filmov
tv
3 SHOCKING Ways Elephant Trunks Are More Useful Than You Think

Показать описание
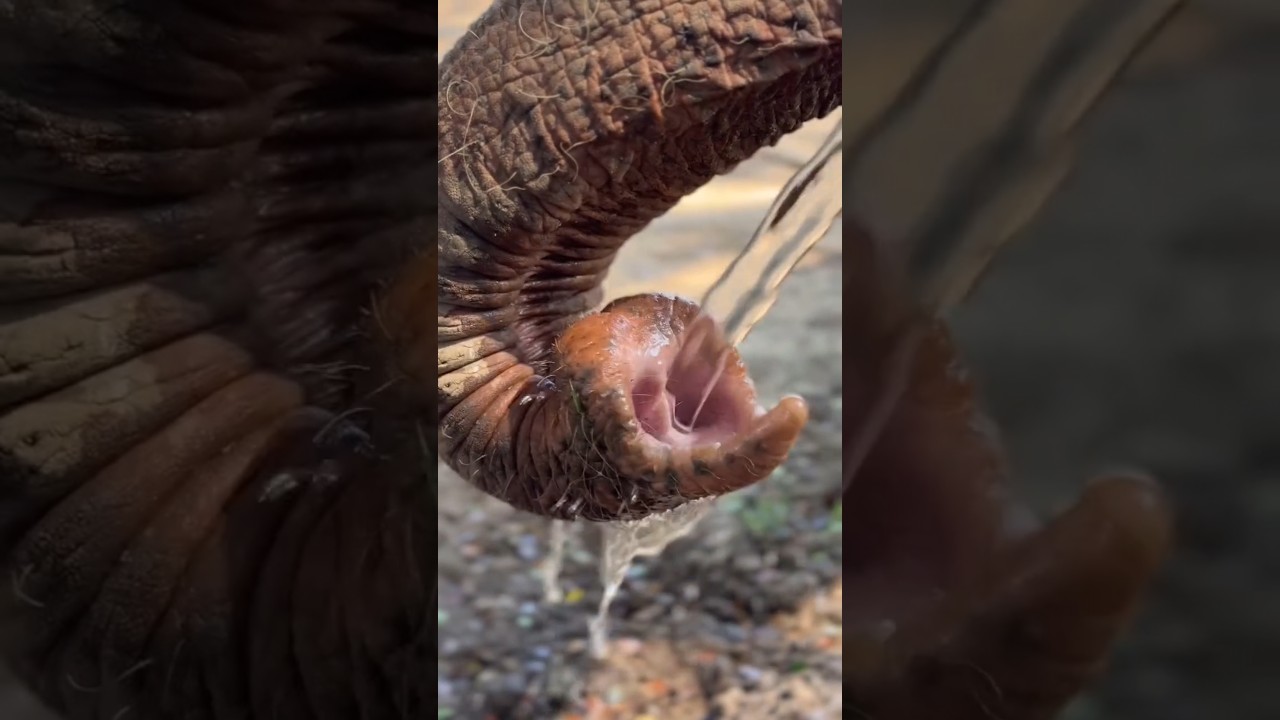
An elephant's trunk is an incredibly versatile and unique feature, with many uses that help the elephant thrive in its environment. Here are some of the key uses of an elephant's trunk:
Breathing: The trunk serves as a vital extension of the elephant's nose and is primarily used for breathing. Elephants can breathe through their trunk when submerged in water or while reaching for high branches.
Grasping and Manipulating Objects: The trunk is highly flexible and strong, allowing elephants to pick up objects of varying sizes. They can grasp food, branches, or tools with great dexterity, and even manipulate small items like a pencil or a piece of fruit.
Eating and Drinking: Elephants use their trunks to gather food, such as picking leaves from trees, grasses, or fruits. They can also suck up water into their trunks and then pour it into their mouths to drink. The trunk is instrumental in feeding, especially in reaching food that is high up or out of reach.
Communication: Elephants use their trunks to communicate with each other through gestures and vocalizations. They can trumpet, grunt, or make other sounds while using their trunks to signal others. The trunk is also used for gentle touching and social bonding.
Sensing: The trunk is equipped with an array of sensitive nerve endings, allowing elephants to sense their surroundings. They can use their trunks to detect scents, vibrations, and even the presence of other animals. The trunk also helps them navigate through dense foliage or dark environments by sensing obstacles.
Social Interaction: Elephants often use their trunks to greet and interact with other elephants. This might involve caressing, intertwining trunks, or touching each other as a form of social bonding, affection, or reassurance.
Bathing and Cleaning: Elephants frequently use their trunks to spray water or mud onto their bodies, which helps to cool them off, remove dirt, and protect their skin from sunburn or insect bites. This behavior is essential for maintaining their hygiene and comfort.
Defense and Protection: In times of danger, an elephant may use its trunk as a tool for defense, either to push away threats or to strike predators. It can also use the trunk to protect young elephants by placing them behind themselves or creating a barrier.
Thermoregulation: Elephants use their trunks to help regulate their body temperature. By spraying water over their bodies or using the trunk to flap their ears, they can help cool themselves in hot environments.
Drinking and Breathing Underwater: Elephants can use their trunks like a snorkel when swimming, allowing them to breathe while submerged. They can submerge their bodies and use their trunks to keep their noses above water, enabling them to swim long distances.
The elephant's trunk is truly a remarkable evolutionary adaptation, giving them an advantage in their environment and helping them carry out a wide range of essential activities.
Breathing: The trunk serves as a vital extension of the elephant's nose and is primarily used for breathing. Elephants can breathe through their trunk when submerged in water or while reaching for high branches.
Grasping and Manipulating Objects: The trunk is highly flexible and strong, allowing elephants to pick up objects of varying sizes. They can grasp food, branches, or tools with great dexterity, and even manipulate small items like a pencil or a piece of fruit.
Eating and Drinking: Elephants use their trunks to gather food, such as picking leaves from trees, grasses, or fruits. They can also suck up water into their trunks and then pour it into their mouths to drink. The trunk is instrumental in feeding, especially in reaching food that is high up or out of reach.
Communication: Elephants use their trunks to communicate with each other through gestures and vocalizations. They can trumpet, grunt, or make other sounds while using their trunks to signal others. The trunk is also used for gentle touching and social bonding.
Sensing: The trunk is equipped with an array of sensitive nerve endings, allowing elephants to sense their surroundings. They can use their trunks to detect scents, vibrations, and even the presence of other animals. The trunk also helps them navigate through dense foliage or dark environments by sensing obstacles.
Social Interaction: Elephants often use their trunks to greet and interact with other elephants. This might involve caressing, intertwining trunks, or touching each other as a form of social bonding, affection, or reassurance.
Bathing and Cleaning: Elephants frequently use their trunks to spray water or mud onto their bodies, which helps to cool them off, remove dirt, and protect their skin from sunburn or insect bites. This behavior is essential for maintaining their hygiene and comfort.
Defense and Protection: In times of danger, an elephant may use its trunk as a tool for defense, either to push away threats or to strike predators. It can also use the trunk to protect young elephants by placing them behind themselves or creating a barrier.
Thermoregulation: Elephants use their trunks to help regulate their body temperature. By spraying water over their bodies or using the trunk to flap their ears, they can help cool themselves in hot environments.
Drinking and Breathing Underwater: Elephants can use their trunks like a snorkel when swimming, allowing them to breathe while submerged. They can submerge their bodies and use their trunks to keep their noses above water, enabling them to swim long distances.
The elephant's trunk is truly a remarkable evolutionary adaptation, giving them an advantage in their environment and helping them carry out a wide range of essential activities.
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:01:48
0:01:48
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:04:59
0:04:59
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:00:16
0:00:16