDK complexes in the cell cycle?
Answer: The Cyclin-CDK complexes have specific functions in different phases of the cell cycle. For example, in the G1 phase, the Cyclin-CDK complex helps to ensure that the cell has enough nutrients and energy to divide, and in the G2 phase, the complex helps to check for DNA damage before the cell can divide.Question: What happens when the Cyclin-CDK complex is not functioning properly?
Answer: When the Cyclin-CDK complex is not functioning properly, errors in the cell cycle can occur. These errors can lead to cell death or even cancer.Question: How does the cell cycle progress?
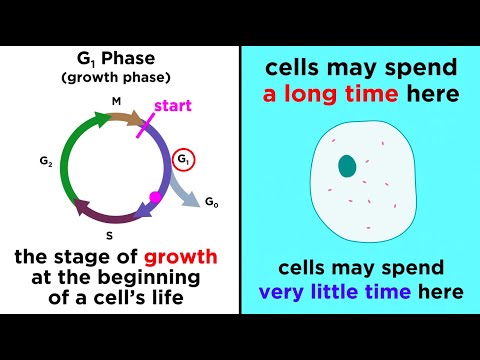
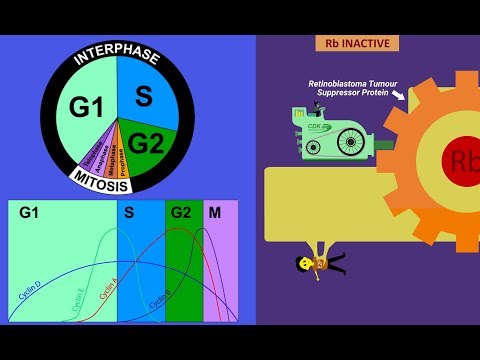
Answer: The cell cycle progresses through a series of stages, including interphase (G1, S, G2) and the mitotic phase (M). The Cyclin-CDK complex plays a key role in coordinating the progression of the cell cycle by activating and inactivating at appropriate times.Question: How does Rb protein relate to the Cyclin-CDK complex?
Answer: The Rb protein is one of the proteins that the Cyclin-CDK complex phosphorylates. When the Rb protein is phosphorylated, it releases other proteins that help to move the cell into the next phase of the cell cycle. Question: How does the Cyclin-CDK complex regulate the cell cycle?
Answer: The Cyclin-CDK complex regulates the cell cycle by phosphorylating other proteins, such as Rb, at key points in the cell cycle. This phosphorylation leads to the release of other proteins that help to move the cell into the next phase of the cell cycle.Question: How does the Cyclin-CDK complex ensure the cell has enough nutrients and energy to divide?
Answer: The Cyclin-CDK complex plays a role in ensuring that the cell has enough nutrients and energy to divide by phosphorylating proteins that control the cell's metabolism. This helps to ensure that the cell has enough energy and resources to support cell division.Question: How does the Cyclin-CDK complex check for DNA damage before the cell can divide?
Answer: The Cyclin-CDK complex plays a role in checking for DNA damage before the cell can divide by phosphorylating proteins that are involved in DNA repair. This helps to ensure that any DNA damage is repaired before the cell divides, which helps to prevent genetic mutations or errors.Question: How does the regulation of Cyclin-CDK complex relate to cancer?
Answer: The regulation of the Cyclin-CDK complex is closely related to cancer. When the Cyclin-CDK complex is not functioning properly, it can lead to errors in the cell cycle, which can cause cells to divide uncontrollably. This uncontrolled cell growth is a key characteristic of cancer. Additionally, mutations in genes that regulate the Cyclin-CDK complex can also contribute to the development of cancer.
Answer: Cyclin-dependent kinases are constitutively expressed but inactive when not bound to cyclin.Question: What are Cyclin-CDK Complexes?
Answer: Cyclin-CDK Complexes are formed when Cyclins, which are phase-specific regulatory proteins, activate CDKs when stimulated by growth factors. The complex can then phosphorylate other proteins to coordinate cell cycle progression.Question: How does the cyclin-CDK complex coordinate cell cycle progression?
Answer: The cyclin-CDK complex coordinates cell cycle progression by phosphorylating other proteins, such as Rb, when it is activated.Question: Why is it important that the cyclin-CDK complex be activated/inactivated at appropriate times for cell cycle to progress?
Answer: The cyclin-CDK complex must be activated and inactivated at appropriate times for the cell cycle to progress. If the complex is not activated and inactivated at the right times, it can lead to errors in the cell cycle, which can lead to cell death or even cancer. Question: How do Cyclins activate CDKs?
Answer: Cyclins activate CDKs when they are stimulated by growth factors.Question: What are the specific functions of Cyclin-CDK complexes in the cell cycle?
Answer: The Cyclin-CDK complexes have specific functions in different phases of the cell cycle. For example, in the G1 phase, the Cyclin-CDK complex helps to ensure that the cell has enough nutrients and energy to divide, and in the G2 phase, the complex helps to check for DNA damage before the cell can divide.Question: What happens when the Cyclin-CDK complex is not functioning properly?
Answer: When the Cyclin-CDK complex is not functioning properly, errors in the cell cycle can occur. These errors can lead to cell death or even cancer.Question: How does the cell cycle progress?
Answer: The cell cycle progresses through a series of stages, including interphase (G1, S, G2) and the mitotic phase (M). The Cyclin-CDK complex plays a key role in coordinating the progression of the cell cycle by activating and inactivating at appropriate times.Question: How does Rb protein relate to the Cyclin-CDK complex?
Answer: The Rb protein is one of the proteins that the Cyclin-CDK complex phosphorylates. When the Rb protein is phosphorylated, it releases other proteins that help to move the cell into the next phase of the cell cycle. Question: How does the Cyclin-CDK complex regulate the cell cycle?
Answer: The Cyclin-CDK complex regulates the cell cycle by phosphorylating other proteins, such as Rb, at key points in the cell cycle. This phosphorylation leads to the release of other proteins that help to move the cell into the next phase of the cell cycle.Question: How does the Cyclin-CDK complex ensure the cell has enough nutrients and energy to divide?
Answer: The Cyclin-CDK complex plays a role in ensuring that the cell has enough nutrients and energy to divide by phosphorylating proteins that control the cell's metabolism. This helps to ensure that the cell has enough energy and resources to support cell division.Question: How does the Cyclin-CDK complex check for DNA damage before the cell can divide?
Answer: The Cyclin-CDK complex plays a role in checking for DNA damage before the cell can divide by phosphorylating proteins that are involved in DNA repair. This helps to ensure that any DNA damage is repaired before the cell divides, which helps to prevent genetic mutations or errors.Question: How does the regulation of Cyclin-CDK complex relate to cancer?
Answer: The regulation of the Cyclin-CDK complex is closely related to cancer. When the Cyclin-CDK complex is not functioning properly, it can lead to errors in the cell cycle, which can cause cells to divide uncontrollably. This uncontrolled cell growth is a key characteristic of cancer. Additionally, mutations in genes that regulate the Cyclin-CDK complex can also contribute to the development of cancer.
Комментарии
 0:39:36
0:39:36
 0:12:40
0:12:40
 0:06:16
0:06:16
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:23:37
0:23:37
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:19:31
0:19:31
 0:17:08
0:17:08
 0:47:16
0:47:16
 0:48:19
0:48:19
 0:10:11
0:10:11
 0:14:33
0:14:33
 0:10:10
0:10:10
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:24:31
0:24:31
 0:09:41
0:09:41
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:55:31
0:55:31